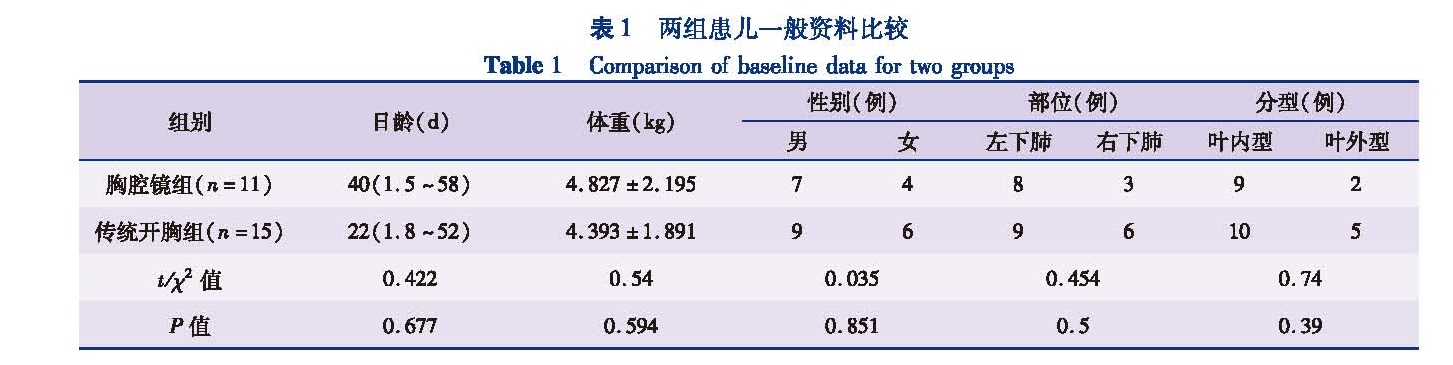
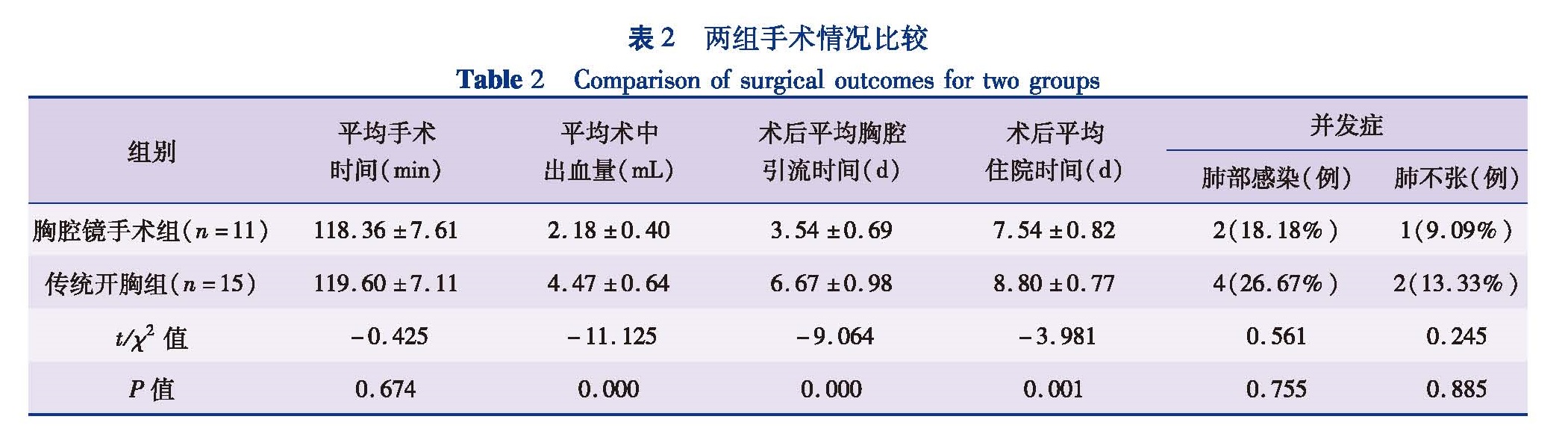
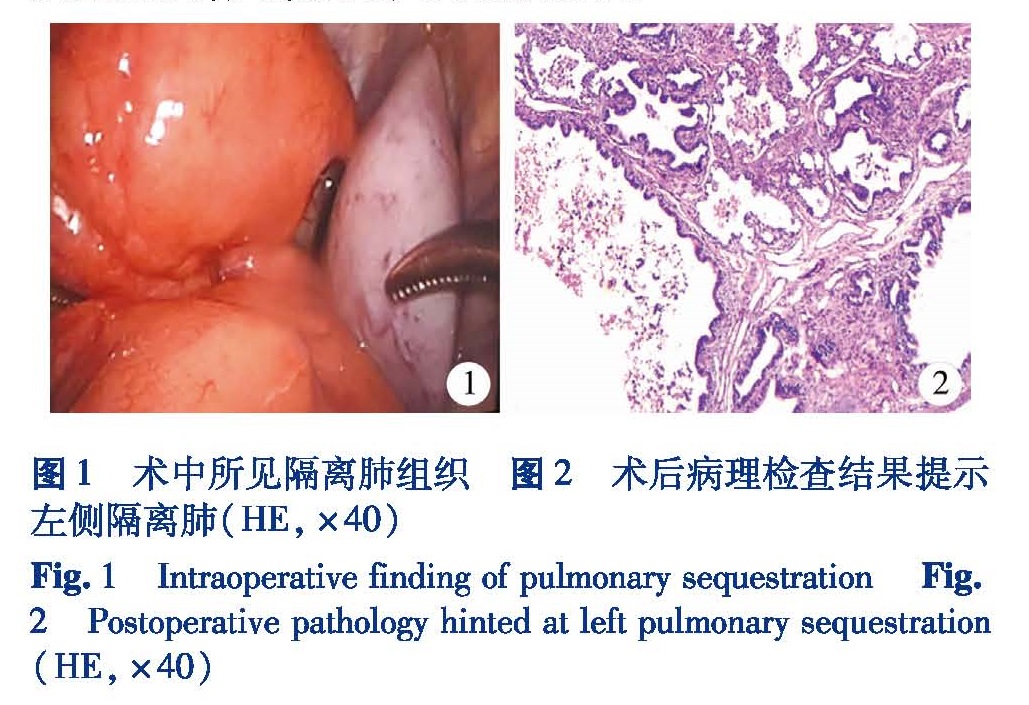
目的 比较胸腔镜手术与传统开胸手术治疗小儿肺隔离症的临床疗效,探讨胸腔镜手术治疗小儿肺隔离症的优势。方法 收集2012年3月至2017年3月入住本院小儿外科并实施手术治疗的26例肺隔离症患儿临床资料,根据采用手术方式的不同分为胸腔镜手术组和传统开胸手术组。比较两组手术时间、术中出血量、术后胸腔引流时间及住院时间。结果 26例均顺利完成手术,无手术死亡病例。平均手术时间:胸腔镜手术组(118.36±7.61)min,传统开胸手术组(119.60±7.11)min,差异无统计学意义(t=-0.425,P=0.674)。平均术中出血量:胸腔镜手术组(2.18±0.40)mL,开胸手术组(4.47±0.64)mL,差异有统计学意义(t=-11.125,P=0.000)。胸腔引流管平均留置时间:胸腔镜手术组(3.54±0.69)d,开胸手术组(6.67±0.98)d,差异有统计学意义(t=-9.064,P=0.000)。术后平均住院时间:胸腔镜手术组(7.54±0.82)d,开胸手术组(8.80±0.77)d,差异有统计学意义(t=-3.981,P=0.001)。术后并发症:胸腔镜手术组3例,其中肺部感染2例,肺不张1例; 开胸手术组6 例,其中肺部感染4例,肺不张2例,差异无统计学意义(P<0.05)。除4例失访以外,其余22例随访1~2年,其中2例发生肺炎,其余病例均恢复良好。结论 胸腔镜手术治疗肺隔离症较传统开胸手术具有切口小、术中出血少、恢复快、术后住院时间短等优点,是一种安全可靠的手术方式。
Objective To compare the clinical efficacy of thoracoscopy versus traditional thoracotomy for pediatric pulmonary sequestration(PS). Methods Twenty-six cases of PS were operated from March 2012 to March 2017.According to different surgical approaches,they were divided into thoracoscopy and traditional thoracotomy groups.The parameters of operative duration,blood loss,postoperative chest drainage time and postoperative hospitalization stay were analyzed. Results All procedures were successfully completed without mortality.Independent sample t test indicated that the mean operative duration was(118.36±7.61)min in thoracoscopy group and(119.60±7.11)min in traditional thoracotomy group(t=-0.425,P=0.674).The intraoperative blood loss in endoscopic group was less than that in open thoracotomy group [(2.18±0.40)vs(4.47±0.64)mL](t=-11.125,P=0.000).The average length of chest tube placement was(3.54±0.69)days in endoscopic group and(6.67±0.98)days in open thoracotomy group.The thoracoscopic group had less postoperative chest drainage time than thoracotomy group.And there were significant inter-group differences(t=-9.064, P=0.000).The mean postoperative hospitalization stay of thoracoscopic group was less than that of thoracotomy group [(7.54±0.82)vs(8.80±0.77)days].And the inter-group difference was statistically significant(t=-3.981,P=0.001).Three postoperative complications occurred in thoracoscopic group,including pulmonary infection(n=2)and atelectasis(n=1).And 6 cases of postoperative complications occurred in thoracotomy group,including pulmonary infection(n=4)and atelectasis(n=2).And the inter-group incidence of postoperative complications was not statistically significant by chi-square test.Four patients were lost and the remainder was followed up for 1 to 2 years.Among them,2 patients developed pneumonia and others recovered well. Conclusion Thoracoscopy for PS has smaller incision,less bleeding,faster recovery,shorter length of postoperative hospitalization stay and fewer postoperative complications,etc.