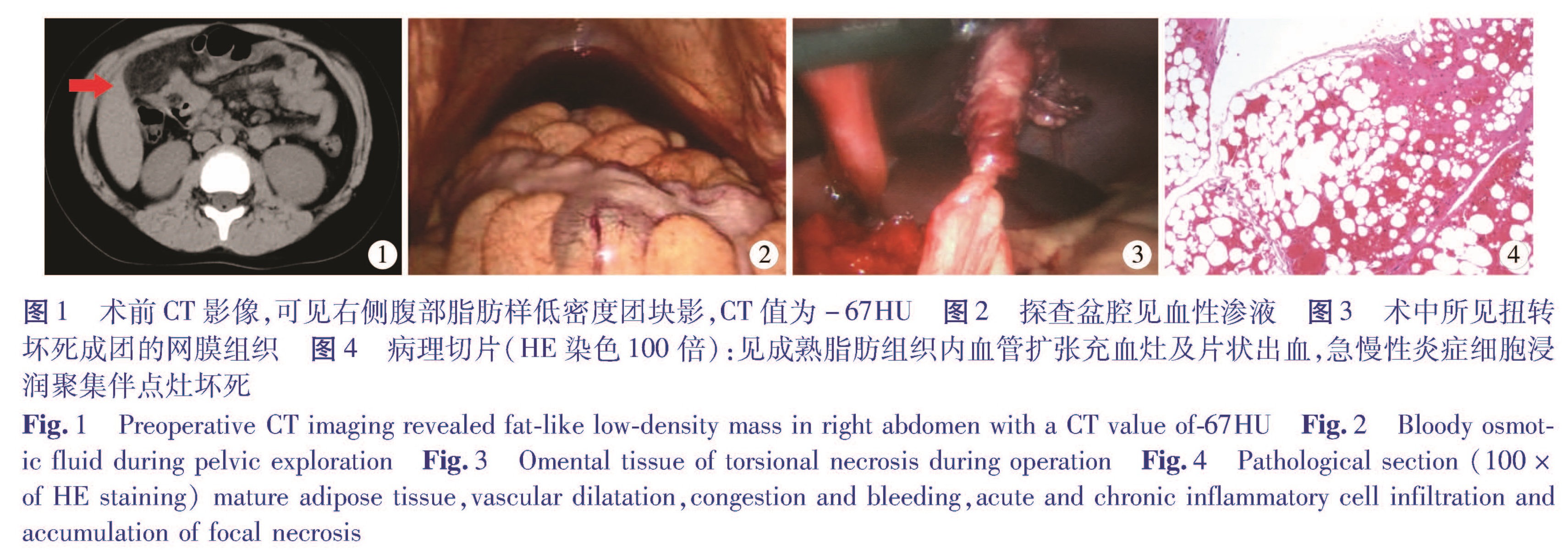
目的 初步探讨儿童原发性大网膜扭转的诊断方法,对治疗经验和体会进行总结。方法 以2012年6月至2017年9月上海市儿童医院/上海交通大学附属儿童医院普外科收治的7例原发性大网膜扭转患儿为研究对象,收集患儿资料(包括临床表现、实验室检查、影像学检查、手术探查及术后随访资料)并进行统计分析。结果 7例患儿均为男性体重指数BMI均高于正常同龄男性儿童; 发病至手术时间21~120 h,平均(64.43±44.00)h; 患儿术前CT均发现右侧腹部低密度团块,CT值(-67~-55)HU,均为脂肪密度,团块最大直径5~8 cm,平均(6.29±1.11)cm; 术前诊断的真阳性率为57.14%(4/7); 所有患儿均采用腹腔镜手术,其中1例因术前诊断为阑尾炎,术中探查为网膜坏死而中转开腹手术,住院时间5~8 d,平均为(6.29±0.95)d,术后随访5个月至5年,无1例出现并发症。结论 肥胖是儿童原发性大网膜扭转发病的重要因素,CT检查对儿童原发性大网膜扭转诊断价值较高,腹腔镜手术切除坏死网膜组织为该病的首选治疗方法。
Objective To explore the diagnosis and treatment of primary omental torsion in children. Methods The clinical data were retrospectively reviewed for 7 boys with primary omental torsion.Clinical manifestations,laboratory tests,imaging examinations,surgical exploration and postoperative follow-ups were performed. Results All of the 7children were male and The values of body mass index(BMI)were higher than those of normal counterparts.The average operative duration was(64.43±44.00)(21-120)h.Low-density lumps were detected preoperatively at the right side of abdomen.Computed tomography value was -67~-55 hu and average fat density(-61.57±5.26)HU.The maximal diameter of mass was 5-8 cm with an average of(6.29±1.11)cm.The preoperative diagnosis was acute appendicitis(n=3)and necrotic omental torsion(n=4).The correct preoperative diagnostic ratio was 57.14%(4/7).All 7 cases underwent laparoscopy.Only one misdiagnosed case was converted into open surgery.The average length of hospital stay was(6.29±0.95)days.No postoperative complications occurred during a follow-up period of 5 months to 5 years. Conclusion Obesity is an important cause of acute primary omental torsion in children.And CT examination is an effective diagnostic method of detecting fat density mass.Laparoscopic removal of necrotic tissue is preferred.