Hunan Children's Hospital, Chiangsha 410007,china.Corresponding author:Wang Jiangping,Email:hneywjp@163.com
Carbon Dioxide; Laparoscopic; Pneumoperitoneum; Cerebral Oxygen Saturation; Child
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671— 6353.2018.04.017
备注
引言
腹腔镜手术以其微创、恢复快等优势广泛应用于临床[1]。但腹腔镜手术中,CO2气腹可引起脑血流量和颅内压升高[2],导致脑血容量和脑脊液增加,并且静脉压也相应增加,最终使得静脉回流受阻,降低脑组织灌注,导致脑氧饱和度(rSO2)下降[3]。无创rSO2可以实时反映局部脑组织的氧饱和度,是反映脑氧供需状态的重要指标[4,5]。目前国内外研究CO2气腹对成人无创脑氧饱和度的影响已有相关报道[6,7],而小儿相关研究报道较少。本研究拟探讨腹腔镜手术中二氧化碳气腹对小儿rSO2的影响,为此类手术麻醉管理提供参考。
1 材料与方法
1.1 临床资料选择2017年5月至2017年11月在本院行全身麻醉下腹腔镜阑尾切除手术的患儿30例,其中男18例,女12例,年龄3岁至11岁,体重14 kg至38 kg。ASA分级为Ⅰ或Ⅱ级,术前无心、肺、脑功能异常。本研究经医学中心伦理委员会批准,并获得患儿法定监护人知情同意。
1.2 麻醉方法术前检查校正麻醉机,更换钠石灰,校正呼气末二氧化碳分压检测仪。患儿术前禁食6 h,禁饮2 h。入室后常规监测心率(HR)、血压(MAP)及血氧饱和度(SpO2)。麻醉诱导静脉注射咪唑安定0.1 mg/kg,舒芬太尼0.2~0.3 μg/kg,丙泊酚1~2 mg/kg,罗库溴铵0.6 mg/kg。气管插管后所有患儿使用Drager麻醉机行控制呼吸,根据呼末二氧化碳分压(PetCO2)调节呼吸参数,氧流量2 L/min,FiO260%。术中泵入丙泊酚4 mg·kg-1·h-1,瑞芬太尼0.2 μg/kg/min维持麻醉深度。二氧化碳气腹压力设定8~10 mmHg。
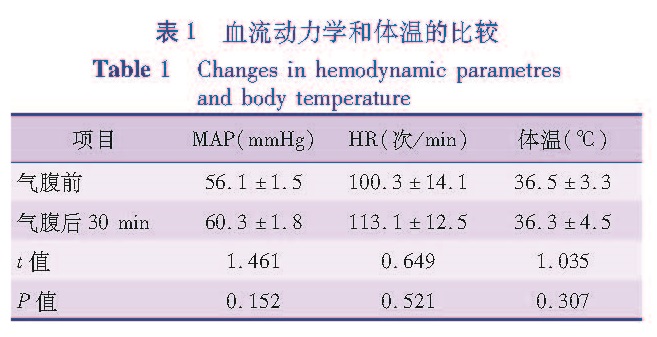
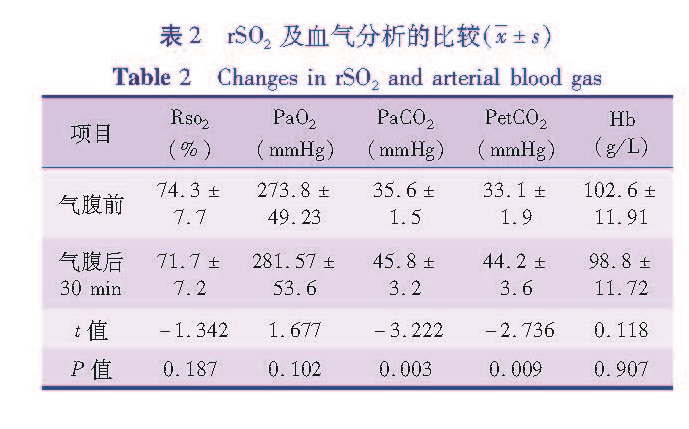
1.3 观察指标在患儿前额部以酒精棉球脱去皮脂,应用INVOS 5100C近红外光仪监测(柯惠医疗器材国际贸易有限公司,上海),两个脑氧饱和度电极片对称放置于患儿额部中线两侧,以黑色遮光布遮盖,贴膜固定,持续术中监测。收集气腹前、气腹30 min后的rSO2、动脉氧分压(PaO2)、动脉二氧化碳分压(PaCO2)、PetCO2、HR、MAP、红细胞压积(HCT)、体温。
.4 统计学处理
所有数据采用SPSS19.0软件进行统计学分析,计量资料采用均数±标准差( x^-±s)表示,气腹前后采用配对t检验,P<0.05认为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果
3 讨 论
腹腔镜手术日益增多,麻醉期间大家均会关注气腹对于心肺造成的影响,目前关于气腹对患者心肺相关影响的研究报道较多[8,9],而气腹对脑供血供氧及脑代谢的影响受关注与监测略显不足。目前在成人研究中发现,二氧化碳气腹对成人脑氧代谢有可能造成影响,而且在不同的手术中,其影响及研究结果不同。Kalmar[10]发现成人前列腺切除术中,头低脚高位的状态下,建立气腹期间rSO2会随着气腹的增加而增加。Lee[11]在妇产科腹腔镜手术中发现,术中采取头低脚高位下气腹时rSO2会下降,当其下降超过基线值50%时,术后患者会出现头痛等并发症。
而关于小儿腹腔镜手术中,气腹对脑氧饱和度的影响如何,国内暂无相关研究报道,国外研究报道结果也不一致。Tuna[12]通过对40例小儿阑尾炎患者分别行开腹和腹腔镜两种不同的术式,分析气腹对小儿脑氧饱和度的影响,其研究结果认为小儿腹腔镜手术气腹对于患儿脑氧饱和度不会造成影响。 Bishay[13]等学者在研究术中气腹对婴幼儿先天性膈疝和食道闭锁的脑氧饱和度的影响时,却发现气腹会导致患儿脑氧饱和度有明显的下降,甚至影响患儿的脑发育。
本研究主要通过红外光技术间接无创测定rSO2,观察腹腔镜气腹手术rSO2的变化。由于近红外光谱技术监测脑氧饱和度技术具有简单,灵敏,无创,能够实时监测rSO2的变化等优点,目前在临床应用比较广泛。脑氧饱和度的测量可以准确评价脑组织氧合情况及脑血流动力学的变化。术中通过持续实时监测术中脑氧饱和度的变化,根据其数值的波动可以指导临床。
但rSO2容易受多种因素影响,内在因素包括有脑血流量、血氧含量及脑代谢率等,外在因素包括年龄、体温、血红蛋白、PetCO2、吸入氧浓度、麻醉及手术体位[14]。本研究中患儿气腹前后体位均是头低脚高仰卧位,排除了体位对患儿的影响。所有患儿均是采用相同吸入氧浓度和同一种麻醉方法,术中3例麻醉药物过敏的患儿也剔除了病例组,排除了麻醉对其造成影响。研究结果显示气腹前后血红蛋白浓度以及体温差异均无统计学意义,故排除血红蛋白以及体温对结果造成的影响。脑氧饱和度的监测是连续实时监测,故排除术中脑氧监测数据不完善病例3例。
气腹期间,腹内压的增高会导致全身血管阻力增加,影响下腔静脉、肾静脉以及门静脉回流,降低心输出量,迷走神经张力增加,患儿易出现心动过缓,甚至心跳骤停[15]。为了将生理影响降到最低,推荐小儿气腹不能超过15 mmHg[16]。而气腹压在10 mmHg以内患儿可以通过内在调节,减少气腹对患儿循环的影响[17]。故本研究中气腹压力值设定为8~10 mmHg。40例患儿中,有4例患儿术中逐步调高气腹压力值,最终超过10 mmHg,该4例患儿剔除研究组。而本研究30例患儿气腹前后平均动脉压和心率的变化无明显差异,也证实当气腹压力值在10 mmHg范围内,患儿气腹前后血流动力学变化差异不大。
与气腹前相比,气腹30 min后PetCO2以及PaCO2有所升高。二氧化碳分压增加可以引起脑血流增加,颅内压升高,rSO2应随着二氧化碳分压的升高而升高,有研究表明rSO2的升高与PaCO2增加脑血流密切相关[18]。但从本研究结果rSO2未出现相应增高,反而在数值上呈现下降的趋势,由气腹前的(74.3±7.7)%下降到(71.7±7.2)%,但其数值仍在正常范围,差异无统计学意义。
分析其可能有以下几个原因: ①本研究中一个干扰因素年龄未能排除,本研究群体年龄从3~11岁。研究发现不同年龄阶段,腹膜厚度不一,腹膜表面积不一致,二氧化碳的吸入不同,机体自身的调节机制也不一致[19]。Tuna AT[12]学者的研究群体也是2~18岁患儿,其研究结果也不能排除年龄对其结果的影响。②Moka E[20]等认为腹腔镜手术中,二氧化碳气腹对脑血管系统的影响会经历适应性改变。本研究中,患儿气腹后二氧化碳分压值最高是50 mmHg,说明二氧化碳分压值在此范围,脑氧供是充分的。Bishay M[13]的研究中,其二氧化碳分压值超过了70 mmHg,最高达到了90 mmHg,该值明显超过了机体对二氧化碳的代偿能力,故其研究结果与本研究结果不一致。
综上所述,小儿腹腔镜阑尾炎切除手术中,暂不能证明二氧化碳气腹对脑氧饱和度有明显影响。本研究只观察了气腹时间30 min以内手术患儿,长时间的手术是否会造成影响,还需进一步研究。
-
1 陈小林,刘志新,陈乜明,等.腹腔镜下自制缝针腹膜内补片治疗小儿术后儿童复发性腹股沟疝的体会诊治经验[J].临床小儿外科杂志,2017,16(3): 273 — 276.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671 — 6353.2017.03.018.
-
2 Ito H,Kanno I,Ibaraki M,Hatazawa J,et al.Changes in human cerebral blood flow and cerebral blood volume during hypercapnia and hypocapnia measured by positron emission tomography[J].Cereb Blood Flow Metab,2003,23:665 — 670.DOI:10.1097/01.WCB.0000067721.64998.
-
3 Lee JR.Lee PB,Do SH,et al.The effect of gynaecological laparoscopic surgery on cerebral oxygenation[J].J Int Med Res,2006,34(5):531 — 536.
-
4 Zheng F,Sheinberg R,Yee MS,et al.Cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy monitoring and neurologic outcomes in adult cardiac surgery patients:a systematic review [J].Anesth Analg,2013.116(3):663 — 676.
-
5 杨芳芳,金孝岠.近红外线光谱仪用于脑氧饱和度监测的临床进展[J].国际麻醉学与复苏杂志,2017,38(9):837 — 841.DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673 — 4378.2017.09.016.
-
6 Jo YY,Kim JY,Lee MG.Changes in cerebral oxygen saturation and early postoperative cognitive function after laparoscopic gastrectomy: a comparison with conventional open surgery.[J].Korean J Anesthesiol,2016,69(1):44 — 50.
-
7 史景发,洪四名,李元海.术中调控不同呼气末二氧化碳分压对老年腹腔镜手术患者术后认知功能的影响[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2013,29(10):989 — 992.
-
8 Tytgat SH,van Herwaarden MY,Stolwijk LJ,et al.Neonatal brain oxygenation during thoracoscopic correction of esophageal atresia[J].Surg Endosc,2016,30:2811 — 2817.DOI:10.1007/s00464 — 015 — 4559 — 1.
-
9 Bishay M,Giacomello L,Retrosi G,et al.Decreased cerebral oxygen saturation during thoracoscopic repair of congenital diaphragmatic hernia and esophageal atresia in infants[J].J Pediatr Surg,2011,46:47 — 51.DOI:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2010.09.062.
-
10 Kalmar AF,Dewaele F,Foubert L,et al.Cerebral haemodynamic physiology during steep Trendelenburg position and CO2 pneumoperitoneum[J].Br J Anaesth,2012,108(3):478.
-
11 Lee JR,lee PB,Do SH,et al.The effect of gynaecological laparoscopic surgery on cerebral oxygenation [J].J Int Med Res,2006,34(5):531.
-
12 Tuna AT,Akkoyun I,Darcin S,et al.Effects of carbon dioxide insufflation on regional cerebral oxygenation during laparoscopic surgery in children: A prospective study[J].Rev Bras Anestesiol,2016,66:249 — 53.
-
13 Bishay M,Giacomello L,Retrosi G,et al.Decreased cerebral oxygen saturation during thoracoscopic repair of congenital diaphragmatic hernia and esophageal atresia in infants[J].J Pediatr Surg,2011,46:47 — 51.DOI:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2010.09.062.
-
14 Kishi K,Kawaguchi M,Yoshitani K,et al.Influence of patient variable and sensor location on regional cerebral oxygen saturation measured by INVOS 4100 near-infrared spectrophotometers[J].J Neurosurg Anesthesiol,2003,15:302 — 306.DOI:10.1097/00008506 — 200310000 — 0002.
-
15 Nguyen NT,Wolfe BM.The physiologic effects of pneumoperitoneum in the morbidly obese[J].Ann Surg,2005,241:219 — 26.
-
16 Nwokomo NJ,Tsang T.Laparoscopy in children and infants.Advanced Laparoscopy Prof.Ali Shamsa.Intech,China.2011,27:46 — 8.
-
17 Tobias JD.Anesthesia for minimally invasive surgery in children[J].Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol,2002,16:115 — 30.
-
18 Choi SH,Lee SJ,Rha KH,et al.The effect of pneumoperitoneum and Trendelenburg position on acute cerebral blood flow-carbon dioxide reactivity under sevoflurane anaesthesia[J].Anaesthesia,2008,63:1314 — 1318.DOI:10.1111/j.1365 — 2044.2008.05636.
-
19 Lasersohn L.Anesthetic considerations for pediatriclaparoscopy[J].S Afr J Surg,2011,49:22 — 6.
-
20 Moka E.Cerebral oximetry and laparoscopic surgery[J].J Minim Access Surg,2006,2:47 — 8.DOI:10.4103/0972 — 9941.26644.