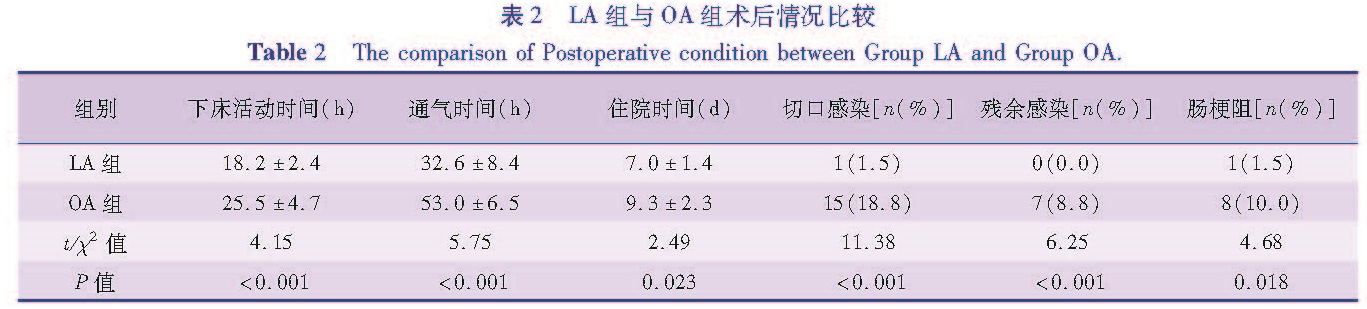
目的 比较腹腔镜与开腹手术治疗小儿穿孔性阑尾炎的临床疗效。 方法 收集本院2013年10月至2016年9月确诊为穿孔性阑尾炎患儿148例,其中68例采用腹腔镜(LA组)手术治疗,80例采用开腹(OA组)手术治疗,对比分析两组患儿术后疗效及并发症情况。结果 术后下床活动时间:LA组较OA组短(18.2±2.4 h vs 25.5±4.7 h),差异有统计学意义(t=4.15,P<0.001); 术后排气时间:LA组较OA组短(32.6±8.4 h vs 53.0±6.5 h),差异有统计学意义(t=5.75,P<0.001); 住院时间:LA组较OA组短(7.0±1.4 d vs 9.3±2.3 d),差异有统计学意义(t=2.49,P=0.023); 术后切口感染发生率:LA组1例(1.5%),OA组15例(18.8%),差异有统计学意义(χ2 =11.38,P<0.001); 残余感染发生率:LA组0例,OA组7例(8.8%),差异有统计学意义(χ2 =6.25,P<0.001); 肠梗阻发生率:LA组1例(1.5%),OA组8例(10%),差异有统计学意义(χ2 =4.68,P=0.018)。结论 腹腔镜阑尾切除术治疗小儿穿孔性阑尾炎的临床效果明显优于开腹阑尾切除术,术后恢复快,住院时间短,并且可以明显降低术后并发症的发生率,是治疗小儿急性穿孔性阑尾炎的理想术式。
Objective To compare the postoperative recovery effect of laparoscopic and open appendectomy in children with perforated appendicitis. Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on 148 cases with perforated appendicitis in Anqing Hospital Affiliated to Anhui Medical University from October 2013 to September 2016.In the cohort,68 cases were treatment with laparoscopic procedure(LA group)and 80 cases were treatment by open appendectomy(OA group).The complications and therapeutic effects were compared between the two groups. Results Postoperative exercise time was significantly shorter in the LA group than in the OA group(18.2 h±2.4 h vs 25.5 h±4.7 h,t=4.15,P<0.001).The time required for postoperative restoration of anal exhaust was significantly shorter in the LA group than in the OA group(32.6 h±8.4 h vs 53.0 h±6.5 h,t=5.75,P<0.001).Hospitalization time in the LA group was significantly shorter than that in the OA group(7.0 d±1.4 d vs 9.3 d±2.3 d,t=2.49,P<0.05).Wound infection occurred in 1 child in the LA group and in 15 children in the OA group(P<0.001).Postoperative abdominal residual infection occurred in 7 children in the OA group and no infection in the LA group.(χ2=11.38,P<0.001).Bowel obstruction occurred in 1 child in the LA group and in 8 children in the OA group(χ2=4.68,P<0.05). Conclusion LA has many advantages over OA in the treatment of perforated appendicitis in children,such as early recovery,short hospital stay,and low complication rate.Therefore,LA is a satisfactory method in the treatment of perforated appendicitis in children.