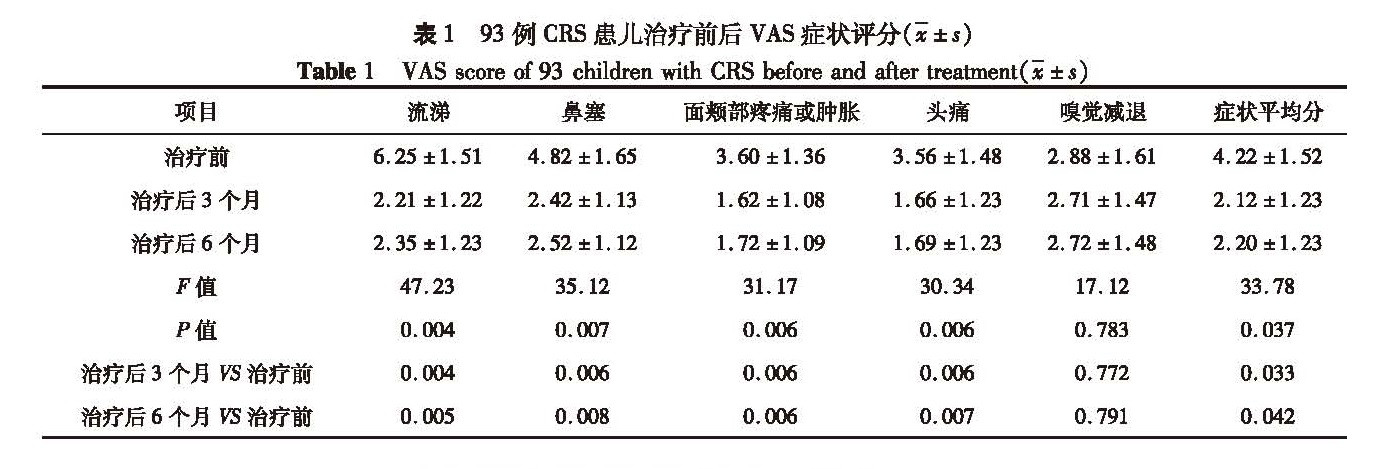
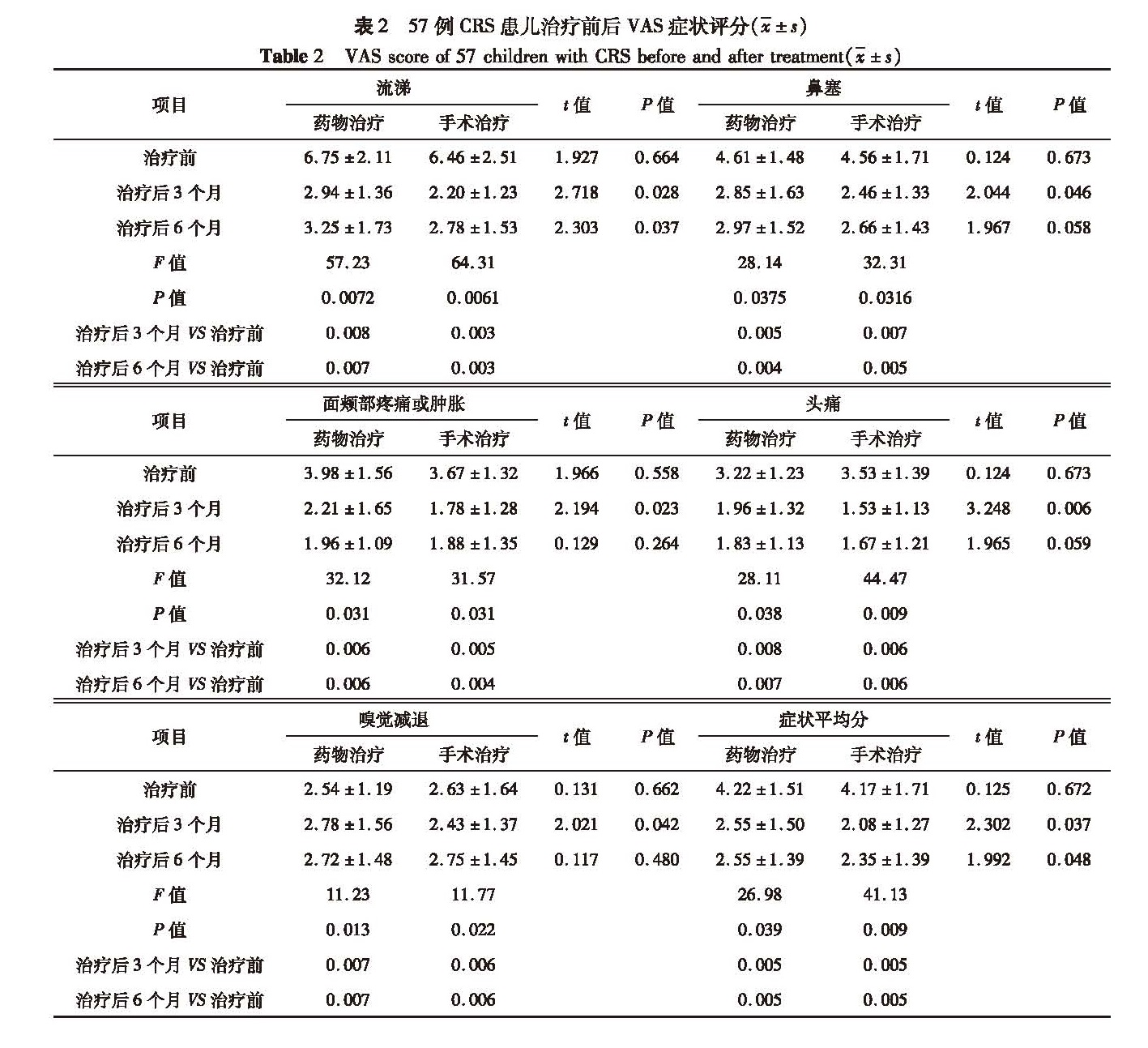
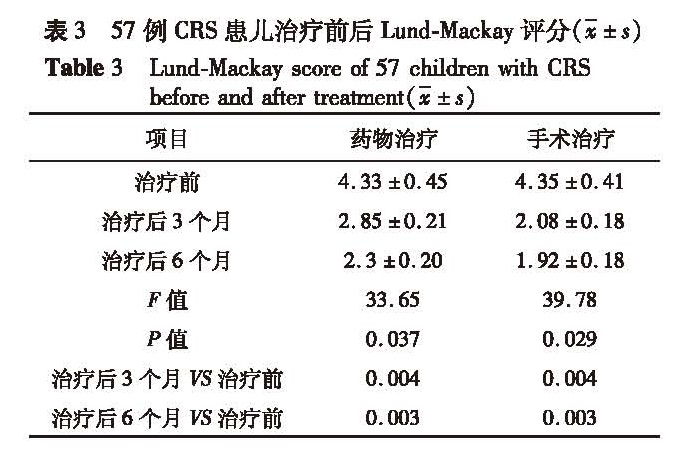
目的 探讨儿童慢性鼻-鼻窦炎(chronic rhinosinusitis,CRS)的个体化治疗方法。 方法 回顾性分析本院近10年来收治的189例儿童CRS病例资料,其中93例儿童单纯性CRS,予采取药物保守治疗; 57例伴腺样体肥大的CRS中,31例合并腺样体扁桃体肥大,予手术切除双侧扁桃体和腺样体,26例合并腺样体肥大,其中14例手术切除腺样体,12例予药物保守治疗; 39例伴鼻息肉的CRS患儿均行鼻内镜鼻窦微创手术。 结果 93例单纯性CRS经保守治疗后3个月和6个月检查视觉模拟量表(visual analogue scale,VAS)、Lund-Mackay评分均较治疗前明显下降(P<0.05)。57例伴腺样体肥大的CRS中,药物治疗和手术治疗后3个月、6个月检查VAS,Lund-Mackay评分和治疗前比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.01); 治疗相同时间的手术治疗组和药物治疗组症状平均分相比,差异也具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。39例伴鼻息肉手术治疗后3个月和6个月VAS检查,Lund-Mackay评分均较治疗前明显下降(P<0.05)。 结论 儿童慢性鼻-鼻窦炎的治疗在遵循阶梯性治疗的基础上,要制定个性化治疗方案,单纯性慢性鼻-鼻窦炎主要选择药物保守治疗,合并腺样体和(或)扁桃体肥大的患儿,建议行腺样体和(或)扁桃体切除术,可提高治疗效果。
Objective To explore the individual treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis(CRS)in children. Methods Ninety-three children with simple CRS were treated conservatively with medicine. Thirty-one CRS children with tonsil-adenoid hypertrophy underwent tonsillecto-adenoidectomy. Fourteen CRS children with adenoid hypertrophy underwent adenoidectomy. Twelve CRS children with adenoid hypertrophy were treated conservatively with medicine. Thirty-nine CRS children with nasal polyps had endoscopic minimally surgery. Results At Months 3 and 6 post-treatment, VAS and Lund-Mackay scores significantly decreased than before treatment in 93 children with simple CRS. In 57 CRS children with tonsil and/or adenoid hypertrophy, significant difference existed between surgical and medical groups during the same period(P<0.05). And significant difference existed in VAS and Lund-Mackay scores in 39 CRS cases with nasal polyp after endoscopic minimally surgery(P<0.05). Conclusion Besides a ladder protocol, individualized treatment should be formulated for CRS children. Medical treatment is reserved for patients with simple CRS. For CRS children with tonsil and/or adenoid hypertrophy, tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy should be performed for better efficacies.