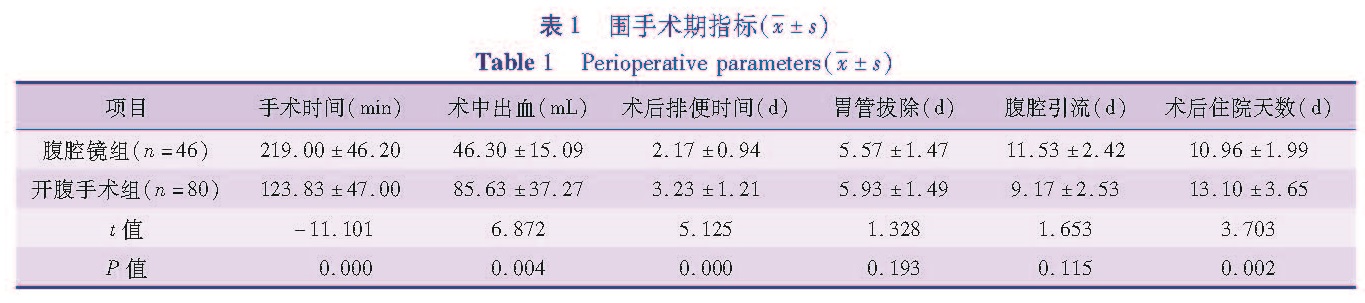
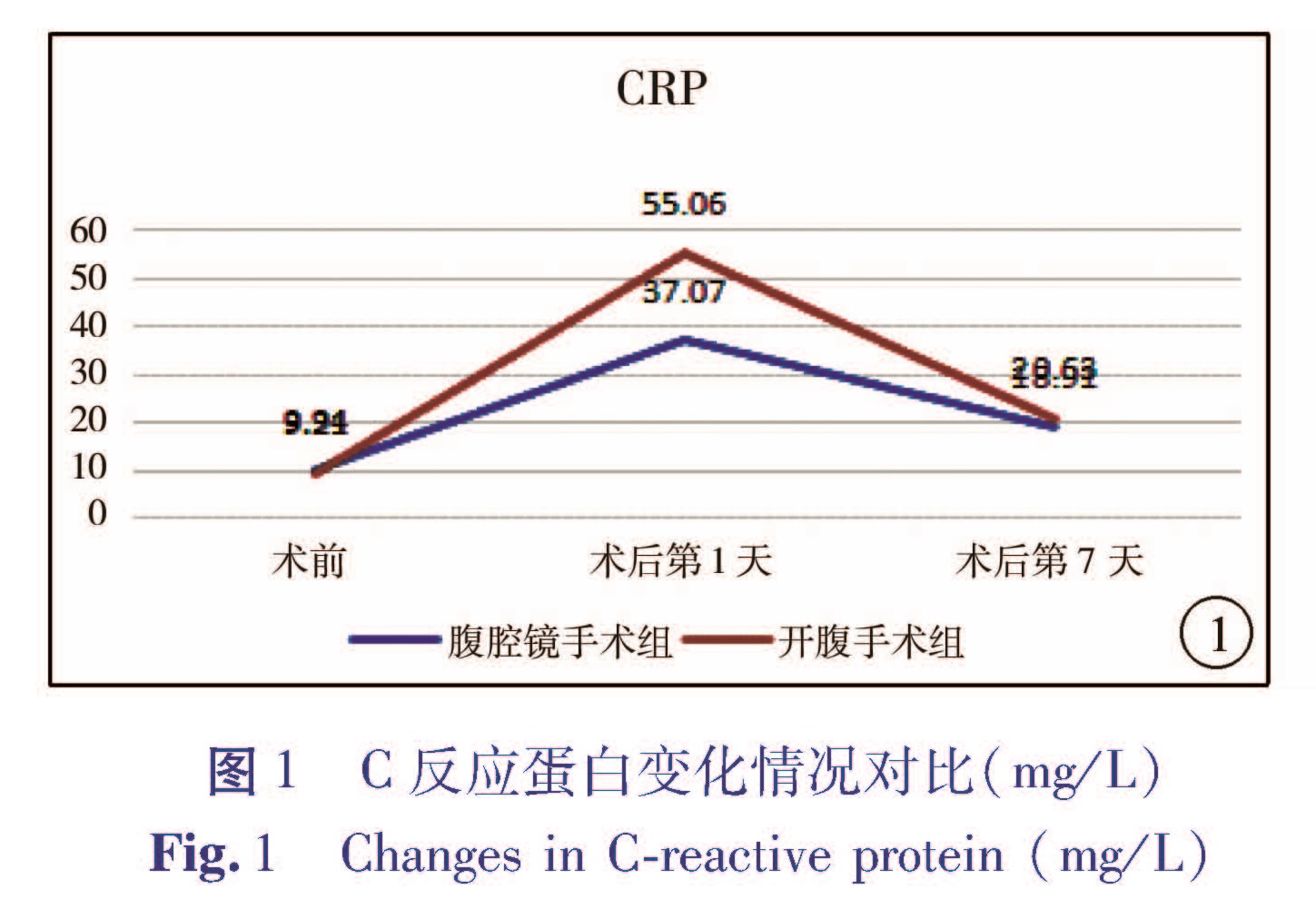
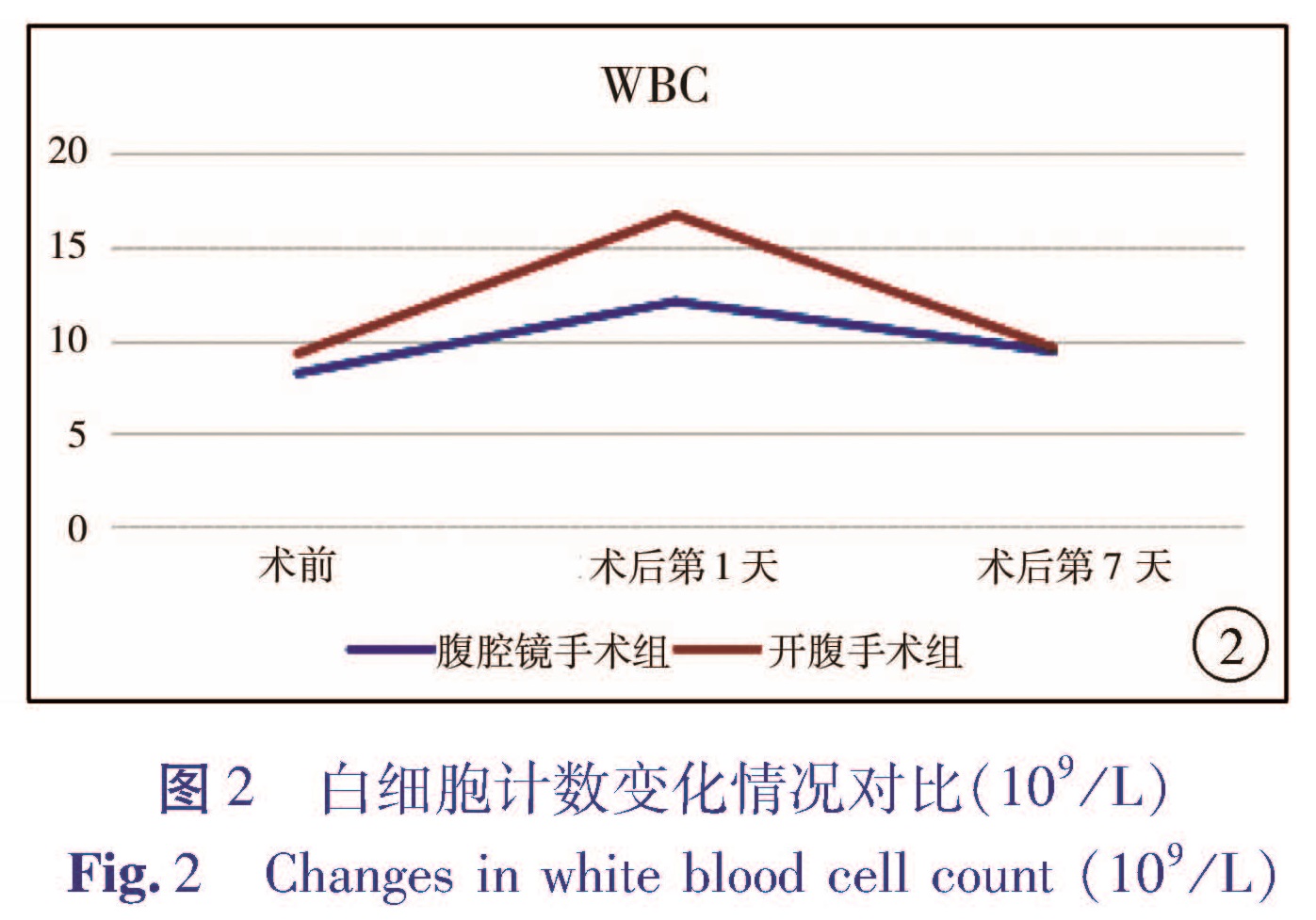
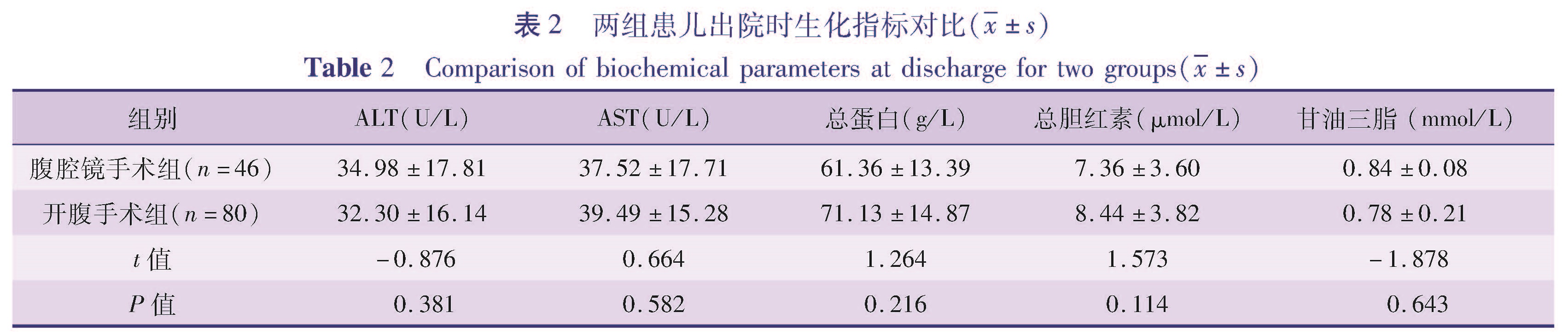
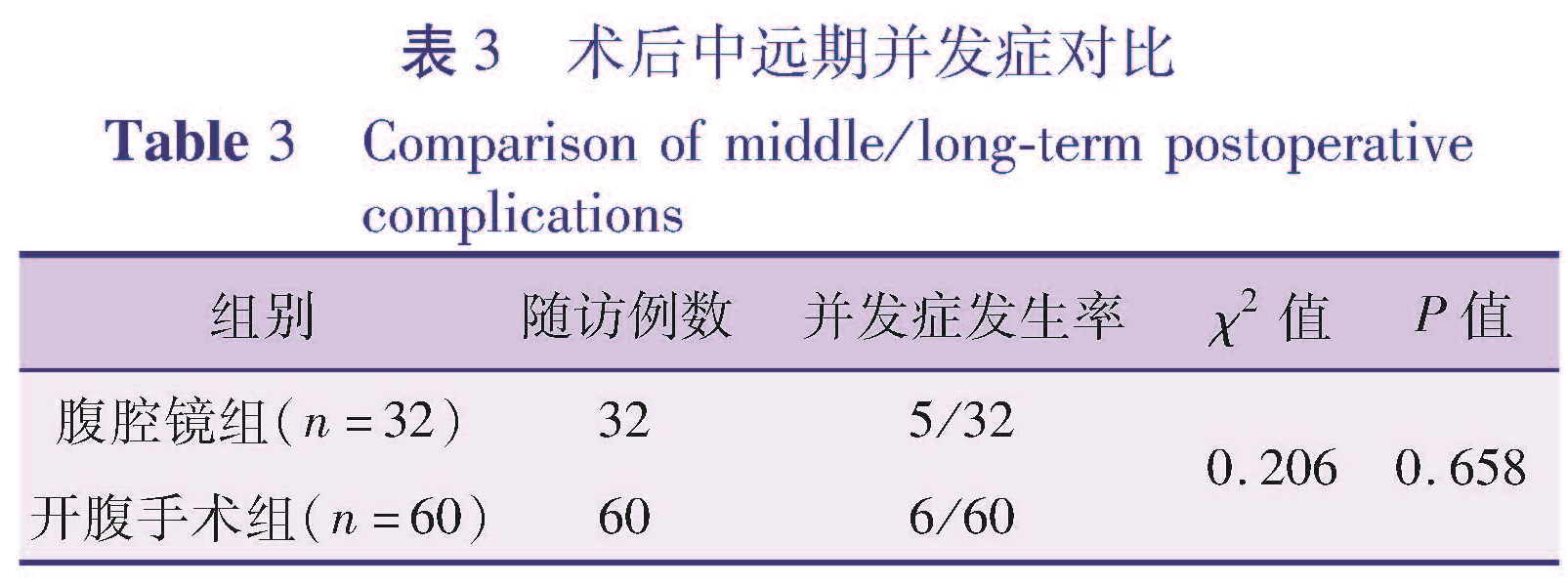
目的 通过回顾性分析,比较开腹手术与腹腔镜辅助手术治疗胆总管囊肿在围手术期指标、术后并发症、对患儿生长发育和心理行为的影响等方面的差异,对比两种手术效果的优劣,为先天性胆总管囊肿的治疗决策提供参考。方法 选取2005年7月1日至2015年7月1日在本院行腹腔镜辅助下胆总管囊肿根治术的患儿46例(腹腔镜手术组),行开腹手术的患儿80例(开腹手术组),比较两组患儿围手术期情况及术后近远期并发症情况。对术后随访时间达到5年的患儿进行复查,其中26例行腹腔镜辅助下胆总管囊肿根治术,40例行开腹手术,比较两组患儿生长发育和心理行为情况。结果 围手术期,腹腔镜手术组在术中出血、肠道功能恢复时间、白细胞计数、CRP恢复水平、住院时间上均优于开腹手术组(P<0.05),而两组胃肠减压管、腹腔引流管的拔管时间比较差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。不同手术方式患儿出院后血生化指标(AST、ALT、总蛋白、总胆红素)无统计学差异(P>0.05)。腹腔镜手术组出现发热5例,不全性肠梗阻1例,胆瘘1例; 开腹手术组发热7例,不全性肠梗阻2例,胆瘘2例,活动性出血1例,两组患儿近期并发症的发生率无统计学差异(P>0.05)。随访生长发育指标无统计学差异。腹腔镜手术组、开腹手术组心理测评得分均在正常范围,但开腹手术组心理测评得分低于腹腔镜手术组。结论 腹腔镜辅助下胆总管囊肿根治手术患儿术中出血量少,手术切口小,愈合快,住院时间短,较开腹手术有一定的优势。两种手术方式对术后患儿生长发育的影响较小,远期心理影响有待进一步研究。
Objective To study the psychological situations、growth and development of children underwent laparoscopic or laparotomic total cyst excision over the past decade. Methods From July 1,2005 to July 1,2015,a total of 126 children with choledocho cyst underwent laparoscopic(A,n=46)and laparotomic(B,n=80)total cyst excision.Retrospective analysis was performed for perioperative profiles of two groups.The follow-up period was 5 years. Results During perioperative period,laparoscopy was superior to laparotomy in terms of intraoperative bleeding,recovery time of intestional function,white blood cell count,restoring level of C-reactive protein and hospitalization length(P<0.05).Yet two groups had no statistical differences in removal durations of gastrointestinal decompression and abdominal irrigation tubes(P>0.05).And no obvious statistical differences existed in the post-discharge levels of biochemical parameters(aspartate aminotransferase,alanine aminotransferase,total protein and total bilirubin)(P>0.05).In laparoscopic group,there were fever(n=5),incomplete intestinal obstruction(n=1)and biliary fistula(n=1); in laparotomic group,fever(n=7),incomplete intestinal obstruction(n=2),biliary fistula(n=2)and active bleeding(n=1).No inter-group statistical difference existed in immediate complications(P>0.05). Conclusion The advantages of laparoscopic versus laparotomic total cyst excision include minimal bleeding,smaller incision,faster healing and shorter postoperative hospital day.No significant inter-group difference exists in growth and development.The long-term psychological impact requires further studies.