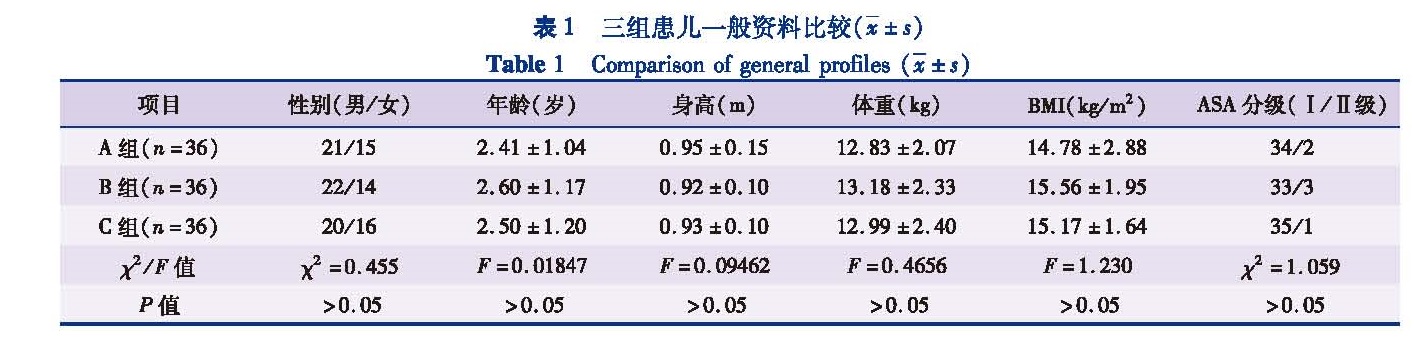
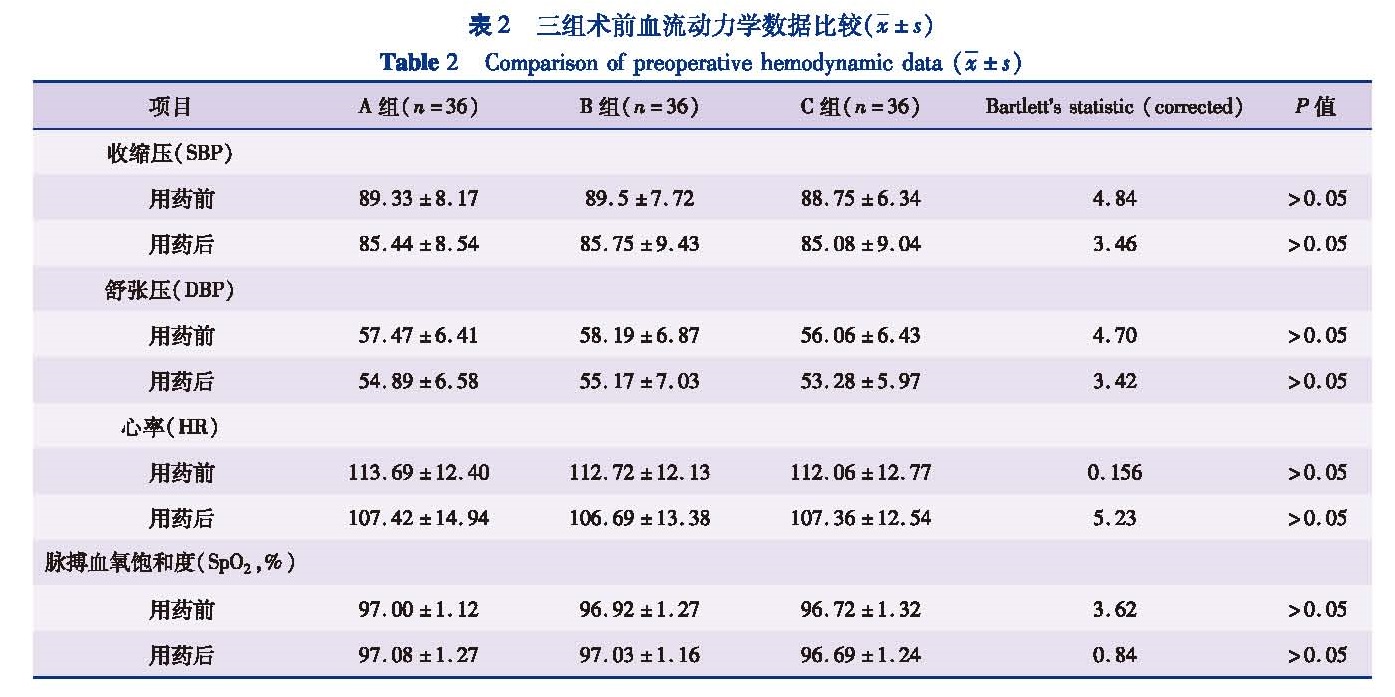
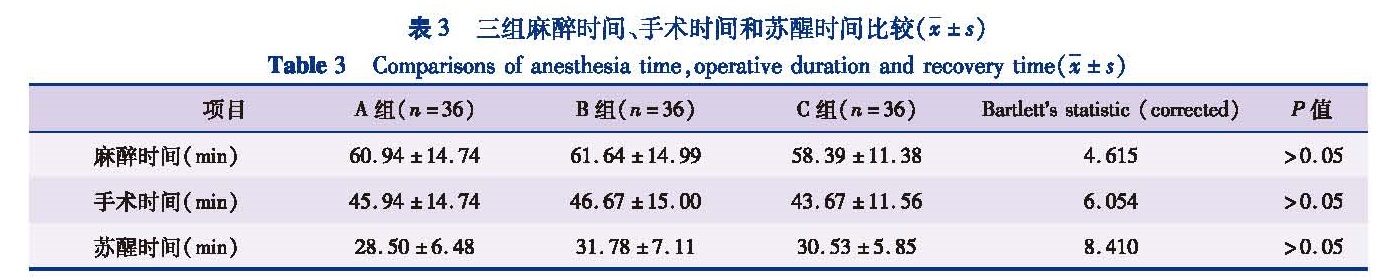
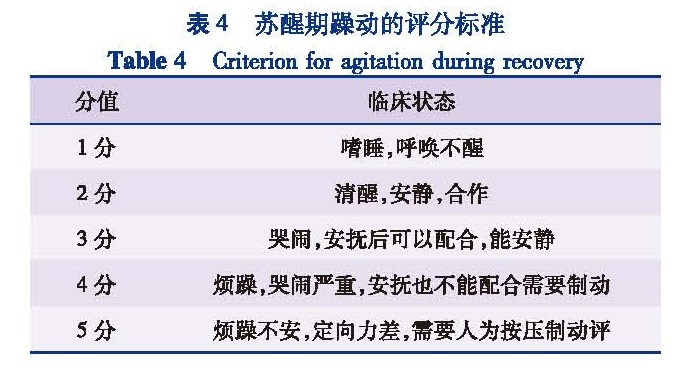
目的 观察并对比右美托咪定和咪达唑仑对小儿静脉吸入复合麻醉苏醒期躁动的影响。方法 将2013年3月至2016年6月本院108例1~4岁择期实施腹腔镜下疝囊高位结扎术的患者,按照随机原则分为A组(右美托咪定组)、B组(咪达唑仑组)和C组(生理盐水组),每组各36例。三组均予七氟烷诱导并维持。比较三组年龄、身高、体重、BMI和ASA分级等一般资料,用药前后血流动力学数据,麻醉时间、手术时间和苏醒时间,以及对麻醉后苏醒期躁动的影响等指标。结果 三组患儿年龄、身高、体重、BMI和ASA分级等一般资料组间比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),各组患儿用药前后SBP、DBP、HR和SpO2存在波动,但差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),三组患儿麻醉时间、手术时间和苏醒时间比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。A组在拔管后5 min(T1)、10 min(T2)、15 min(T3)、20 min(T4)躁动发生率与C组相比明显降低,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05); 拔管后即刻(T0)和拔管后30 min(T5)A组、C组间躁动发生率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05); B组各时间点躁动发生率较C组无显著性差异(P>0.05)。结论 临床剂量右美托咪定对小儿静脉吸入复合麻醉苏醒期躁动的疗效优于咪达唑仑。
Objective To observe the roles of dexmedetomidine and midazolam on emergence agitation after pediatric intravenous-inhalation combined anesthesia. Methods A total of 108 children aged 1~4 years undergoing laparoscopic high-ligation of hernia sac were selected and randomly divided into group A(dexmedetomidine),group B(midazolam)and group C(normal saline)(n=36 each).All patients were induced and maintained by general anesthesia of sevoflurane.Age,height,weight,body mass index(BMI),ASA grade and hemodynamic data before and after drug dosing were compared.Also the times of operation,anesthesia and recovery and the effect of drugs on emergence agitation after anesthesia were analyzed. Results No significant differences existed in age,height,weight,BMI or ASA classification among three groups(P>0.05).There were fluctuations in SBP,DBP,HR and SpO2 among three groups,yet there were no significant differences(P>0.05).No significant differences existed in times of operation,anesthesia and postanaesthetic among three groups(P>0.05).The incidences of agitation in group A were lower than those in group C at T1,T2,T3 and T4 and the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).No significant differences existed between groups A and C at T0 and T5(P>0.05)and groups A and B at various timepoints(P>0.05). Conclusion The effect of dexmedetomidine is better than that of midazolam on emergence agitation induced by intravenous-inhalation combined anesthesia.
![表5 三组苏醒期躁动发生率的比较[n(%)]<br/>Table 5 Comparing the incidence of restlessness during recovery [case(%)]](2018年07期/pic31.jpg)
