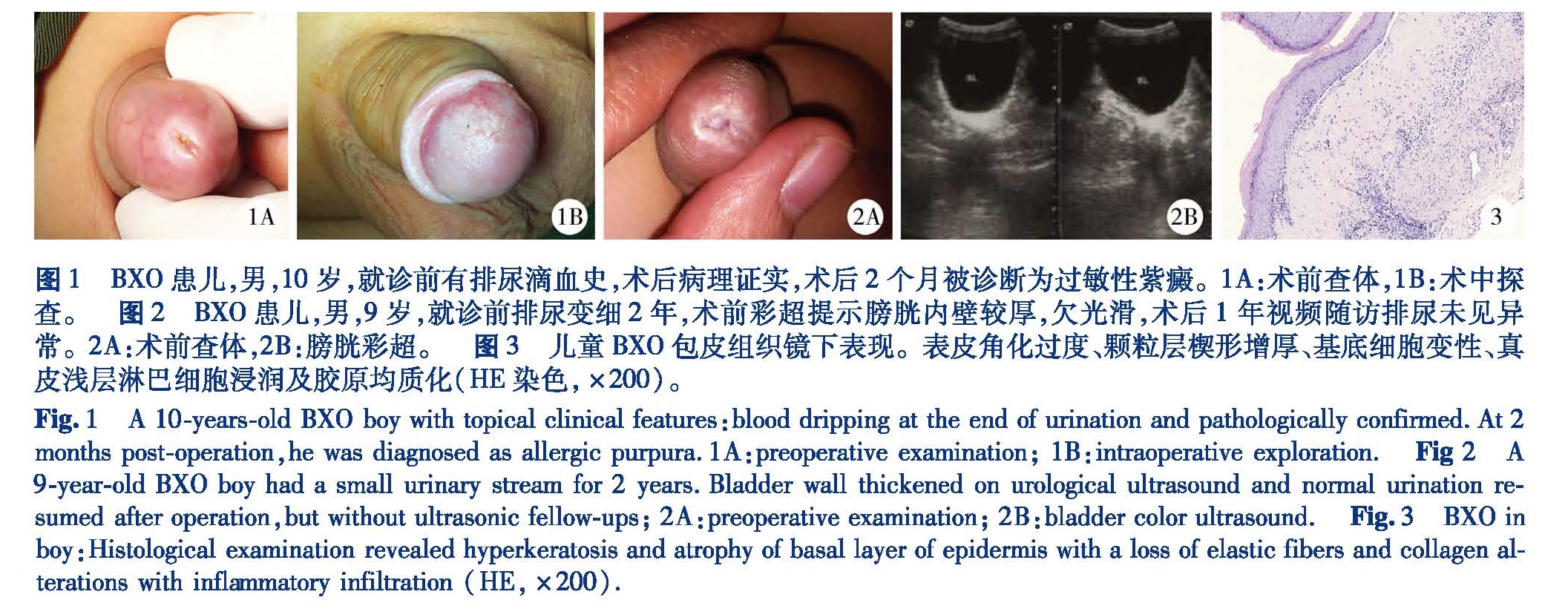
干燥性闭塞性阴茎龟头炎(BXO)既往又被称为男性生殖器硬化性苔藓样病(male genital lichen sclerosus,MGLSc),是一种伴有皮肤萎缩纤维化病变的慢性复发性疾病,病程长且有逐渐加重趋势。1887年由Hallopeau首先报道,1928年Sruhmer将其更新定义为BXO,与男性生殖器LS通用。1962年Caterall和Oates报道了第1例儿童BXO。流行病学研究发现BXO可发生在任何年龄,高发于成年期和儿童期,被认为是继发性包茎(secondary phimosis,SP),因感染或不明原因引起包皮口狭窄,不能完全上翻包皮显露龟头的主要病因[1-2,4]。
3.1 BXO的发病率
国外对BXO发病率的估计在0.1%~0.3%,儿童占7%~15%[4]。儿童发病率伴随对SP包皮标本送检的重视,检出率高达10%~50%,但确切发病率仍不清楚[1,5]。2005年Kiss等[6]对1 178例匈牙利包茎儿童(2~16岁,除外社会及宗教因素的包皮环切术)进行前瞻性研究,发现BXO高达40%(471/1 178),占SP的65%(438/674),高发于9~11岁儿童(76%)。Becker等[2]系统回顾2004—2008年间英文文献发现儿童BXO占SP的10%~40%,并估算德国儿童BXO的发病率约占0.1%~0.4%,认为美国德州报道10岁以下儿童BXO发病率仅为0.07%,可能得益于当地新生儿包皮手术的流行。2014年,Celis等[1]收集1995—2013年间发表于泌尿或小儿外科杂志的18岁以下男童BXO英文文献,并回顾了作者单位近10年儿童BXO的情况,认为BXO占所有包皮病理检查病例的35%(816/2 294),平均发病年龄在6~10岁。但值得重视的是,在Jayakumar等[5]的研究中, 5岁以下的BXO儿童占19.3%(35/182)。这提示我们应在更早期考虑该病的存在。虽然近年来我国成人BXO就诊量的增加已引起部分成人泌尿外科医生的关注,但主要还是少量个案报道[7]; 在儿童,除偶尔在尿道下裂术后顽固尿道狭窄段的病理检测中获得诊断外,赵冬艳等[8]报道儿童BXO占所有包茎手术后病理检查病例的27.4%(29/106),总的发病率仍不详[3]。本组患儿中SP占17.8%(35/197),其中BXO发生率为22.9%(8/35)。提示该病在我国可能也不少见,但确切的发病率尚需大样本深度研究。
3.2 BXO与包皮慢性炎症及其他
BXO是一种淋巴细胞介导的男性外生殖器上皮慢性炎症性疾病,以包皮累及最为明显,其确切病因仍不清楚,推测与尿液慢性刺激、自身免疫性疾病、遗传因素、传染性因素等有关,包皮腔温暖湿润的环境可能是儿童BXO的重要促进因素[1,9]。
传统认为局部因素如阴茎头炎和(或)尿道梗阻后尿液慢性刺激,导致包皮变性是BXO的主要病因。已有不少流行病学研究证实超过一半的BXO患儿伴有SP。近期有研究发现尿道下裂并发症中合并BXO达30%(47/157),包括梗阻性并发症:尿道外口狭窄(40%,18/45)、尿道狭窄(25%,7/28)、尿道裂开(30%,15/50)及与感染有关的尿道瘘(20.6%,7/34)。所有病理活检样本阳性率高达39.5%(124/314)[10]。在分子病理学研究方面,Pilatz等[11]应用RT-PCR发现儿童BXO中存在11个与促炎因子及组织重建关键蛋白相关的基因上调,这与既往在成人方面的发现一致[12]。
也有研究发现BXO儿童行包皮环切术后仍有一定比例患儿继续表现BXO病变,包括包皮切口处的同形反应,甚至高达20%的尿道外口狭窄发生率 [2,13,14]。Snodgrass等[15]在尿道下裂伴BXO患儿术后尿路梗阻中发现,在移植成形尿道的口腔颊粘膜出现BXO侵袭性病变。本组8例诊断BXO病例均无明显的包皮感染病史,1例术后2个月出现尿道外口狭窄,1例术前包皮口瘢痕化,但彩超下可见尿道外口膀胱壁压力有改变。
上述研究提示包皮局部炎症和尿道梗阻可能是BXO的主要诱发因素,同时也可能存在引起皮肤原发损害的内因。已有证据显示BXO可能与自身免疫性疾病相关,如在BXO的病理组织中发现大量炎性渗出、细胞毒性T淋巴细胞自动激活、细胞外基质代谢受损及自身抗体的生成等[1],这也符合BXO的进行性临床改变。本组有1例临床和病理均诊断BXO的患儿,在术后2个月被确诊自身免疫性疾病(过敏性紫癜)。此外,BXO的遗传倾向也偶有报道,Becker等[2]在225例BXO患儿中发现有3对双胞胎及1对兄弟同时患病。
3.3 BXO的临床及病理诊断
在国外,外生殖器典型皮损、临床症状明显的患儿通常可以直接临床诊断为BXO[6,13,16]。包皮是儿童BXO的好发部位,包皮(口)出现白色硬化、瘢痕化改变,形成SP,可伴有龟头的慢性硬化和萎缩,严重时可致尿道狭窄(尿道外口为主),表现为不同程度的排尿不畅,包括包皮腔尿液充盈、尿线细、排尿滴沥、包皮口滴血、膀胱壁毛糙增厚甚至肾衰竭等[1-2,17]。本组6例获临床诊断的病例均没有明显诱因,1例包皮口环状瘢痕化明显,可显露尿道外口,但尿线细,存在膀胱壁增厚毛糙,术后1年随访排尿基本正常; 1例包皮口极度瘢痕狭窄,术中探查龟头及背侧包皮内板颜色红润,腹侧包皮内板硬化明显,系带毁损,尿道外口正常,但术后2个月开始出现尿道外口膜性狭窄,尿线极细; 其余4例均为典型的BXO皮损改变及排尿不畅,术后排尿和随访均无异常。虽然综合各文献报道临床诊断BXO的准确率通过病理检查校准后平均在53%,但也有稳定在83%~84%的报道[1,14,18],这可能与活检部位或病理切片的选取有关,也与临床医生对BXO典型皮损表现的认识密切关联。
但对于缺乏特异性症状的早期BXO,病理检查是诊断的金标准[19]。在BXO的定义里实际涵盖了3个主要的临床、病理表现,分别是B(balanitis):阴茎龟头的慢性炎症; X(xerotica):病变部位异常干燥的外观; O(obliterans):阴茎头皮下的动脉内膜炎表现。在病理检查中,最具有特征性和诊断价值的病理变化包括:表皮角化过度、颗粒层楔形增厚、基底细胞变性、真皮浅层淋巴细胞浸润及胶原均质化[19]。有研究发现在没有典型临床表现的SP患儿中病理也检出BXO,可见病理诊断的重要性[19]。目前国际上较为统一的意见是:所有SP患儿手术后包皮均应送检,病理诊断可对BXO进行分期。早期:基底细胞水肿变性,真皮层水肿,表真皮交界处炎性细胞浸润; 中期:上部真皮层胶原均质化; 晚期:表皮角化过度、萎缩,淋巴细胞浸润带以上真皮层可见大量胶原均质化改变[6,19]。在保证SP患儿包皮标本送检情况下,也应重视临床诊断,因为部分早期患儿可因此通过局部药物治疗而获益,避免手术[14,16]。
3.4 激素和手术治疗先后的选择
与成人不同,儿童BXO的治疗主要包括局部使用糖皮质激素和手术[13,14,16]。有研究显示,局部使用糖皮质激素安全,且不良反应少,不仅在疾病早期和中期可明显改善BXO症状,手术后还可有效减缓BXO的继续发展,可作为临床诊断BXO的治疗首选[1,14,16]。但更多学者认为,诊断早期BXO并不容易,在非SP患儿中也常有BXO的报道[1],且新生儿包皮手术与BXO低发生率的关系也十分密切[2],因此激素类药物仅起辅助作用,应更多强调阴茎包皮局部的清洁卫生,去除可能持续存在的刺激性因素(如包茎),首选包皮环切术 [1,13,14,16],且不提倡仅行包皮侧切术,因为术后高复发率和不满意的外观往往需要再次手术[14]。针对因宗教原因需保留包皮或存在尿道下裂的患儿,有学者认为:包皮侧切术应联合皮下局部注射激素(曲安奈德),对抑制包皮特异性慢性炎症和减少尿道外口狭窄的发生也有一定的作用[13]。
对BXO术后发生尿道外口狭窄的患儿,先使用激素的效果已被肯定,只有在激素治疗无效的情况下(一般治疗6~12周)才考虑尿道外口成形术[15,16]。针对原发或术后发生尿道狭窄的患儿,如有BXO病理支持,建议用外生殖器外的其他部位皮瓣转移成形尿道,如口腔颊黏膜[15,16,18]。
此外,有研究者探讨非糖皮质激素对儿童BXO的疗效[1],如免疫抑制剂他克莫司软膏(0.1%)用于BXO包皮环切术后的局部辅助治疗,尤其是伴尿道外口或龟头炎症时,可作为激素的替代药物,但其疗效目前仍缺乏大样本的统计研究[4,15,20]。
3.5 预后及随访时间的确定
大量临床研究及随访表明,经积极干预的BXO预后良好。SP患儿早期局部使用糖皮质激素可部分有效缓解BXO症状,这已被多家中心纳入儿童BXO的诊疗流程。有报道指出儿童BXO术后切口出血的发生率(2.3%,6/262)要比无BXO儿童(0.3%,8/2 123)高,考虑除皮肤本身的慢性炎症外,是否存在早期使用激素的原因,但综合既往文献仍无一致的结论[21]。对儿童BXO使用激素无效而转手术治疗的时间,一般认定为6~12周,但对术后随访的时间却意见不一(6个月至2年不等)。手术干预的BXO早期并发症多发生在术后30 d内,包括:切口感染、出血及急性尿潴留等,仅做对症处理,效果好; 超过30 d,BXO症状复现,即定义为晚期并发症,主要表现为残留包皮萎缩变白、尿道外口狭窄和尿道狭窄,激素和手术联合治疗效果肯定。BXO晚期并发症存在阴茎癌的发生风险,在成人,这种关系已被确认:阴茎鳞状细胞癌中,2.2%~28%伴有BXO,但由于缺乏长期随访及重视不足,这种癌变与儿童期发生BXO的相关性未见报道。随着健康与疾病发育源说(developmental origins of health and disease,DOH-aD)的提出,联合小儿和成人泌尿外科医生对这些病人实现长期的随访、观察和诊断是非常有必要的[1]。我们建议,儿童BXO行包皮环切术后,予预防性局部激素治疗(最少6周)和长期随访,以便早期诊断BXO复发和(或)排尿性梗阻,并进一步明确与阴茎癌变的关系。
3.6 我们的经验
针对早期BXO有一定的临床漏诊率,我们建议SP患儿均行包皮环切术,尤其是不明原因出现包皮失去弹性、苍白者,应保留包皮标本送病理检查。根据病理检查结果,阳性者阴茎头部给予氟轻松软膏外用4~8周,长期随访,注意排尿情况; 对术后出现尿道外口/尿道瘢痕狭窄者,早期可尝试给予曲安奈德局部注射,无效后需重新成形尿道外口/尿道,切除可疑包皮瓣; 对于尿道下裂存在可疑BXO包皮瓣者,应尽量切除并采用生殖器外的其他部位皮瓣转移成形尿道。
总之,BXO在儿童中是存在的,且其发病率可能不低。BXO早期除可能有SP局部表现外,并无特殊临床症状,容易漏诊误诊。加强对该病的认识和重视,增加可疑病例包皮组织送检率,对明确诊断,做好儿童健康管理,有重要的促进作用。