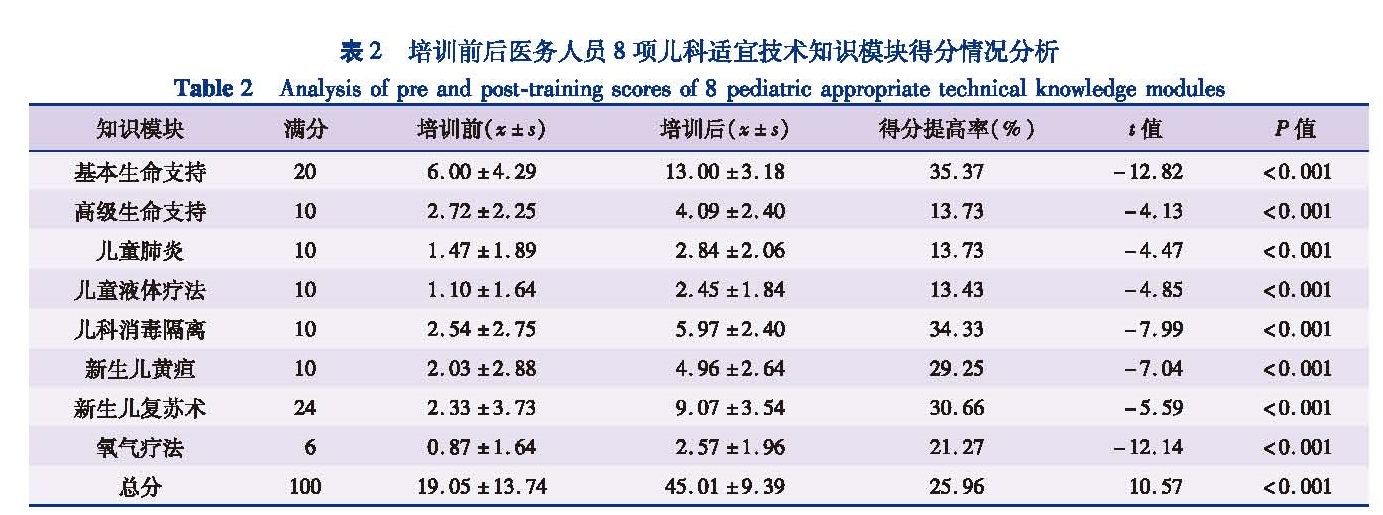
目的 探讨儿科适宜技术在柬埔寨培训的效果,为其在柬埔寨推广提供科学依据。方法 选取67名柬埔寨医护人员作为研究对象,开展8项儿科适宜技术培训,培训前后进行问卷调查和知识考核。结果 研究对象培训前儿科适宜技术知识总得分较低,仅为(19.05±13.74)分; 8项儿科适宜技术的得分均较低,其中儿童基本生命支持为(6.00±4.29)分; 儿童高级生命支持为(2.72±2.25)分; 儿童肺炎为(1.47±1.89)分; 儿童液体疗法为(1.10±1.64); 儿科消毒隔离为(2.54±2.75)分; 新生儿黄疸为(2.03±2.88)分; 新生儿复苏术为(2.33±3.73)分; 氧气疗法为(0.87±1.64)分。培训后儿科适宜技术总得分(45.01±9.39)明显高于培训前(19.05±13.74),差异具有统计学意义(t=10.57,P<0.05); 培训后8项适宜技术知识得分均明显高于培训前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。从得分提高率来看,基本生命支持的得分提高最为明显,儿科消毒隔离次之。 结论 柬埔寨国家儿童医院医护人员对儿科适宜技术的理论知识普遍缺乏,儿科急救能力偏低; 中国的儿科适宜技术培训在短期内能够有效提高柬埔寨儿科医护人员对儿科适宜技术的掌握度,但整体培训效果并不理想,有必要后续加强培训。
Objective To explore the outcomes of Chinese pediatric appropriate technology training in Cambodia and provide scientific rationales for enhancing pediatric appropriate technology training in Cambodia. Methods Based upon surveying at Cambodian National Children's Hospital,67 Cambodian medical staffs were selected as research subjects for receiving 8 subjects of pediatric appropriate technology training.Questionnaires and knowledge assessments were adopted before and after training courses. Results The total pre-training score of pediatric appropriate technology knowledge was low at(19.05±13.74)points.And the scores of 8 pediatric appropriate technologies were low,among pediatric basic life support score was(6.00±4.29)points; pediatric advanced life support(2.72±2.25)points; pediatric pneumonia(1.47±1.89)points; pediatric fluid therapy(1.10±1.64)points; pediatric disinfection & isolation score(2.54±2.75)points; neonatal jaundice score(2.03±2.88)points; neonatal resuscitation score(2.33±3.73)points; oxygen therapy score(0.87±1.64)points.The total post-training score of pediatric appropriate technology was significantly higher than that pre-training [(45.01±9.39)vs.(19.05±13.74)points].And the difference was statistically significant(t=10.57,P<0.05).The post-training scores of 8 appropriate technical knowledge modules were higher than that pre-training.And the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).In terms of score improvement rate,improvement of basic life support was the most obvious,followed by pediatric disinfection & isolation technology. Conclusion The participants of National Children's Hospital in Cambodia lacked theoretic knowledge of pediatric appropriate technology and their emergency abilities were quite inadequate.Training combining theory and simulation training could improve the proficiency of pediatric appropriate technologies within a short period.However,training outcomes have failed to reach the expected goals.It is imperative to strengthen such training.