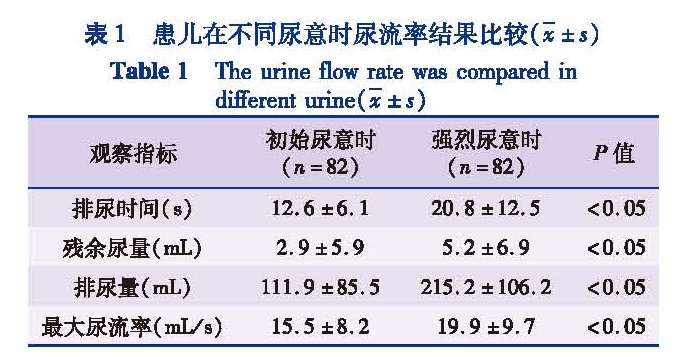
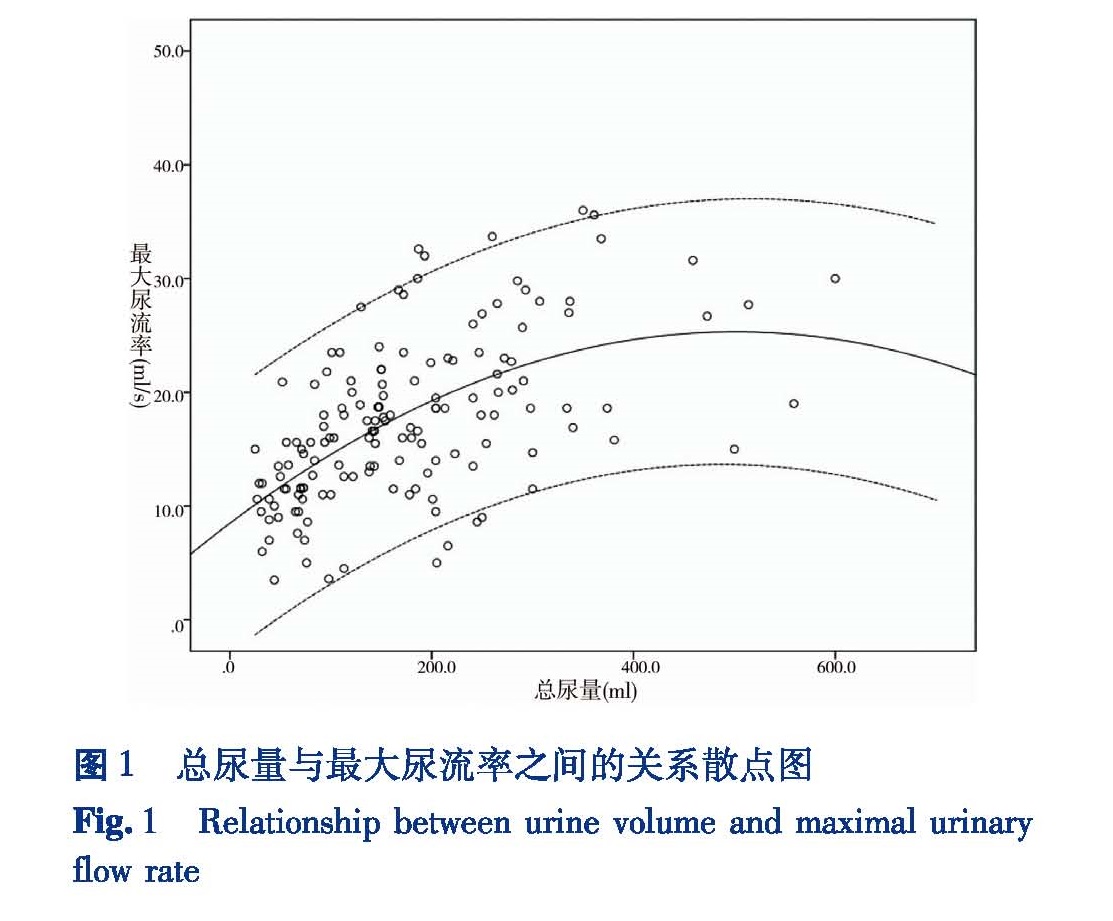
目的 分析遗尿患儿在初始尿意和强烈尿意两种不同情况下尿流率和残余尿测定结果的差异,为临床应用尿流率测定来判断遗尿患儿膀胱功能提供参考。方法 对来本院就诊的102例原发性遗尿症患儿(男性60例,女性42例),在初始尿意和强烈尿意时分别进行尿流率和残余尿测定,比较两种情况下尿流率参数(排尿量、排尿时间、最大尿流率)及每次残余尿量检查结果。结果 初始尿意时测得患儿最大尿流率为(15.5±8.2)mL/s,残余尿量为(2.9±5.9)mL; 强烈尿意时测得患儿最大尿流率为(19.9±9.7)mL/s,残余尿量为(5.2±6.9)mL; 初始尿意与强烈尿意下最大尿流率和残余尿比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。最大尿流率随尿量的增加而增加,但当尿量增加到一定程度后最大尿流率反而有下降趋势。男性与女性在初始尿意时的最大尿流率和残余尿没有显著差异,但在强烈尿意时,男性的最大尿流率显著低于女性,(18.5±8.2)mL/s vs(24.2±12.5)mL/s(P<0.05),而残余尿量没有差异。结论 遗尿患儿在初始尿意和强烈尿意下尿流率-残余尿测定结果有显著差异,遗尿患儿进行自由尿流率测定时不宜过度憋尿,临床上分析尿流率及残余尿测定结果时要考虑尿意状态和排尿量对尿流测定参数的影响。
Objective To explore the efficacies of modified diamond-shaped anastomosis for annular pancreas in newborns.To observe the differences of urine flow rate and post-voiding residual urine volume(PVR)in patients with enuresis in first desire to void(FD)and strong desire to void(SD)and provide rationales for examining urinary bladder function. Methods For 60 boys and 42 girls with primary nocturnal enuresis(PNE),urinary flow rate and PVR were measured respectively in FD and SD and the differences compared. Results The maximum urine flow rate was(15.5±8.2)mL/s and PVR(2.9±5.9)mL in FD; The maximum urine flow rate was(19.9±9.7)mL/s and PVR(5.2±6.9)mL in SD; Statistically significant differences existed in maximum urinary flow rate and PVR(P<0.05).The maximum urine flow rate increased with rising voided volume,but the maximum urine flow rate decreased at a height of voided volume.No significant difference existed in maximum urine flow rate in FD among children of different genders.However,the maximum urine flow rate in SD of boys was significantly lower than that of girls(18.5±8.2 vs 24.2±12.5 mL/s,P<0.05). Conclusion Urine flow rate and PVR examination results are significantly different between FD and SD.Children with urinary incontinence should not retain excessive urination during free flow rate examination.And voided volume should be taken into account during the analyses of urine flow rate and PVR.