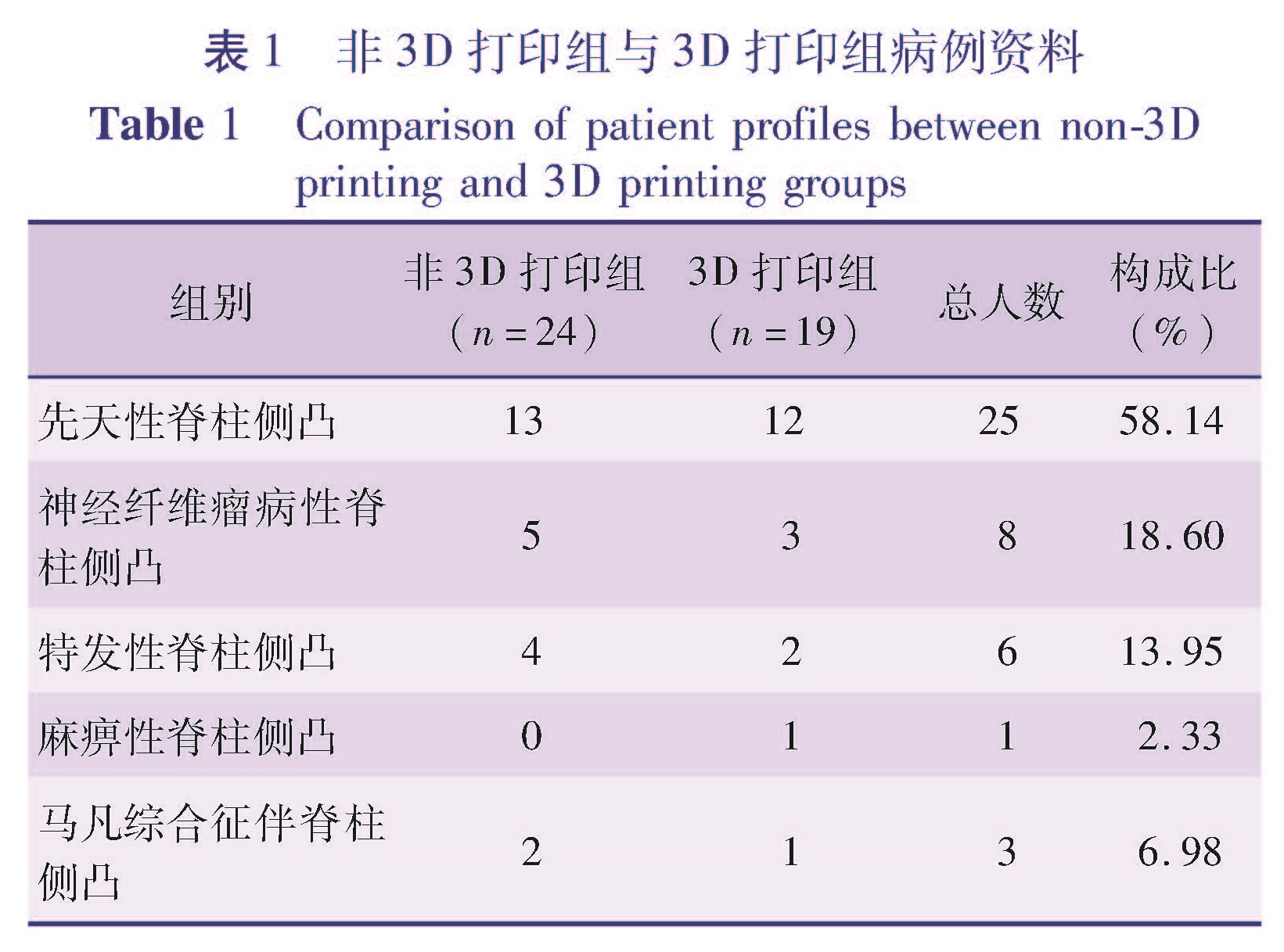
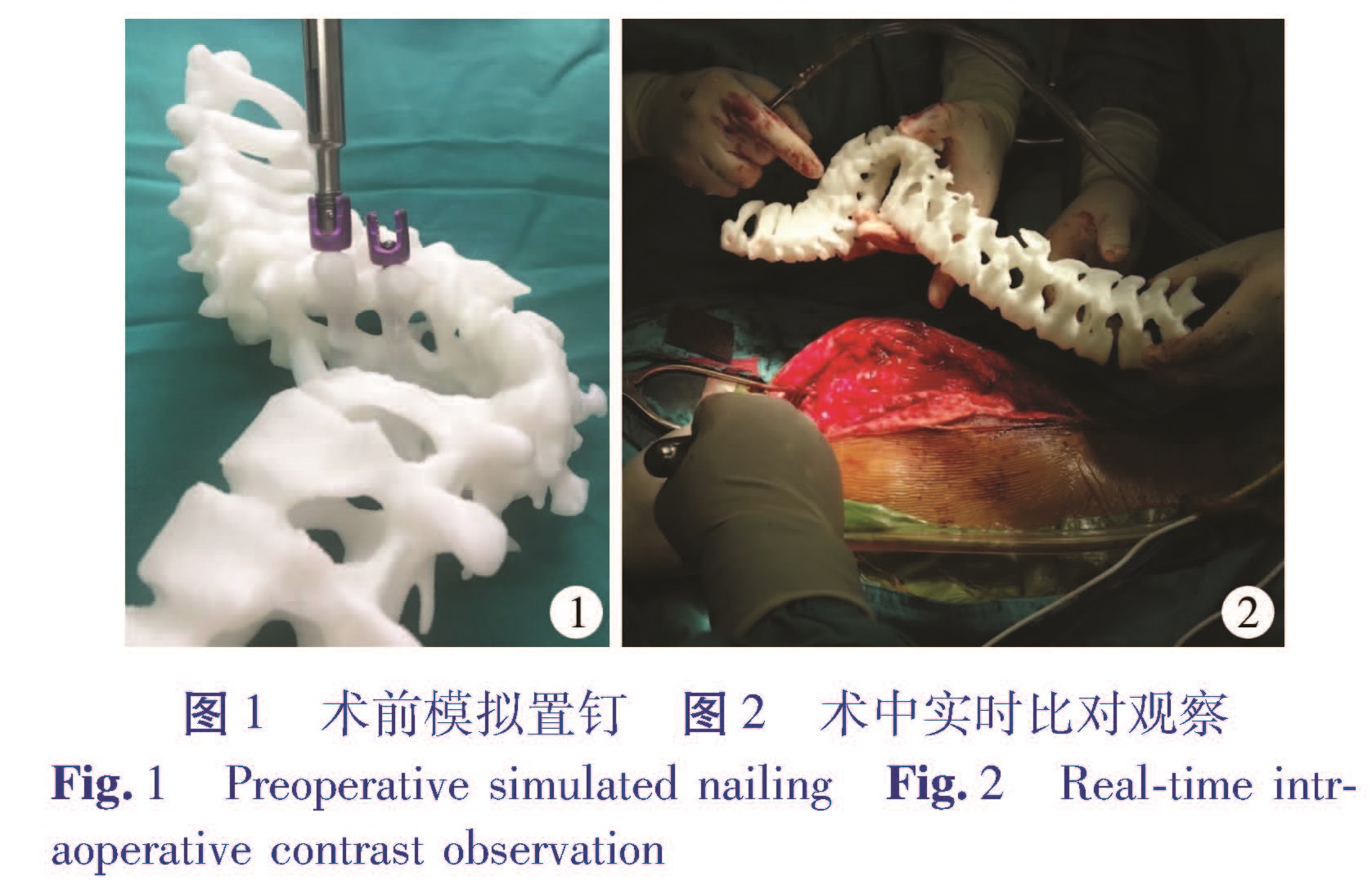
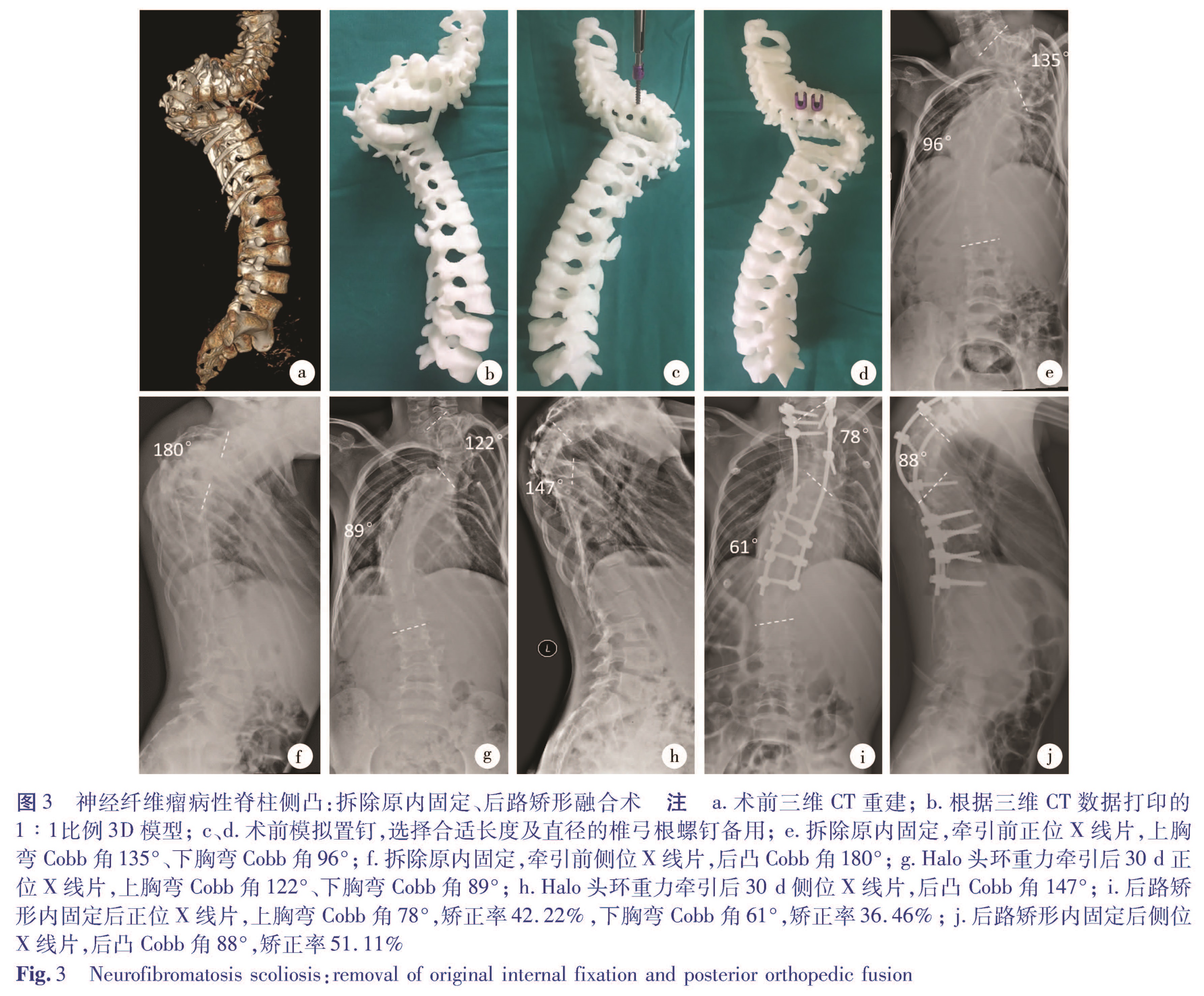
目的 探讨3D打印技术辅助手术治疗儿童重度脊柱侧凸的疗效。方法 以2013年9月至2017年9月于本院接受手术治疗的重度脊柱侧凸患儿为研究对象,符合入选标准的病例根据术前是否定制3D打印模型,分为3D打印组和非3D打印组。记录患儿年龄、手术时间、术中透视次数、手术前后侧凸Cobb角、脊柱侧凸矫正率、脊髓损伤情况等资料,并进行统计分析。结果 3D打印组共19例,男8例,女11例,平均年龄146.7个月; 非3D打印组共24例,男13例,女11例,平均年龄148.5个月。3D打印组手术用时显著少于非3D打印组(t=2.326,P<0.05),3D打印组术中透视次数显著少于非3D打印组(t=6.663,P<0.05),两组患儿胸膜损伤、硬膜损伤、神经根、脊髓损伤的发生率及脊柱侧凸矫正率比较均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论 应用3D打印技术辅助手术治疗儿童重度脊柱侧凸的优势在于术中透视次数更少、手术时间缩短; 但在矫正效果和并发症控制方面则无明显优势。
Objective To evaluate the efficacy of 3D printing technique for severe scoliosis in children. Methods The clinical and imaging data were retrospectively analyzed for hospitalized children with severe scoliosis treated from September 2013 to September 2017.Operations were performed by the same surgeon.And patient age(month),operative duration(min),frequency of intraoperative fluoroscopy,Cobb's angle(degree)before and after operation,correction rate of scoliosis and intraoperative injuries of pleural,dura,nerve root and spinal cord were recorded.They were divided into 3D printing(n=19)and non-3D printing(n=24)groups according to the preoperative 3D printing model.The 3D printing group had 8 boys and 11 girls with an average age of 146.7(83-200)months while the non-3D printing group had 13 boys and 11 girls with an average age of 148.5(94-187)months. Results The operative duration of 3D printing group was shorter than that of non-3D printing group(P<0.05).The number of intraoperative fluoroscopy was significantly lower in 3D printing group than that in non-3D printing group(P<0.05).No significant inter-group difference existed in correction rate of scoliosis(P>0.05)and pleural/dura injury(P>0.05).And there was no injury of nerve root or spinal cord. Conclusion No significant inter-group difference exists in correction effect or complications in children with severe scoliosis.However,intraoperative fluoroscopy is less frequent and operative duration shorter.