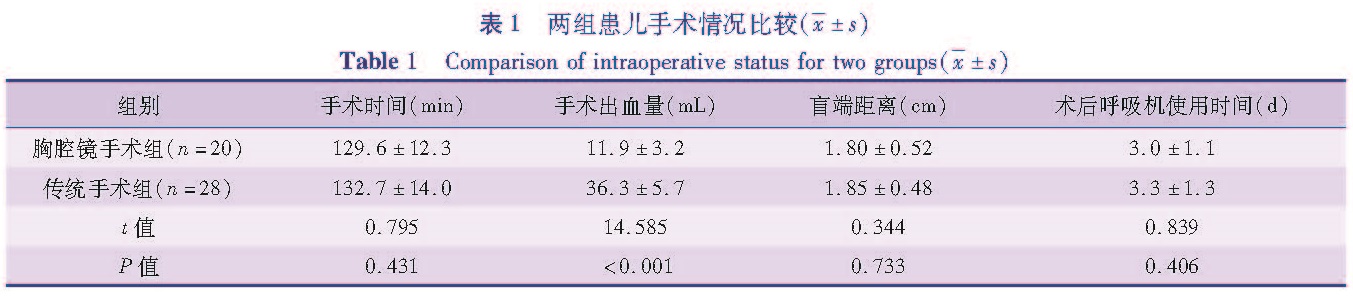
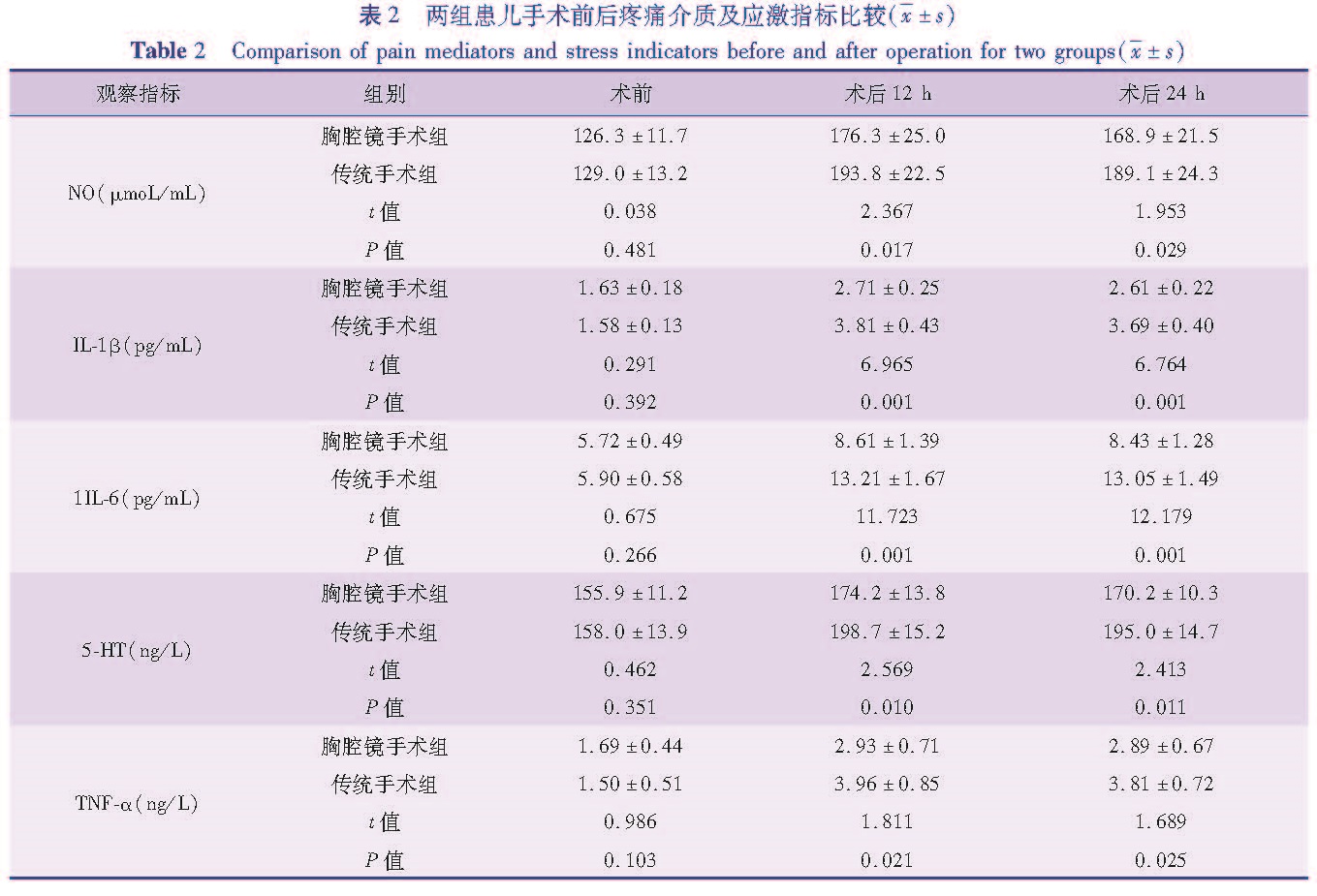
目的 比较两种手术方式治疗先天性食管闭锁并食管气管瘘的结果,探讨胸腔镜在先天性食管闭锁并食管气管瘘患儿治疗中的应用价值。方法 选取本院2014年2月至2017年2月经手术治疗的48例先天性食管闭锁并食管气管瘘病例进行回顾性分析,其中28例采用传统开胸手术治疗(传统手术组),20例采用胸腔镜手术治疗(胸腔镜手术组),比较两种手术方法的治疗效果以及两组患儿手术前后疼痛应激相关血液指标变化。结果 胸腔镜手术组患儿手术出血量显著低于传统手术组(t=14.585,P<0.05),两组在手术时间、盲端距离、术后呼吸机使用时间上比较,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05); 胸腔镜手术组20例均顺利完成手术,无一例中转开胸手术; 传统手术组28例均顺利完成手术,其中2例予胃造瘘术; 两组手术前血清NO、IL-1β、IL-6、5-HT、TNF-α水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),术后12 h、24 h,胸腔镜手术组患儿血清NO、IL-1β、IL-6、5-HT、TNF-α水平均显著低于传统手术组(P<0.05); 胸腔镜手术组术后并发症的发生率为35%,传统手术组术后并发症的发生率为28.57%,差异无统计学意义(χ2=1.222,P=0.269)。胸腔镜手术组治愈率(90.00%)与传统手术组治愈率(92.86%)比较,差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.125,P=0.724)。 结论 胸腔镜手术较开胸手术具有一定的优势,可以减少术中出血量,减轻术后炎症及疼痛应激反应,改善预后,具有在临床上推广应用的价值。
Objective To explore the clinical value of thoracoscopy in the treatment of congenital esophageal atresia(CEA)complicated with esophagotracheal fistula(ETF). Methods Forty-eight CEA/ETF children were operated from February 2014 to February 2017. Twenty-eight underwent traditional thoracic surgery(traditional group)while another 20 cases had thoracoscopy(thoracoscopy group). The clinical efficacies of two methods were compared and the levels of pain, stress and other related blood parameters before and after operation in two groups were detected and compared. Results The amount of operative bleeding was significantly lower in thoracoscopy group than that in traditional group(t=14.585,P<0.05). No significant difference existed in operative duration, blind-end distance and postoperative breathing machine using time between two groups(P>0.05). In thoracoscopy group, 20 patients were successfully operated and there was no conversion into thoracotomy; in traditional group, 2/28 patients underwent gastrostomosis. Before operation, no significant inter-group differences existed in serum levels of nitrogen oxide(NO), interleukin-1β(IL-1β), interleukin-6(IL-6), 5-hydroxytryptamine(5-HT)or tumor necrosis factor-alpha(TNF-α)(P>0.05); at 12 h and 24 h post-operation, the serum levels of NO, IL-1β, IL-6, 5-HT and TNF-αwere significantly lower in thoracoscopy group than those in traditional group(P<0.05); After operation, the complication rates of thoracoscopy and traditional groups were 35% and 28.57% respectively. No significant inter-group difference existed in the incidence of operative complications(χ2=1.222,P=0.269). The cure rate was 90% in thoracoscopy group versus 92.86% in traditional group. The difference was not statistically significant(χ2=0.125, P=0.724). Conclusion As compared with thoracotomy, thoracoscopy offers such advantages as reducing the amount of intraoperative bleeding, effectively reducing postoperative inflammation, pain and stress response and improving prognosis. It has the value of clinical popularization.
![表3 两组术后并发症和治愈情况比较[n(%)]<br/>Table 3 Comparison of complications and cure between the two group[n(%)]](2018年03期/pic09.jpg)
