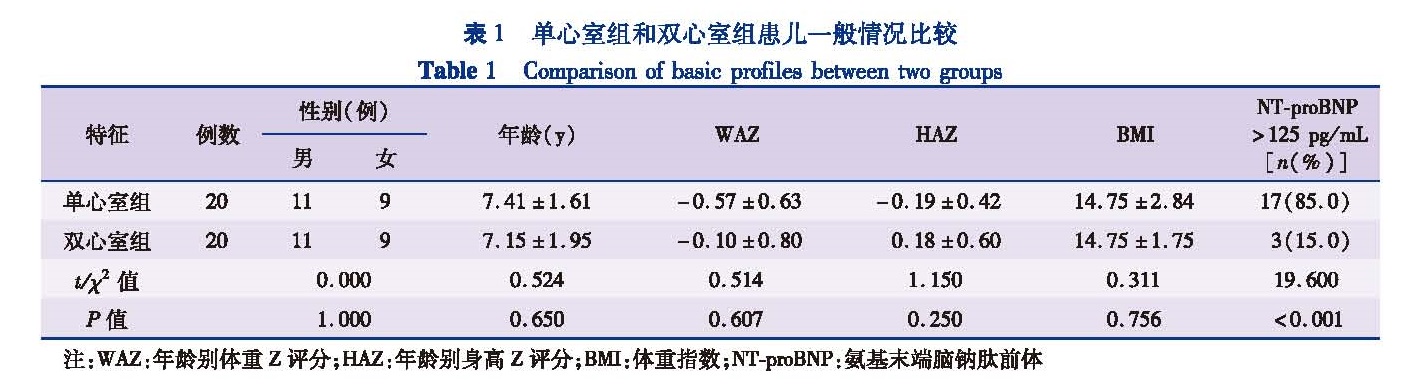
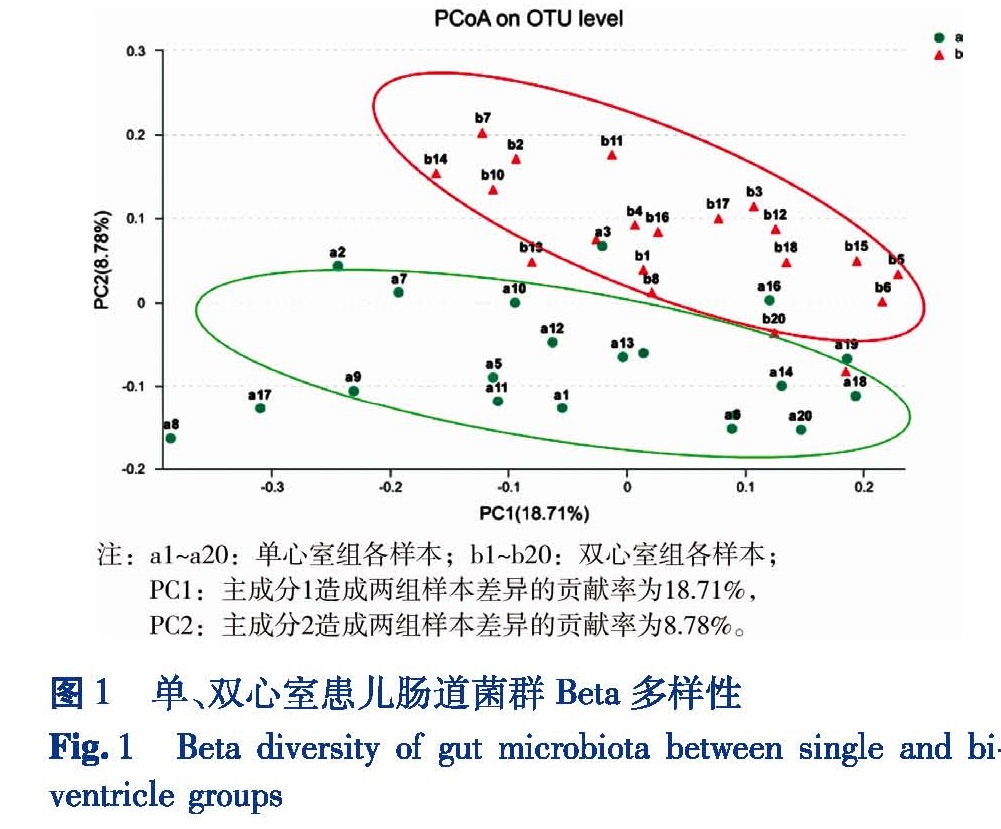
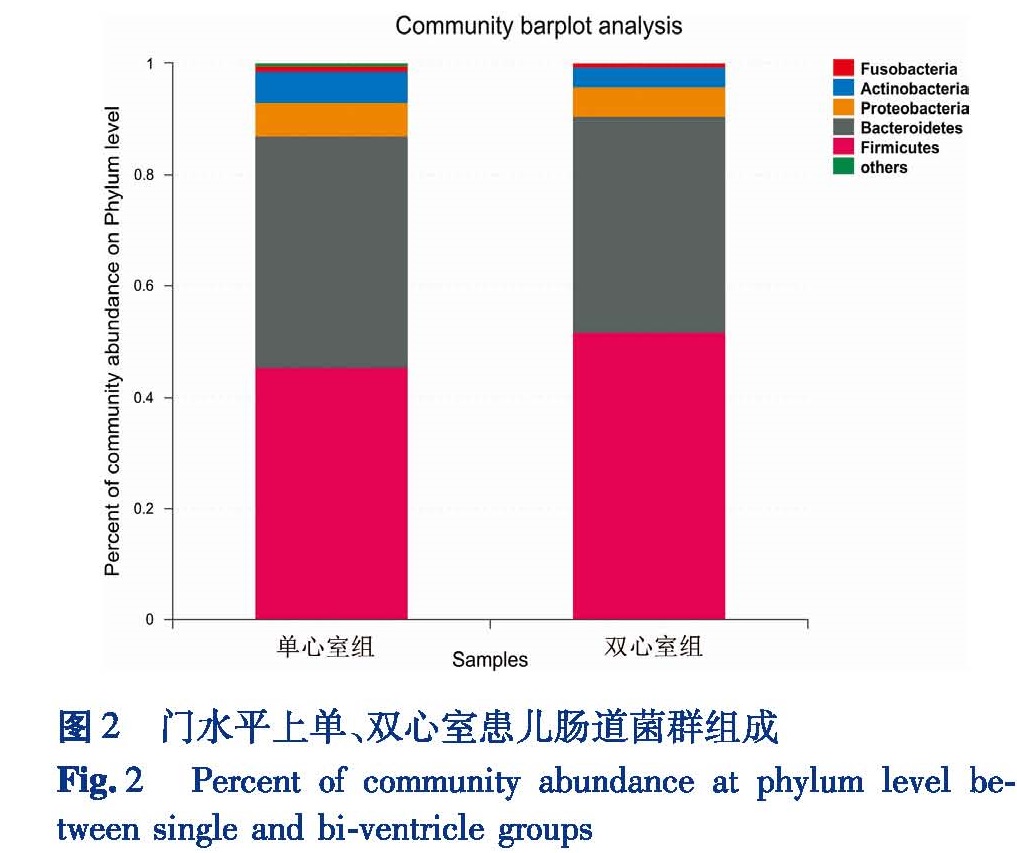
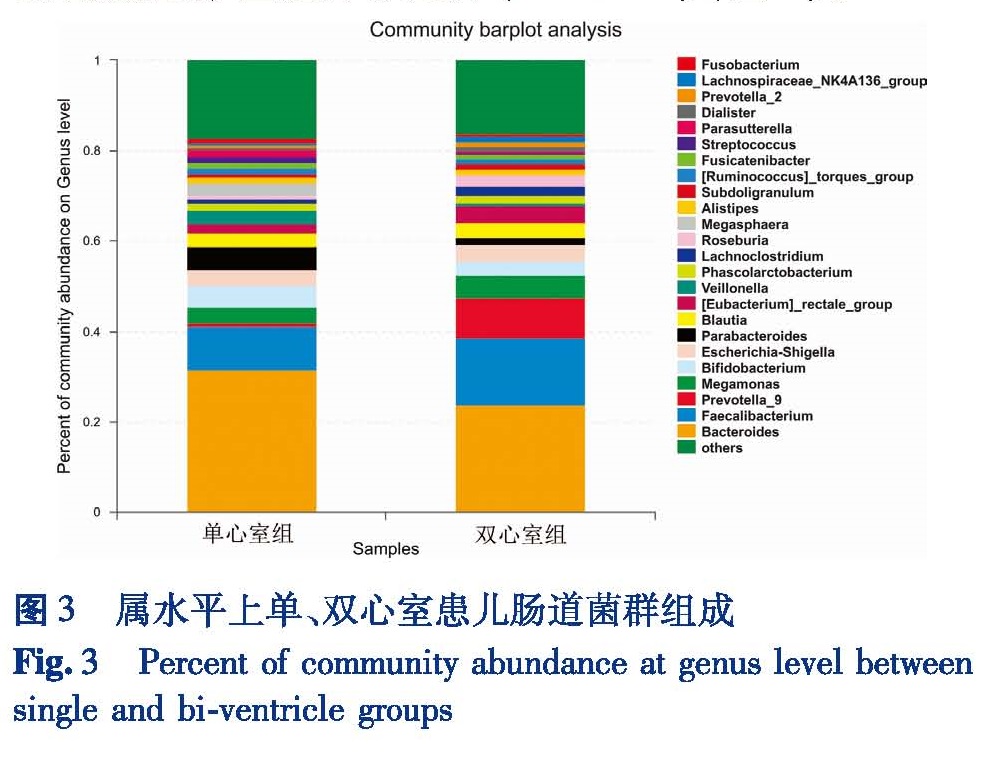
目的 通过Illumina高通量测序技术提取单心室和双心室患儿粪便样本中细菌总DNA,比较两组患儿肠道菌群的异同。方法 选取在本院行全腔静脉肺动脉连接术的单心室患儿20例(男11例,女9例,年龄3~10岁)作为单心室组,选取同期在本院性别相同、年龄(±1岁)相匹配的双心室患儿作为双心室组,收集患儿粪便标本并提取样本中细菌的DNA,进行16S rRNA高通量测序,获得肠道菌群结构数据。结果 在OTU(operational taxonomic units)水平上,单心室组和双心室组的丰富度指数(Ace:190.88 vs.201.28和Cho:188.27 vs.201.90)、多样性指数(Shannon:3.140 vs.3.090和Simpson:0.109 vs.0.110)、覆盖率指数(Coverage:0.999 vs.0.999)差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。门水平上两组均以厚壁菌门、拟杆菌门、变形菌门、放线菌门为主要优势菌群,其中蓝细菌门构成比存在统计学差异(P<0.05)。在属水平上,两组共检测到224种不同菌属,其中柔嫩梭菌属(9.55% vs14.91%),韦荣氏球菌属(3.08% vs.0.50%),Lachnoclostridium(1.02% vs.2.12%),罗斯伯里氏菌属(0.62% vs.2.51%),嗜胆菌属(0.25% vs.0.05%),放线菌属(0.312% vs.0.008%)等菌属的构成比存在统计学差异(P<0.05)。结论 单心室患儿与双心室患儿相比,菌群多样性指数无明显差异,但是菌群结构上发生了一些变化,在门水平、属水平均存在差异。
Objective Total DNA of stool samples was extracted from children with single and bi-ventricle physiology by Illumina high-throughput sequencing technology and the differences of intestinal microbiota between two groups were compared. Methods Twenty cases of single-ventricle children(11 males,9 females,age of 3~10 years)undergoing total cavopulmonary connection were selected as single-ventricle group while 20 bi-ventricle children of matching gender and age(±1 year)as bi-ventricle group.Total bacterial DNA was extracted from stool samples of two groups and 16S rRNA gene was sequenced by high-throughput sequencing.Then the structural data of intestinal microflora were obtained. Results At the level of operational taxonomic units,no significant inter-group difference existed in richness index(Ace:190.88 vs.201.28 and Cho:188.27 vs.201.90),diversity index(Shannon:3.140 vs.3.090 and Simpson:0.109 vs.0.110)and coverage index(coverage:0.999 vs.0.999)of gut microbiota(P>0.05).The predominant 4 phyla of intestinal microbiota were Firmicutes,Bacteroidetes,Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria.In addition,Cyanobacteria had significant inter-group difference(P<0.05).A total of 224 different genera of bacteria were obtained in two groups,among which Faecalibacterium(9.55% vs.14.91%),Veillonella(3.08% vs.0.50%),Lachnoclostridium(1.02% vs.2.12%),Roseburia(0.62% vs.2.51%),Bilophila(0.25% vs.0.05%)and Actinomyces(0.312% vs.0.008%)had significant inter-group difference(P<0.05). Conclusion No significant difference exists in diversity index of gut microbiota between single and double-ventricle groups.However,the structure of intestinal microbiota has changed in some specific bacteria.