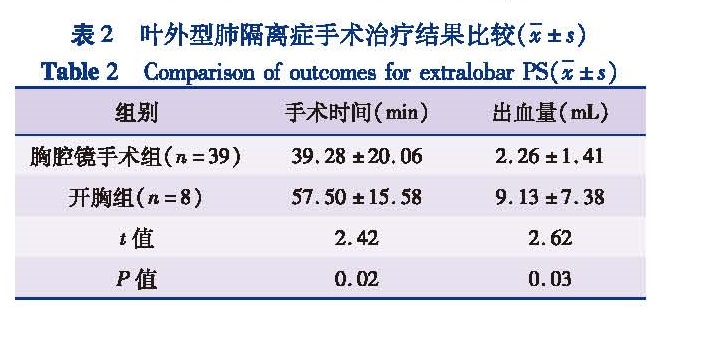
目的 对比分析胸腔镜下手术与开胸手术治疗不同类型肺隔离症(pulmonary sequestration,PS)的疗效及优缺点,为肺隔离症手术方式的选择提供参考依据。方法 回顾性收集2005年1月至2017年10月由本院收治的肺隔离症患儿208例,其中男性138例,女性70例,年龄1个月至14岁,平均年龄(19.70±48.82)个月; 叶内型143例,叶外型62例,叶内叶外同时存在3例。将叶内、叶外型按手术方式的不同分为开胸手术组和胸腔镜手术组,分别比较两型开胸手术组和胸腔镜手术组的术中出血量、手术时间、胸腔引流量、留置胸腔引流时间以及术后住院时间。结果 208例均顺利完成手术。叶内型143例中,53例予开胸手术,90例予胸腔镜手术; 叶外型62例中,10例予开胸手术,48例予胸腔镜手术,颈部手术2例,腹腔镜手术2例。叶内型病例中:胸腔镜手术组平均手术时间(72.53±40.80)min,开胸手术组平均手术时间(107.86±40.56)min,差异有统计学意义(t=4.77,P<0.001); 胸腔镜手术组平均术中出血量(4.86±7.76)mL,开胸手术组平均术中出血量(36.53±38.40)mL,差异有统计学意义(t=5.70,P<0.001); 胸腔镜手术组平均胸腔闭式引流时间(5.12±2.46)d,开胸手术组平均胸腔闭式引流时间(5.67±0.82)d,差异无统计学意义(t=0.54,P=0.59); 胸腔镜手术组平均胸腔引流量(310.16±265.96)mL,开胸手术组平均胸腔引流量(315.50±120.92)mL,差异无统计学意义(t=0.03,P=0.98); 胸腔镜手术组平均术后住院时间(7.42±3.04)d,开胸手术组平均术后住院时间(10.50±2.07)d,差异有统计学意义(t=2.42,P<0.05)。叶外型病例:胸腔镜手术组平均手术时间(39.28±20.06)min,开胸手术组平均手术时间(57.50±15.58)min,差异有统计学意义(t=2.42,P<0.05)。胸腔镜手术组平均术中出血量(2.26±1.41)mL,开胸手术组平均术中出血量(9.13±7.38)mL,差异有统计学意义(t=2.62,P<0.05)。结论 胸腔镜手术治疗肺隔离症尤其叶外型隔离肺,较传统开胸手术伤口小,术中出血少,恢复快,住院时间短,是一种安全可靠的手术方式,胸腔镜手术在隔离肺的治疗上较传统开胸手术有更多优势,可作为肺隔离症手术治疗的首选术式。
Objective To compare the advantages and disadvantages of thoracoscopy versus thoracotomy for different types of pulmonary sequestration(PS)so as to provide rationales for its optimal treatments. Methods A retrospective study was performed for 208 hospitalized PS children from January 2005 to October 2017.They were divided into extralobar(ELS)and intralobar(ILS)groups.And each group was further divided into thoracotomy and thoracoscopic surgery(VAT)sub-groups.Intraoperative loss of hemorrhage,operative duration,chest drainage,thoracic drainage time and postoperative hospitalization length were compared between two groups. Results All 208 cases were operated successfully.In intralobar PS group,thoracotomy(n=53)and thoracoscopy(n=90)were performed.In extralobar PS group,thoracotomy(n=10)and thoracoscopy(n=48),neck surgery(n=2)and laparoscopy(n=2)were performed.In intralobar PS group,the mean operative durations of VAT and thoracotomy groups were(72.53±40.80)versus(107.86±40.56)min.And the inter-group difference was statistically significant(t=4.77,P<0.001).The mean intraoperative hemorrhage was(4.86±7.76)mL in VAT group versus(36.53±38.40)mL in thoracotomy group.And the inter-group difference was statistically significant(t=5.70,P<0.001).The mean thoracic drainage time was(5.12±2.46)days in VAT group versus(5.67±0.816)days in thoracotomy group.And the inter-group difference was statistically insignificant(t=0.54,P=0.60).The mean chest drainage was(310.16±265.96)mL in VAT group versus(107.86±40.56)mL in thoracotomy group.And the inter-group difference was statistically insignificant(t=0.03,P=0.98).The mean postoperative hospitalization length was(7.42±3.04)days in VAT group versus(10.50±2.07)days in thoracotomy group.The postoperative hospitalization length was less in VAT group than that in thoracotomy group and the difference was statistically significant(t=2.42,P<0.05).In extralobar PS group,the mean operative duration was(39.28±20.060)min in VAT group versus(57.50±15.58)min in thoracotomy group.And the difference was statistically significant(t=2.42,P<0.05).The mean intraoperative hemorrhage was(2.26±1.41)mL in VAT group versus(9.13±7.38)mL in thoracotomy group.And the intraoperative hemorrhage of VAT group was less than that of thoracotomy group and the difference was statistically significant(t=2.62,P<0.05). Conclusion For PS,especially extralobar,thoracoscopy has smaller surgical incision,less intraoperative hemorrhage,faster recovery and shorter hospitalization stay than those of traditional thoracotomy.Both reliable and safe,thoracoscopy offers more advantages than thoracotomy and it is preferred for PS.