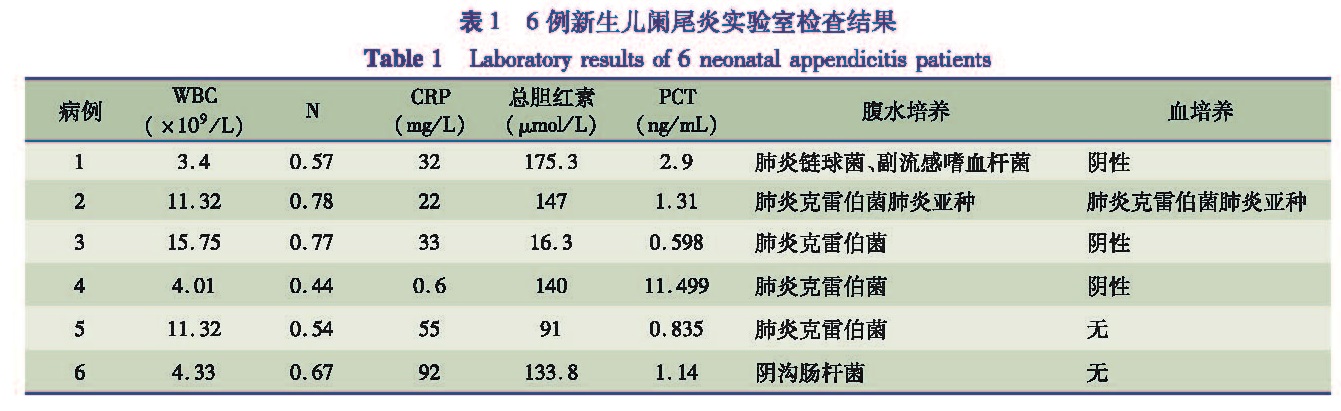
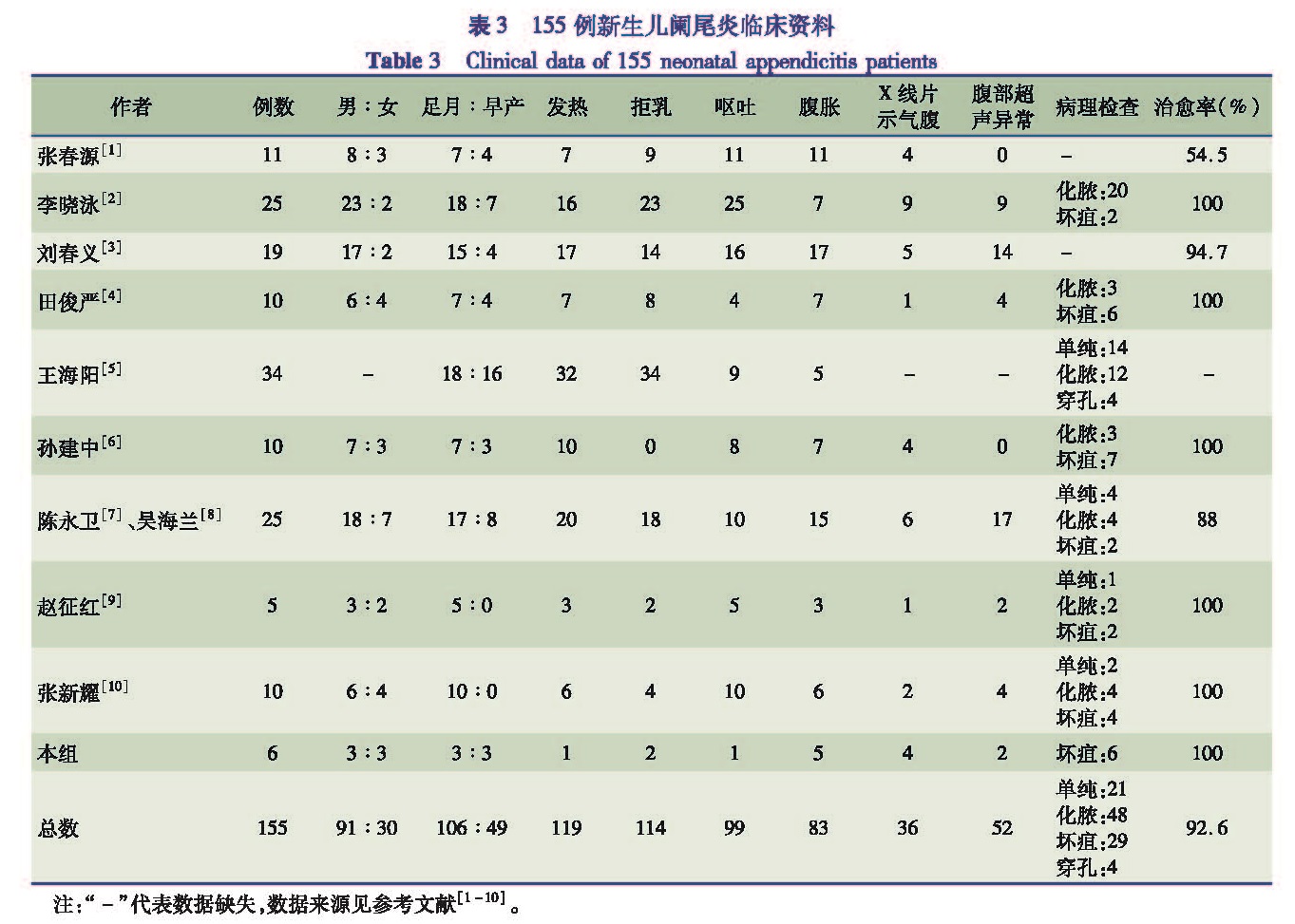
目的 分析并总结新生儿阑尾炎的临床及病原学特点,为临床诊治提供参考。 方法 回顾性分析本院收治的6例及近20年来国内报道的149例新生儿阑尾炎病例资料,总结其临床及病原学特点。 结果 155例新生儿阑尾炎症状前四位为发热、拒乳、呕吐和腹胀,其发生率分别为76.8%、73.5%、 63.9%和53.5%; 腹部平片提示气腹36例(占23.2%),腹部超声异常52例(占33.5%); 本院收治的6例患儿腹腔分泌物培养4例为肺炎克雷伯菌,1例为副流感嗜血杆菌合并肺炎链球菌,1例为阴沟肠杆菌; 6例患儿均经手术切除阑尾,均痊愈出院,平均住院时间(15.0± 7.8)d。 结论 新生儿阑尾炎临床表现不典型,以腹胀、拒乳、发热、呕吐为主要表现,病情进展快,病原学以肺炎克雷伯菌感染为主,尽早手术,预后良好。
Objective To provide references for clinical diagnosis and treatment of neonatal appendicitis by analyzing its clinical manifestations and etiology. Methods The clinical data were analyzed for 6 cases of neonatal appendicitis at our hospital and 149 cases reported during the last two decades. Results Fever,anorexia,vomiting,abdominal distention were four major manifestations in 155 cases of neonatal appendicitis.The incidence was 76.8%,73.5%,63.9% and 53.5% respectively.Pneumoperitoneum was suspected by abdominal plain film(n=36,23.2%)and seroperitoneum by abdominal ultrasonography(n=52,33.5%).Culturing of abdominal secretion was positive in 6 cases.The pathogens were Klebsiella pneumoniae(n=4),Hemophilus parainfluenzae with streptococcus pneumoniae(n=1)and Enterobacter cloacae(n=1).All 6 cases undergoing appendicectomy were cured with an average hospitalization stay of(15.0±7.8)days. Conclusion The manifestations of neonatal appendicitis with rapid progression are atypical.Abdominal distention,anorexia,fever and vomiting are four major symptoms.Klebsiella pneumoniae is a predominant pathogenic bacteria.And early surgery yields an excellent prognosis.