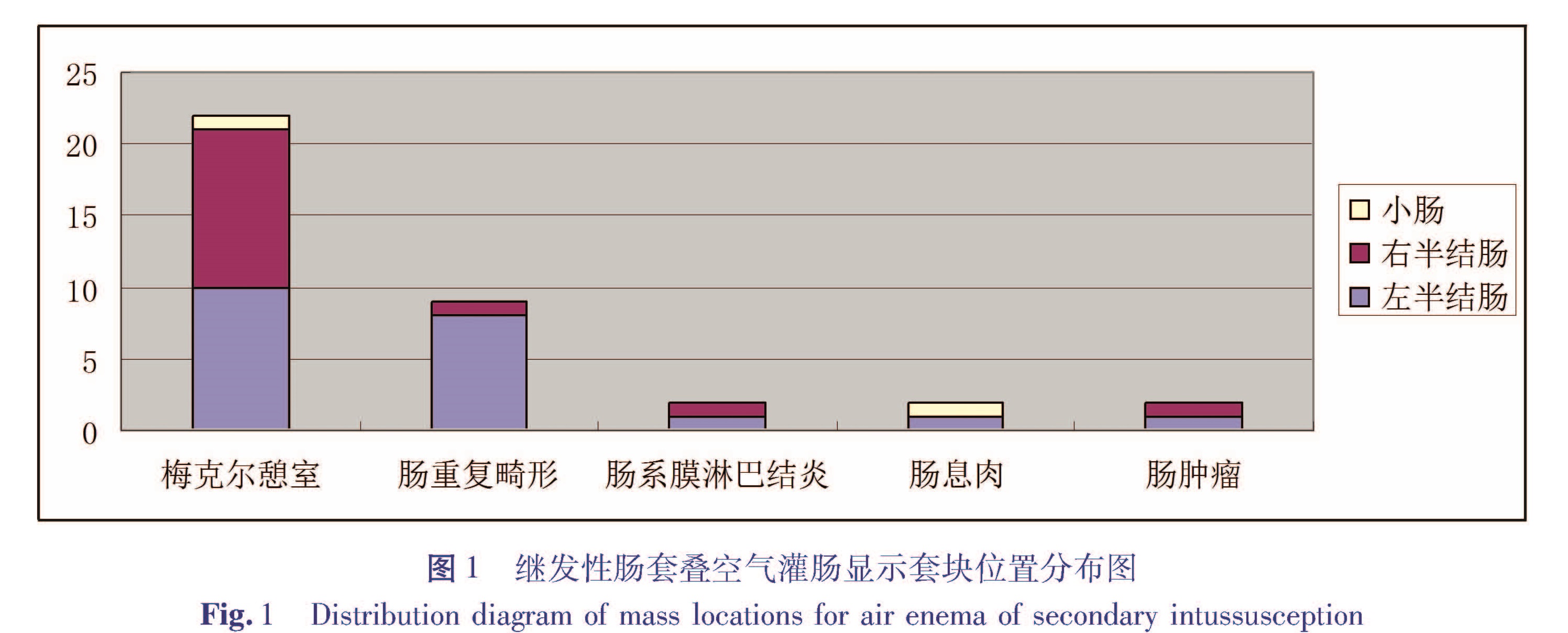
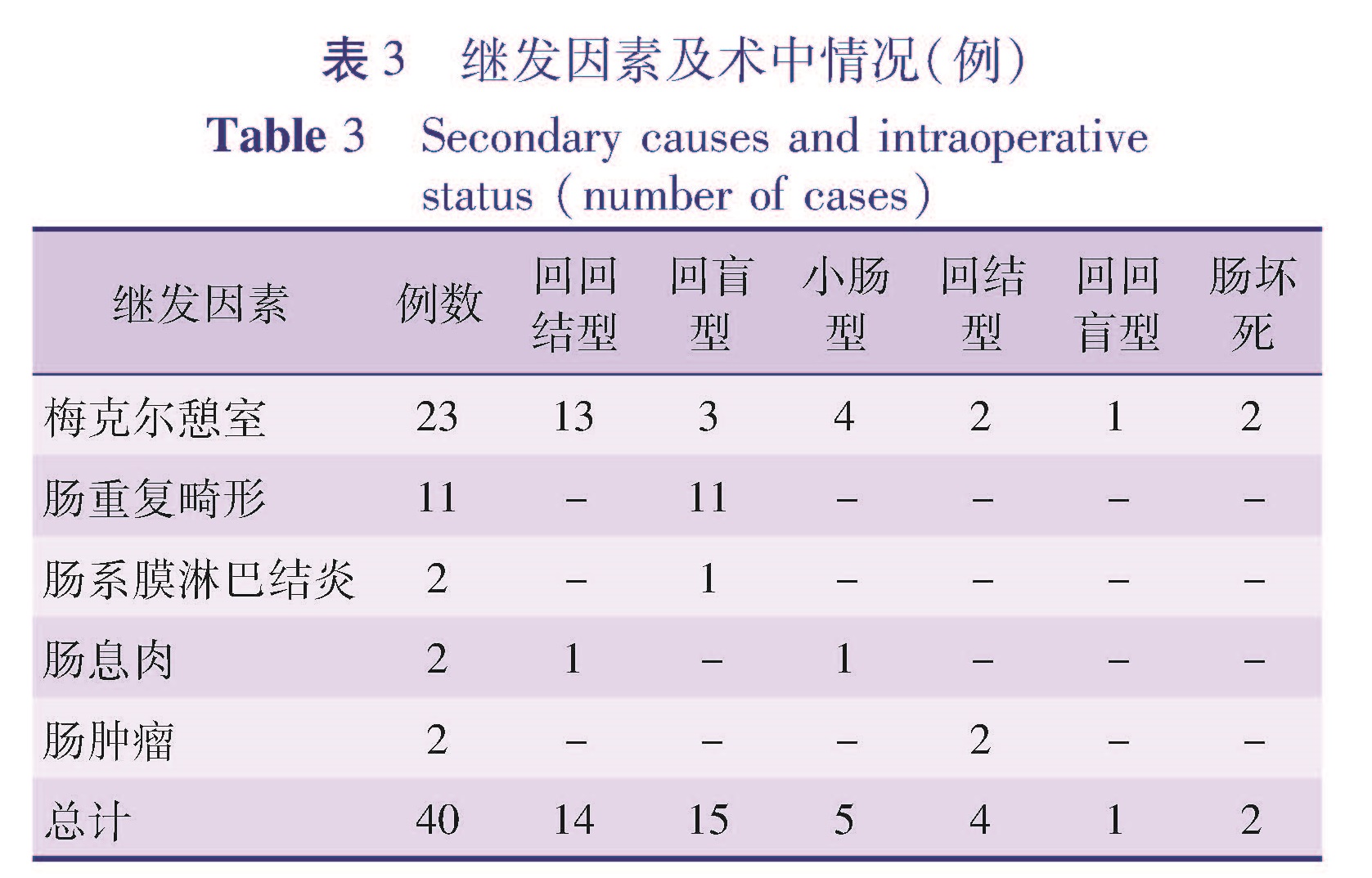
目的 探讨儿童继发性肠套叠的临床特点和发病原因,以期提高儿童肠套叠的诊治水平。方法 回顾性分析本院收治的40例儿童继发性肠套叠患儿的临床表现、发病原因及治疗方法。结果 40例患儿中,临床表现为腹痛32例,呕吐29例,血便20例,腹部扪及包块25例。术中见回回结型14例,回盲型15例,小肠型5例,回结型4例,回回盲型1例,2例肠坏死。发病原因:梅克尔憩室23例,肠重复畸形11例,肠系膜淋巴结炎2例,肠息肉2例,肠肿瘤2例。由梅克尔憩室引起的肠套叠均空气灌肠整复失败,由肠重复畸形引起的肠套叠空气灌肠整复成功率约77.8%,由其它继发因素引起的肠套叠整复成功率约33.3%。结论 当儿童年龄超过2岁时,继发性肠套叠在各年龄段所占比例明显增加,梅克尔憩室是主要继发因素。病程超过1 d或反复发生肠套叠者需警惕继发性肠套叠。
Objective To explore the clinical characteristics and etiologies of secondary intussusception and improve the ability of its diagnosis and therapy. Methods We retrospectively reviewed 40 cases.Clinical manifestations,etiologies and therapeutic modalities were reviewed. Results Clinical manifestations included abdominal pain(n=32),vomiting(n=29),hematochezia(n=20)and abdominal mass(n=25).All reductions by air enema of intussusception caused by Meckel's diverticulum failed while successful reduction rate by air enema of intussusception caused by intestinal duplication was around 77.8% and successful reduction rate by air enema due to other secondary factors stood at around 33.3%.Surgery was performed on 40 cases.Ileo-ileal-colic intussusception(n=14),ileo-cecal intussusception(n=15),small intestinal intussusception (n=5),ileo-colic intussusception(n=4),ileo-ileo-cecal intussusception(n=1)and intestinal necrosis(n=2).The causes were Meckel's diverticulum(n=23),intestinal duplication deformity(n=11),mesenteric lymphnoditis (n=2),intestinal polyp(n=2)and tumor(n=2). Conclusion The risk of secondary intussusception increases markedly in children aged over 2 years.And Meckel's diverticulum remains a major cause.Intussusception lasting more than 1 day or repeated intussusception should have secondary causes examined.
![表1 各年龄段继发性肠套叠与肠套叠住院病例数情况[n(%)]<br/>Table 1 Secondary intussusception of all age groups and admitted intussusception cases[n(%)]](2018年03期/pic10.jpg)
![表2 不同继发性肠套叠患儿的临床表现[n(%)]<br/>Table 2 Clinical features of different secondary intussusceptions[n(%)]](2018年03期/pic11.jpg)
![表4 比较不同继发因素引起的肠套叠的整复率[n(%)]<br/>Table 4 Comparison of reduction rates among differentsecondary intussusceptions[n(%)]](2018年03期/pic14.jpg)
