通信作者:白玉作,Email:baiyz@sj— hospital.org
DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671 — 6353.2018.01.016
备注
通信作者:白玉作,Email:baiyz@sj— hospital.org
引言
急性肠套叠是婴幼儿最常见的一种急腹症,能够引发小儿呕吐、血便、电解质紊乱等症状,严重者会导致肠坏死,出现中毒性休克,影响患儿健康。小儿肠套叠的治疗方法包括手术治疗和非手术治疗两种,其中非手术治疗是应用最为广泛且优先选用的方法[1]。非手术治疗主要是指在超声或透视引导下进行的灌肠复位。目前针对小儿急性肠套叠灌肠复位主要集中于空气灌肠复位和水压灌肠复位(钡剂、盐水)[1,2]。针对空气灌肠和水压灌肠复位的治疗效果,一些学者进行了相应研究,然而二者的安全性和有效性究竟孰优孰劣,尚存在争议。为了寻找出治疗小儿急性肠套叠更理想的方法,我们分析了2004年以来国际上关于空气灌肠复位和水压灌肠复位治疗小儿肠套叠的相关研究文献,阐述两种灌肠复位方法的治疗效果及二者的优缺点,旨在为肠套叠的诊疗提供更优方案。
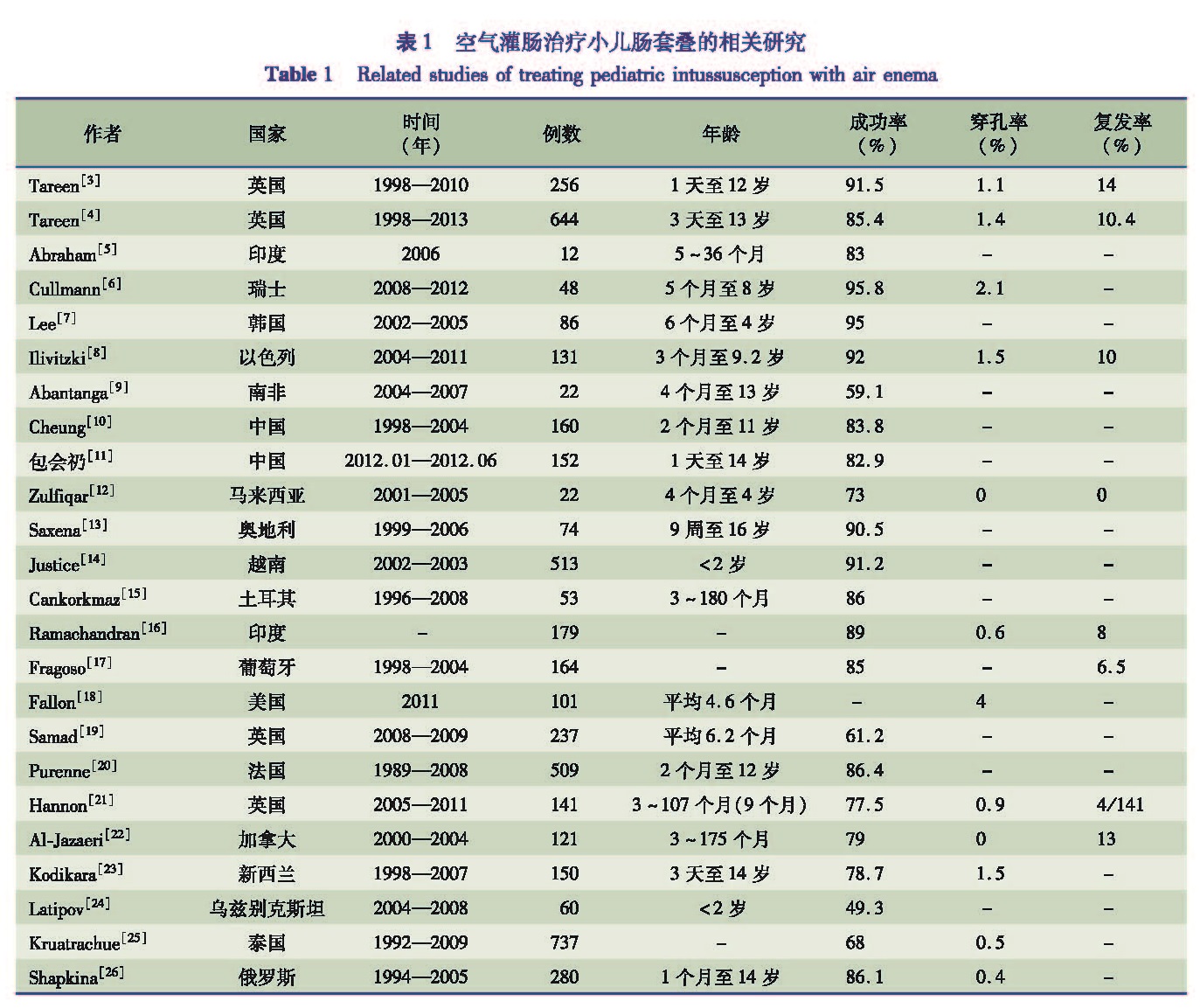
1 空气灌肠治疗小儿肠套叠的相关研究
空气灌肠复位是治疗小儿肠套叠应用最多的方法, 表1列举了2004年以来国际上关于空气灌肠治疗小儿肠套叠的相关研究,从这些研究中可以发现,利用空气灌肠复位治疗小儿肠套叠的成功率为49.3%~95.8%,而穿孔率为0.4%~2.1%,在这23项研究中,仅7项研究提到了复发率,保持在2.8%~14%之间。代表性的研究如英国学者Tareen对 1998年至2010年的256例小儿肠套叠病例进行总结,分析了空气灌肠复位的治疗效果,结果显示这256例小儿肠套叠复位成功率为91.5%,穿孔率为1.1%,复发率为14%[3]。在其另一项研究中将样本量扩大到644例,结果显示在X线监视下和未在X线监视下的空气灌肠复位之间的成功率无统计学差异,因此Tareen不推荐在小儿肠套叠的诊断和治疗过程中应用X线监视[4]。Abraham MK开发了一项用于空气灌肠复位的技术,该技术可以实现在任何医院利用现有装置即可完成空气灌肠复位,成功率达83%,在复位过程中需要外科医生来完成[5]。Cullmann JL[6]采用低辐射剂量透视引导下进行空气灌肠复位,成功率高达95.8%,与之前的高辐射剂量透视引导下气灌肠复位相比,具有明显的优势。与其他研究不同的是,韩国学者Lee在一项研究中指出,其在空气灌肠复位过程中由放射科医生参与,最后得到了95%的复位成功率[7]。Ilivitzk A在空气灌肠复位过程中,采用对患者进行深度镇静的方式,结果显示采用深度镇静的方式进行灌肠复位成功率高,透视时间短,副作用小,因此Ilivitzk A推荐在灌肠复位过程中进行镇静处理[8]。此外,南非学者Abantanga FA在灌肠复位过程中也对患者进行了镇静处理,由于其样本量较少,并没有表现出较好成功率[9]。中国学者Cheung ST总结分析了1998年至2004年间威尔斯亲王医院收治的160例小儿肠套叠病例,这些患儿均行X线引导下空气灌肠复位, 成功率83.8%[10]。中国学者包会[11]通过对152例肠套叠患儿空气灌肠复位的过程及预后进行研究,得出空气灌肠复位是较好的治疗方法,可以有效提高肠套叠的复位成功率。
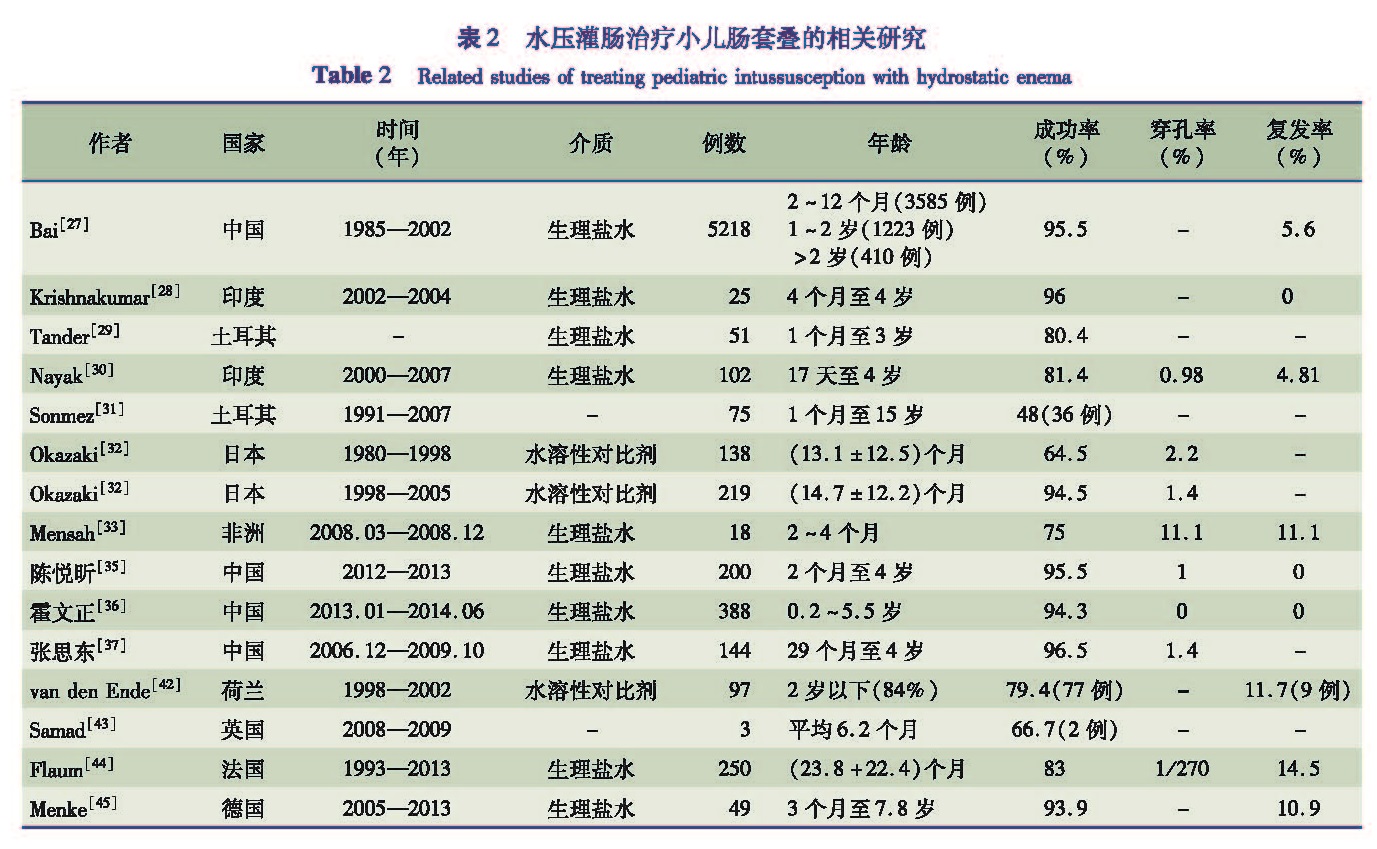
2 水压灌肠治疗小儿肠套叠的相关研究
近年来,利用水压灌肠进行小儿肠套叠复位也逐渐成为临床普遍采用的方法,水压灌肠的介质主要包括盐水(saline)、钡剂(barium)和水溶性对比剂(water-soluble contrast),表2总结的是2004年以来国际上关于水压灌肠方法治疗小儿肠套叠的相关研究[3-26]。中国学者总结了1985年至2002年间中国医科大学附属盛京医院收治的5 218例小儿肠套叠病例,这些患者都采用超声引导下温盐水灌肠复位,结果显示采用超声引导下盐水灌肠复位成功率高,复发率低[27]。在Krishnakumar、Tander B和Nayak D完成的三项研究中,放射科医生参与到了灌肠复位过程中,同样得到了较高的复位成功率[28~30]。而Sonmez K等研究显示利用水压灌肠得
到的复位成功率仅为48%,这项研究中的患者年龄在1个月至15岁之间,其中70%的患者年龄小于1岁,Sonmez K认为年龄低于2岁的患者进行水压灌肠复位更容易获得成功[31]。日本学者Okazak T对比了1980年至1998年和1998年至2005年两个时间段水压灌肠复位效果的差异,结果显示1998年至2005年期间水压灌肠复位效果明显优于1980年至1998年,产生这种差异的原因是1998年之后产生了一种灌肠复位的标准协议,按照这个标准协议进行灌肠复位能够得到良好的复位效果[32]。南非学者Mensah Y对2008年3月至12月期间克里布教学医院收治的18例小儿肠套叠病例进行研究,结果显示,这些患儿利用超声引导下水压灌肠复位成功率为75%,穿孔率为11.1%,复发率为11.1%[33]。澳大利亚学者Chew R利用Meta分析方法对相关研究文献进行总结,认为超声引导下水压灌肠复位与X线引导下空气灌肠复位的有效性和安全性较为相似,同时超声引导下水压灌肠复位具有免辐射暴露的优点[34]。此外,中国学者陈悦昕对200例接受B超下水压灌肠复位的肠套叠患儿进行总结,复位成功率95.5%,穿孔率1%,认为B超下水压灌肠复位是治疗小儿肠套叠较简便、易行的方法,且可进行多次灌肠复位,成功率高[35]。较高的复位成功率也体现在中国学者霍文正的研究上,其对388例接受B超下水压灌肠复位的肠套叠患儿进行分析,复位成功率达94.3%,无一例出现穿孔或复发[36]。中国学者张思东[37]分析144例肠套叠患儿B超下水压灌肠复位前后临床资料发现该方法的治疗成功率达96.5%。
从上述研究中可以发现利用水压灌肠进行小儿肠套叠的复位成功率普遍较高,在这13项研究中,成功率超过80%的研究有10项,其中最高达到96.5%。一些学者分析超声下盐水灌肠复位成功率较高的原因,主要有以下几个方面: ①超声扫描具有高敏感性和高特异性的特点。有研究显示,利用超声扫描诊断肠套叠的敏感度平均为98%~100%,而特异性则高达97.8%[38-40]。因此利用超声引导可以更清楚地观察病变部位,准确进行肠套叠的复位; ②超声扫描具有及时性特点。超声引导下进行肠套叠复位可以随时观察复位情况,以随时调整复位方式,改善治疗效果[27,41]; ③超声引导下水压灌肠复位不会形成空气灌肠过程中出现的多重气体填充环,因此可以很容易辨别肠套叠是否复位成功。鉴于超声下温盐水灌肠复位治疗小儿肠套叠无放射线辐射,成功率高,操作简单,安全可靠,且进行复位时只需小儿外科医师,而无需放射科医生协助等优点,因此推荐应用超声下温盐水灌肠复位治疗小儿肠套叠[27]。
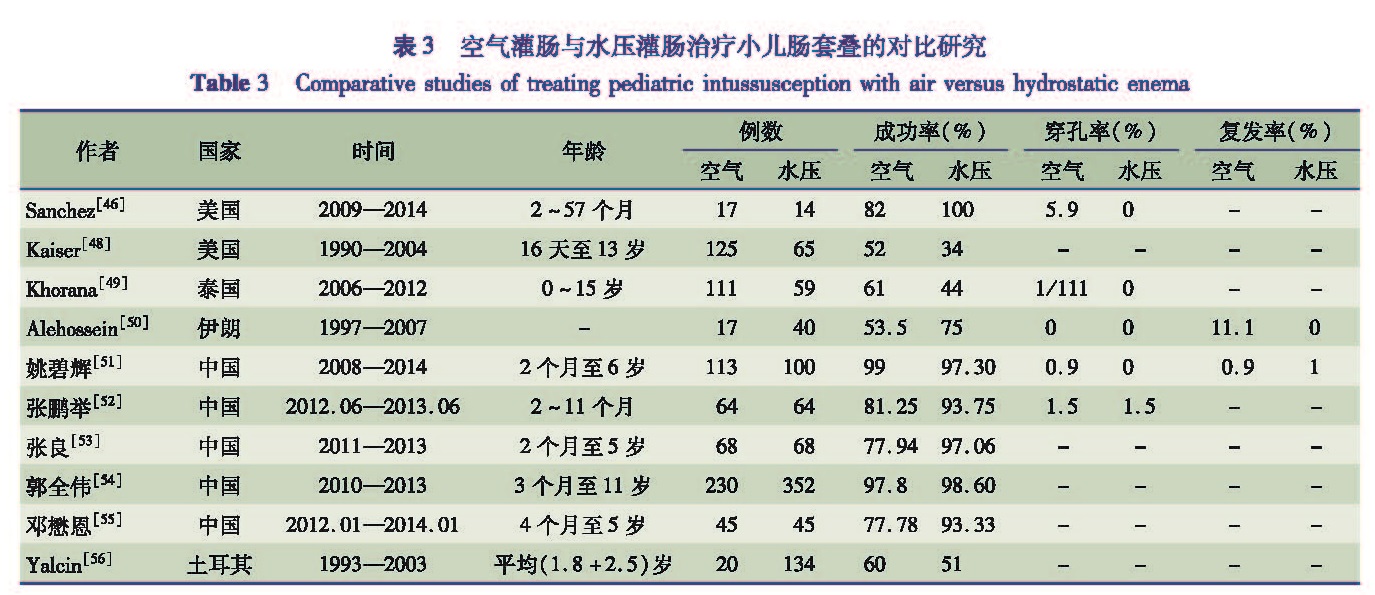
3 空气灌肠与水压灌肠治疗效果的对比研究
为了寻找出更优的灌肠复位方法,一些学者对空气灌肠与水压灌肠治疗效果进行了对比研究。Sanchez TR等[46]通过对美国加州大学戴维斯分校儿童医院诊断并治疗的14例由超声引导下盐水灌肠复位的肠套叠病例和17例由X线引导下空气灌肠复位的肠套叠病例进行对比分析,发现超声引导下盐水灌肠复位的成功率高于由X线引导下空气灌肠复位方法。Sadigh G等[47]应用Meta分析方法,对当前有关X线引导下空气灌肠复位和超声引导下水压灌肠复位的相关临床实验进行评价,该研究结论表明,X线引导下空气灌肠复位比超声引导下水压灌肠更加优越,复位率成功更高,而在穿孔率方面未见差异。Kaiser AD等[48]对比了放射线监视下空气灌肠与水压灌肠之间的差异,灌肠过程中由放射科医生参与,结果显示放射线监视下的空气灌肠复位成功率高于水压灌肠的复位成功率。Khorana J等[49]进行的一项研究显示利用空气灌肠的复位成功率高于水压灌肠,但在111例空气灌肠复位的病例中,有1例发生了穿孔。伊朗学者Alehossein M等[50]统计了1997年至2007年的小儿肠套叠病例,从成功复位率、穿孔率和复发率3个方面对空气灌肠和水压灌肠的治疗效果进行了比较,结果发现水压灌肠的治疗效果明显优于空气灌肠。此外,中国学者姚碧辉[51]对两种灌肠复位方法的临床资料及疗效进行对比分析,发现超声引导下的水压灌肠复位在复位成功率、操作简便程度、复位时间、大便隐血恢复正常时间和平均住院时间方面更具优势。中国学者张鹏举[52]将128例肠套叠患儿进行随机分组,分别给予X线引导下的空气灌肠复位治疗和超声引导下的盐水灌肠复位治疗,得出两组复位成功率的差异有统计学意义,而两组患儿不良反应的发生率差异无统计学意义。
4 两种复位方法的优缺点
通过对现有研究成果的跟踪及文献梳理,我们发现X线监视下空气灌肠复位和超声引导下水压
表3 空气灌肠与水压灌肠治疗小儿肠套叠的对比研究
Table 3 Comparative studies of treating pediatric intussusception with air versus hydrostatic enema灌肠复位各有优缺点,主要表现为以下方面:
4.1 空气灌肠复位X线监视下空气灌肠复位具有操作相对简便、复位时间短的优点[57,58]。Chew R等[34]认为X线下引导的空气灌肠复位具有快速、干净、成功率高的优点。当具备影像学设备资源时,对于没有明确腹膜炎或肠穿孔等外科手术指证的小儿肠套叠,影像学引导下进行灌肠复位是一线的治疗方法。但空气灌肠时肠腔内的压力较高,肠管膨胀显著,空气进入末端回肠后可能产生张力性气腹,如压力过大或骤增,可导致肠穿孔[18]。Zheng JY等[59]在一项研究中发现空气灌肠过程中会出现多重气体填充环(multiple gas-filled loops),因此难以辨别肠套叠是否复位成功。进一步的缺陷被Hedlund GL和Murakami JW[60,61]所证实,他们研究发现,利用空气灌肠复位方法进行回结肠肠套叠复位时会有空气进入回肠末端,会导致并没有完全复位的部位可能被错误地解释为成功复位。此外,X线监视下的空气灌肠复位会导致患儿全面暴露于X 线下,对其生殖及发育等可造成不利影响,正是由于X线辐射对婴幼儿的损害,Tareen F等[4]强调无论是针对小儿肠套叠的诊断还是治疗,都不需要对儿童进行放射线监视。中国学者邓懋恩等[55]认为X线具有一定的辐射,对人体尤其婴幼儿有一定的危害,而且X线对诊断肠套叠往往是通过间接征象,因此具有一定的推测性质,不能如B超一样直接反映从而提供直接证据。冯莲崧等[62]通过回顾性分析疑似肠套叠患儿的临床病例资料,得出腹部X线在诊断肠套叠的灵敏度、特异度、阳性预测值上均明显低于超声。
4.2 水压灌肠复位利用超声引导复位的优点之一是可以发现导致肠套叠的病因,包括息肉、美克尔憩室、肠重复囊肿和其他肿块等,同时可以有效分辨回肠瓣增厚和套叠残留,避免不必要的多次复位尝试[46,63]。Flaum V等[44]通过对1993年6月至2013年7月之间采用超声引导下盐水灌肠复位治疗的小儿急性肠套叠病例进行回顾性总结分析,对超声引导下盐水灌肠复位方法的有效性和安全性进行了评价,他认为这种方法是一种有效且安全的治疗方法,该方法的最大优点是可以有效避免儿童暴露于放射环境中。Menke J等[45]研究发现超声引导下盐水灌肠复位的成功率较高,且无X线辐射对婴幼儿的损害,他认为这种方法可以替代透视引导下的空气灌肠复位方法。超声引导下水压灌肠复位理论上结合了FGPR和超声的优点,具有免辐射暴露、无需昂贵影像设备的优点,同时对于灌肠地点的选择具有更好的灵活性。但是,进行水压灌肠复位的过程不太卫生,结肠内的压力较难控制,容易引发肠穿孔、腹腔内粪质污染等风险[34]。此外,水压灌肠复位的缺点是人工注水能够导致灌肠复位时间较长,并且当穿孔发生时,会产生腹腔污染的后果[64]。
综上所述,空气灌肠复位和水压灌肠复位有着各自的优点和缺点。当前,关于这两种复位方法的治疗效果究竟孰优孰劣,还无法得到明确的结论,主要原因在于: ①绝大多数研究搜集的数据资料中样本量依然较小,研究结果无法全面客观地提供严谨合理的结论。②一些学者在进行大样本Meta分析时缺乏发表偏倚和异质性检验,这在较大程度上会影响研究结论的科学性和准确性。
随着医疗大数据时代的到来和各种医学信息分析技术的不断涌现,精准医疗和个性化医疗正逐步发展起来,关于小儿肠套叠各种复位方法的治疗效果和适用性将进一步明晰,预计未来的临床工作将会根据不同肠套叠患儿的临床指标和生理特点选择合适的治疗方案。
- 1 Daneman A,Navarro O.Intussusception.Part 2:An update on the evolution of management[J].Pediatr Radiol,2004,34(2):97 — 108.DOI:10.1007/s00247 — 003 — 1082 — 7.
- 2 Ko HS,Schenk JP,Tröger J,et al.Current radiological management of intussusception in children[J].Eur Radiol,2007,17(9):2411 — 2421.DOI:10.1007/s00330 — 007 — 0589 — y.
- 3 Tareen F,Ryan S,Avanzini S,et al.Does the length of the history influence the outcome of pneumatic reduction of intussusception in children?[J].Pediatr Surg Int,2011,27(6):587 — 589.DOI:10.1007/s00383 — 010 — 2836 — 6.
- 4 Tareen F,Laughlin DM,Cianci F,et al.Abdominal radiography is not necessary in children with intussusception[J].Pediatr Surg Int,2016,32(1):89 — 92.DOI:10.1007/s00383 — 015 — 3817 — 6.
- 5 Abraham MK,Joy MG,Menon SS,et al.A Simple and Safe Technique for Pneumatic Reduction of Intussusception[J].Asian J Surg,2006,29(3):170 — 172.DOI:10.1016/S1015 — 9584(09)60080 — 4.
- 6 Cullmann JL,Heverhagen JT,Puig S.Radiation dose in pneumatic reduction of ileo-colic intussusceptions-results from a single-institution study[J].Pediatr Radiol,2015,45(5):675 — 677.DOI:10.1007/s00247 — 014 — 3218 — 3.
- 7 Lee JH,Choi SH,Jeong YK,et al.Intermittent sonographic guidance in air enemas for reduction of childhood intussusception[J].J Ultrasound Med,2006,25(9):1125 — 1130.DOI:10.7863/jum.2006.25.9.1125.
- 8 Ilivitzki A,Shtark L G,Arish K,et al.Deep sedation during pneumatic reduction of intussusception[J].Pediatr Radiol,2012,42(5):562 — 565.DOI:10.1007/s00247 — 012 — 2398 — y.
- 9 Abantanga FA,Amoah M,Adeyinka AO,et al.Pneumatic reduction of intussusception in children at the Komfo Anokye Hospital,Kumasi,Ghana[J].East Afr Med J,2008,85(11):550 — 555.
- 10 Cheung ST,Lee KH,Yeung TH,et al.Minimally invasive approach in the management of childhood intussusception[J].ANZ J Surg,2007,77(9):778 — 781.DOI:10.1111/j.1445 — 2197.2007.04228.x.
- 11 包会礽.152例小儿肠套叠空气灌肠法及复位治疗体会[J].浙江创伤外科,2014,19(1):55 — 56.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009 — 7147.2014.01.022.
- HR.Treatment experiences of air enema and reduction for pediatric intussusception:a report of 152 cases[J].ZH J J Traumatic,2014,19(1):55 — 56.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009 — 7147.2014.01.022.
- 12 Zulfiqar MA,Noryati M,Hamzaini AH,et al.Pneumatic reduction of intussusception using equipment readily available in the hospital[J].Med J Malaysia,2006,61(2):199 — 203.
- 13 Saxena AK,Höllwarth ME.Factors influencing management and comparison of outcomes in paediatric intussusceptions[J].Acta Paediatr,2007,96(8):1199 — 2202.DOI:10.1111/j.1651 — 2227.2007.00374.x.
- 14 Justice FA,Campo MD,Liem NT,et al.Accuracy of ultrasonography for the diagnosis of intussusception in infants in Vietnam[J].Pediatr Radiol,2007,37(2):195 — 199.DOI:10.1007/s00247 — 006 — 0381 — 1.
- 15 Cankorkmaz L,Köylüoglu G,Arslan MS,et al.Our childhood cases with intussusception and pneumatic reduction[J].Ulusal Travma Ve Acil Cerrahi Dergisi,2010,16(4):363 — 366.
- 16 Ramachandran P,Gupta A,Vincent P,et al.Air enema for intussusception:Is predicting the outcome important?[J].Pediatr Surg Int,2008,24(3):311 — 313.DOI:10.1007/s00383 — 007 — 2101 — 9.
- 17 Fragoso AC,Campos M,Tavares C,et al.Pneumatic reduction of childhood intussusception.Is prediction of failure important? [J].J Pediatr Surg,2007,42(9):1504 — 1508.DOI:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2007.04.013.
- 18 Fallon SC,Kim ES,Naik-Mathuria BJ,et al.Needle decompression to avoid tension pneumoperitoneum and hemodynamic compromise after pneumatic reduction of pediatric intussusception[J].Pediatric Radiol,2013,43(6):662 — 667.DOI:10.1007/s00247 — 012 — 2604 — y.
- 19 Samad L,Marven S,Bashir HE,et al.Prospective surveillance study of the management of intussusception in UK and Irish infants [J].Br J Surg,2012,99(3):411 — 415.DOI:10.1002/bjs.7821.
- 20 Purenne E,Franchi-Abella S,Branchereau S,et al.General anesthesia for intussusception reduction by enema[J].Pediatric Anesth,2012,22(12):1211 — 1215.DOI:10.1111/pan.12035.
- 21 Hannon EJ,Allan RA,Negus AS,et al.Air enema reduction of intussusception:A registrar-led,protocol-driven service is safe and effective[J].Pediatr Surg Int,2013,29(8):805 — 809.DOI:10.1007/s00383 — 013 — 3328 — 2.
- 22 Al-Jazaeri A,Yazbeck S,Filiatrault D,et al.Utility of hospital admission after successful enema reduction of ileocolic intussusception[J].J Pediatr Surg,2006,41(5):1010 — 1013.DOI:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2005.12.046.
- 23 Kodikara H,Lynch A,Morreau P,et al.Ten-year review of intussusception at Starship Hospital:1998 — 2007[J].N Z Med J,2010,123(1324):32 — 40.
- 24 Latipov R,Khudoyorov R,Flem E.Childhood intussusception in Uzbekistan:Analysis of retrospective surveillance data[J].BMC Pediatr,2011,11(1):1 — 6.DOI:10.1186/1471 — 2431 — 11 — 22.
- 25 Kruatrachue A,Wongtapradit L,Nithipanya N,et al.Result of air enema reduction in 737 cases of intussusception[J].J Medical Assoc Thai,2011,94(3):S22 — S26.
- 26 Shapkina AN,Shapkin VV,Nelubov IV,et al.Intussusception in children:11-year experience in Vladivostok[J].Pediatr Surg Int,2006,22(11):901 — 904.DOI:10.1007/s00383 — 006 — 1764 — y.
- 27 Bai YZ,Qu RB,Wang GD,et al.Ultrasound-guided hydrostatic reduction of intussusceptions by saline enema:a review of 5218 cases in 17 years[J].Am J Surg,2006,192(3):273 — 275.DOI:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2006.04.013.
- 28 Krishnakumar,Hameed S,Umamaheshwari.Ultrasound gui-ded hydrostatic reduction in the management of intussusception[J].Indian J Pediatr,2006,73(3):217 — 220.
- 29 Tander B,Baskin D,Candan M,et al.Ultrasound guided reduction of intussusception with saline and comparison with operative treatment[J].Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg,2007,13(13):288 — 293.
- 30 Nayak D,Jagdish S.Ultrasound guided hydrostatic reduction of intussusception in children by saline enema:our experience[J].Indian J Surg,2008,70(1):8 — 13.DOI:10.1007/s12262 — 008 — 0002 — 3.
- 31 Sonmez K,Turkyilmaz Z,Demirogullari B,et al.Intussusception in children:experience with 105 patients in a department of paediatric surgery,Turkey[J].S Afr J Surg,2012,50(2):37 — 39.
- 32 Okazaki T,Ogasawara Y,Nakazawa N,et al.Reduction of intussusception in infants by a pediatric surgical team:improvement in safety and outcome[J].Pediatr Surg Int,2006,22(11):897 — 900.DOI:10.1007/s00383 — 006 — 1766 — 9.
- 33 Mensah Y,Glover-Addy H,Etwire V,et al.Ultrasound guided hydrostatic reduction of intussusception in children at Korle Bu Teaching Hospital:an initial experience[J].Ghana Med J,2011,45(3):128 — 131.
- 34 Chew R,Ditchfield M,Paul E,et al.Comparison of safety and efficacy of image-guided enema reduction techniques for paediatricintussusception:A review of the literature[J].J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol,2017:1 — 7.DOI:10.1111/1754 — 9485.12601.
- 35 陈悦昕.B超监测水压灌肠治疗小儿肠套叠[J].中国医学工程,2015,23(1):154 — 154.
- RX.Ultrasonic monitoring of treating pediatric intussusception with hydrostatic enema[J].China Medical Engineering,2015,23(1):154 — 154.
- 36 霍文正,刘斌,白锡波.B超监测水压灌肠治疗小儿肠套叠的临床分析[J].中国医药指南,2014,12(31):146.
- WZ,Liu B,Bai XB.Ultrasonic monitoring of treating pediatric intussusception with hydrostatic enema:clinical analysis[J].Guide of China Medicine,2014,12(31):146.
- 37 张思东,罗志钢,梁书增,等.B超引导下水压灌肠治疗小儿肠套叠的临床应用[J].安徽卫生职业技术学院学报,2014,13(1):55 — 56.
- SD,Luo ZG,Liang SZ,et al.Application of ultrasound-guided hydraulic pressure enema treatment of intussusception in children[J].Journal of Anhui Health Vocational & Technical College,2014,13(1):55 — 56.
- 38 Sorantin E,Lindbichler F.Management of intussusception[J].Eur Radiol,2004,14(4):146 — 154.DOI:10.1007/s00330 — 003 — 2033 — 2.
- 39 Lim HK,Bae SH,Lee KH,et al.Assessment of reducibility of ileocolic intussusception in children:usefulness of color Doppler sonography[J].Radiol,1994,191(3):781 — 785.DOI:10.1148/radiology.191.3.8184064.
- 40 Hryhorczuk AL,Strouse PJ.Validation of US as a first-line diagnostic test for assessment of pediatric ileocolic intussusception[J].Pediatr Radiol,2009,39(10):1075 — 1079.DOI:10.1007/s00247 — 009 — 1353 — z.
- 41 Bartocci M,Fabrizi G,Valente I,et al.Intussusception in childhood:role of sonography on diagnosis and treatment[J].J Ultrasound,2014,18(3):205 — 211.DOI:10.1007/s40477 — 014 — 0110 — 9.
- 42 Van den Ende ED,Allema JH,Hazebroek FW,et al.Success with hydrostatic reduction of intussusception in relation to duration of symptoms[J].Arch Dis Child,2005,90(10):1071 — 1072.DOI:10.1136/adc.2004.066332.
- 43 Samad L,Marven S,Bashir HE,et al.Prospective surveillance study of the management of intussusception in UK and Irish infants[J].Br J Surg,2012,99(3):411 — 415.DOI:10.1002/bjs.7821.
- 44 Flaum V,Schneider A,Ferreira CG,et al.Twenty years' experience for reduction of ileocolic intussusceptions by saline enema under sonography control[J].J Pediatr Surg,2016,51(1):179 — 182.DOI:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2015.09.022.
- 45 Menke J,Kahl F.Sonography-guided hydrostatic reduction of ileocolic intussusception in children:Analysis of failure and success in consecutive patients presenting timely to the hospital[J].Eur J Pediatr,2015,174(3):307 — 316.DOI:10.1007/s00431 — 014 — 2394 — 3.
- 46 Sanchez TR,Doskocil B,Stein-Wexler R.Nonsurgical management of childhood intussusception:retrospective comparison between sonographic and fluoroscopic guidance[J].J Ultrasound Med,2015,34(1):59 — 63.DOI:10.7863/ultra.34.1.59.
- 47 Sadigh G,Zou KH,Razavi SA,et al.Meta-analysis of Air Versus Liquid Enema for Intussusception Reduction in Children[J].AJR Am J Roentgenol,2015,205(5):542 — 549.DOI:10.2214/AJR.14.14060.
- 48 Kaiser AD,Applegate KE,Ladd AP.Current success in the treatment of intussusception in children[J].Surgery,2007,142(4):469 — 477.DOI:10.1016/j.surg.2007.07.015.
- 49 Khorana J,Singhavejsakul J,Ukarapol N,et al.Enema reduction of intussusception:the success rate of hydrostatic and pneumatic reduction[J].Ther Clin Risk Manag,2015(11):1837 — 1842.DOI:10.2147/TCRM.S92169.
- 50 Alehossein M,Babaheidarian P,Salamati P.Comparison of different modalities for reducing childhood intussusception[J].Iran J Radiol,2011,8(2):83 — 87.
- 51 姚碧辉,梁鲁,张文正.X射线下空气灌肠复位法治疗小儿肠套叠与超声监视下水压灌肠复位法的比较[J].中国医药指南,2016,14(15):180 — 181.
- BH,Lang L,Zhang WZ.Treating pediatric intussusception with radiographic air enema reduction versus hydrostatic enema reduction under ultrasonic guidance[J].Guide of China Medicine,2016,14(15):180 — 181.
- 52 张鹏举,王丽亚,张哲.B 超引导下水压灌肠治疗小儿肠套叠的研究[J].大连医科大学学报,2014,36,(4):365 — 379.DOI:10.11724/jdmu.2014.04.14.
- PJ,Wang LY,Zhang Z.Ultrasound guided hydrostatic enema in the treatment of pediatric intussusception[J].Journal of Dalian Medical University,2014,36,(4):365 — 379.DOI:10.11724/jdmu.2014.04.14.
- 53 张良,杨健,张文元.超声监测水压灌肠治疗小儿肠套叠68例效果观察[J].中国当代医药,2014,21(6):179 — 181.
- L,Yang J,Zhang WY.Effect observation of hydrostatic enema of ultrasonic monitoring treating intussusception in 68 children[J].China Modern Medicine,2014,21(6):179 — 181.
- 54 郭全伟,王来友.超声监视下水压灌肠与X射线下空气灌肠在小儿肠套叠中的应用比较[J].中国辐射卫生,2014,23(3):269 — 269.
- QW,Wang LY.Application of hydrostatic enema reduction under ultrasonic guidance versus radiographic air enema for pediatric intussusception[J].Chinese Journal of Radiological Health,2014,23(3):269 — 269.
- 55 邓懋恩,杨银广,陈丽珍,等.超声监视下水压灌肠在小儿肠套叠复位治疗中的价值[J].皖南医学院学报,2016,35(1):86 — 89.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002 — 0217.2016.01.026.
- ME,Yang YG,Chen LZ,et al.Hydrostatic enema under ultrasound guidance for reduction of intussusception in children[J].Acta Academiae Medicinae Wannan,2016(1):86 — 89.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002 — 0217.2016.01.026.
- 56 Yalcin S,Ciftci AO,Karaagaoglu E,et al.Presenting clinical features and outcome in intussusception[J].Ind J Pediatr,2009,76(4):401 — 405.
- 57 Blanch AJ,Perel SB,Acworth JP.Paediatric intussusception:Epidemiology and outcome[J].Emerg Med Australas,2007,19(1):45 — 50.
- 58 Shiels WE,Maves CK,Hedlund GL,et al.Air enema for diagnosis and reduction of intussusception:clinical experience and pressure correlates[J].Radiol,1991,181(1):169 — 172.
- 59 Zheng JY,Frush DP,Guo JZ.Review of pneumatic reduction of intussusception:evolution not revolution[J].J Pediatr Surg,1994,29(1):93 — 97.
- 60 Hedlund GL,Johnson JF,Strife JL.Ileocolic intussusception:extensive reflux of air preceding pneumatic reduction[J].Radiol.1990,174(1):187 — 189.
- 61 Murakami JW,Winters WD,Weinberger E,et al.Extensive reflux of air during enema for intussusception without reduction:case report[J].Can Assoc Radiol J,1998,49(5):334 — 335.
- 62 冯莲崧,植金兴.比较分析小儿肠套叠采用超声与腹部X线片诊断临床价值[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2016,37(15):1951 — 1952.
- LS,Zhi JX.Clinical diagnostic values of ultrasonic versus radiographic abdominal imaging of pediatric intussusception[J].Journal of Qiqihar University of Medicine,2016,37(15):1951 — 1952.
- 63 Kitazono MT,Pollock AN.Intussusception:edematous ileocecal valve mimicking incomplete reduction[J].Pediatr Emerg Care,2012,28(3):300 — 301.
- 64 Shiels WE 2nd,Kirks DR,Keller GL,et al.John Caffey Award.Colonic perforation by air and liquid enemas:comparison study in young pigs[J].AJR Am J Roentgenol,1993,160(5):931 — 935.