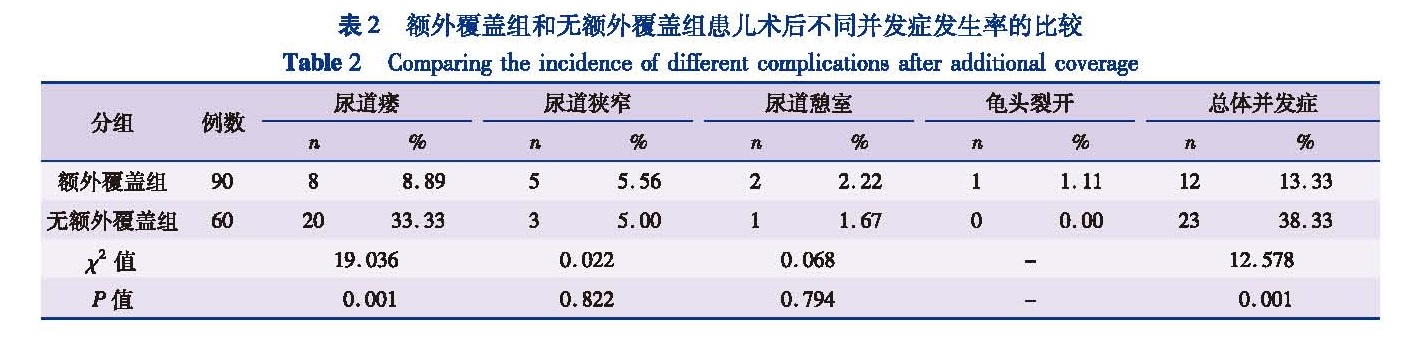
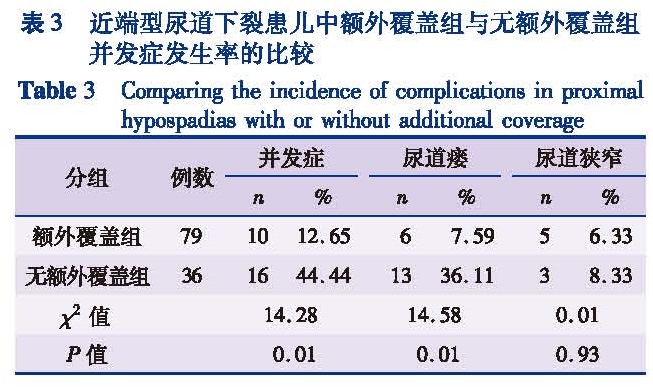
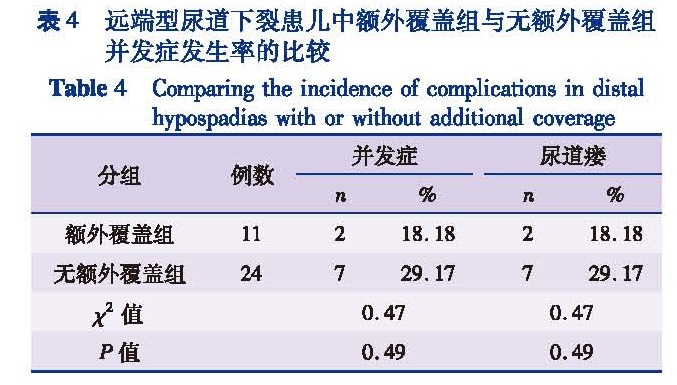
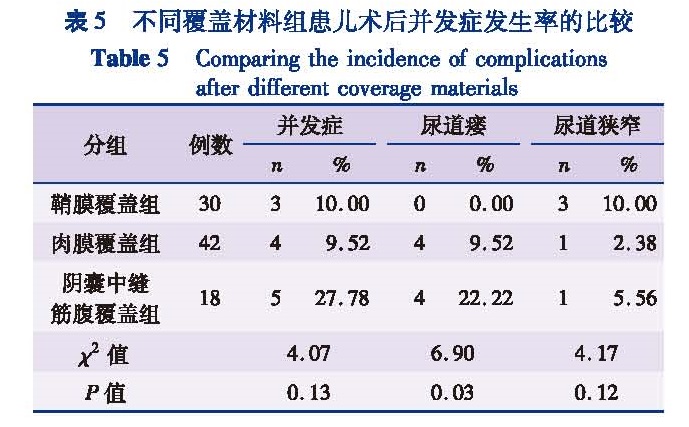
目的 比较尿道下裂手术中有无额外覆盖及不同软组织覆盖并发症发生率的差异,为临床选择最佳额外覆盖材料提供参考依据。方法 回顾性分析2014年1月至2016年12月符合纳入和排除标准由本院收治的尿道下裂患儿150例,依据有无额外覆盖材料分为额外覆盖组(n=90)和无额外覆盖组(n=60); 根据术中探查尿道口位置分为近端型尿道下裂组(n=115)及远端型尿道下裂组(n=35); 根据覆盖组织分为鞘膜覆盖组(n=30)、肉膜覆盖组(n=42)以及阴囊中隔筋膜覆盖组(n=18)。结果 额外覆盖组和无额外覆盖组首次手术的年龄、平均龟头直径、阴茎拉伸长度、阴茎脱套后腹曲角度、尿道缺损长度无统计学差异(P>0.05)。150例中,35例术后出现并发症,发生率为23.33%。额外覆盖组并发症发生率为13.33%(12/90),无额外覆盖组并发症发生率为38.33%(23/60),差异有统计学意义(χ2=12.578,P=0.001); 额外覆盖组尿道瘘发生率为8.89%(8/90),无额外覆盖组尿道瘘发生率为33.33%(20/60),差异有统计学意义(χ2=19.036,P=0.001)。115例近端尿道下裂中,其中79例使用了额外覆盖材料,10例(12.65%)术后发生了并发症,36例未使用额外覆盖材料,16例(44.44%)术后发生了并发症,差异存在统计学意义(χ2=14.28,P=0.01)。同时,额外覆盖组尿道瘘发生率为7.59%(6/79),无额外覆盖组尿道瘘发生率为36.11%(13/36),差异有统计学意义(χ2=14.58,P=0.01)。肉膜覆盖组并发症发生率为9.52%(4/42),睾丸鞘膜覆盖组并发症发生率为10%(3/30),阴囊中缝筋膜覆盖组并发症发生率为27.78%(5/18),三组患儿术后并发症发生率无统计学差异(χ2=4.07,P=0.13); 肉膜覆盖组、睾丸鞘膜覆盖组和阴囊中缝筋膜覆盖组三组患儿术后尿道瘘的发生率分别为9.52%、0.00%和22.22%,差异有统计学意义(χ2=6.90,P=0.03)。结论 额外覆盖可有效降低尿道下裂术后并发症尤其是尿道瘘的发生率,和其他覆盖组织比较睾丸鞘膜可更有效的降低术后尿道瘘的发生率。
Objective To compare the differences of complication rates with additional coverage and select the optimal urethral covering material during hypospadias surgery. Methods A retrospective study was conducted for 150 patients with hypospadics undergoing surgical repair from January 2014 to December 2016.They were divided into additional coverage(n=90)and uncovered(n=60)groups.According to intraoperative exploration of urethral orifice position,they were divided into proximal(n=115)and distal(n=35)hypospadias groups.And the additional coverage group was divided into tunica vaginalis(n=30),dartos flap(n=42)and mid-scrotalfasciocutaneous flap(n=18)groups. Results No statistical difference existed in median age,mean glans diameter,penile traction length,penile curvature degree or urethral defect length between additional coverage and uncovered groups.And 35/150 cases had postoperative complications with a complication rate of 23.33%.The complication rate was 13.33% in additional coverage group and 38.33% in uncovered group.There was inter-group statistical difference(χ2=12.578,P=0.001).While the incidence of urethral fistula rate was 8.89%(8/90)in additional coverage group and 33.33%(20/60)in uncovered group.There was inter-group statistical difference(χ2=19.036,P=0.001).Among 115 proximal hypospadics,79 cases used additional covering materials,10(12.65%)had postoperative complications,36 cases used no additional covering materials and 16 cases(44.44%)had postoperative complications.There was inter-group statistical difference(χ2=14.28,P=0.01).While 7.59% of proximal hypospadics had postoperative urethral fistula with additional covering materials,36.1% of proximal hypospadics had postoperative urethral fistula without additional covering materials(χ2=14.58,P=0.01).The complication rate was 9.52% in dartos flap group,10% in tunica vaginalis flap group and 27.78% in mid-scrotal fasciocutaneous flap group.No statistical difference existed among three groups(χ2=4.07,P=0.13).Urethral fistula was 9.52% in dartos flap group,0.00% in tunica vaginalis flap group and 22.22% in mid-scrotal fasciocutaneous flap group.Statistical differences existed among three groups(χ2=6.90,P=0.03). Conclusion Additional coverage may effectively reduce the complication rate of hypospadias.As compared with other cover tissues,tunica vaginalis effectively lower the incidence of postoperative urethral fistula.
![表1 额外覆盖组与无额外覆盖组患儿基本情况的比较[M(P25~P75)]<br/>Table 1 Comparison between additional coverage group and uncovered group[M(P25~P75)]](2018年08期/pic05.jpg)