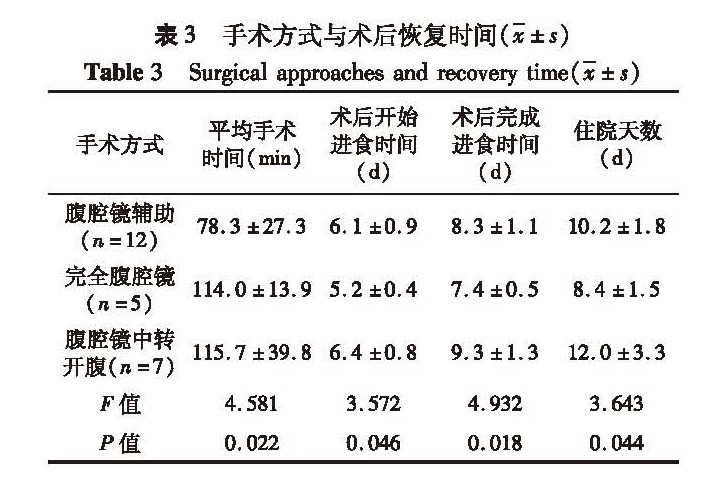
目的 总结和介绍本院腹腔镜下儿童肠重复畸形的治疗体会。 方法 回顾2013年3月至2016年11月本院收治的24例儿童肠重复畸形的病例资料,其中男11例,女13例,最小年龄5天,最大12岁,平均年龄3岁1个月, 3岁以下患儿17例。胃重复畸形1例,十二指肠重复畸形1例,空肠重复畸形3例,回肠重复畸形10例,回盲部重复畸形9例。 结果 24例均完成手术,12例行腹腔镜辅助下肠重复畸形切除术,平均手术时间(78.3±27.3)min,5例行完全腹腔镜下肠重复畸形切除术,平均手术时间(114.0±13.9)min,7例行腹腔镜探查后中转开腹手术,平均手术时间(115.7±39.8)min,三组间比较差异有统计学意义(F=4.581,P=0.022)。开始进食时间,完全腹腔镜组(5.2±0.4)d,早于腹腔镜辅助组(6.1±0.9)d和腹腔镜中转开腹组(6.4±0.8),三组间比较差异有统计学意义(F=3.572,P=0.046)。完成进食时间,完全腹腔镜组(7.4±0.5)d,早于腹腔镜辅助组(8.3±1.1)d和腹腔镜中转开腹组(9.3±1.3)d,三组间差异有统计学意义(F=4.932,P=0.018)。三组患儿平均住院日(10.5±2.7)d,完全腹腔镜组短于腹腔镜辅助组和腹腔镜中转开腹组,三组间差异有统计学意义(F=3.643,P=0.044)。所有患儿平均随访时间(19.2±15.8)个月,无并发症,无复发。 结论 腹腔镜下治疗儿童肠重复畸形是一种较好的手术方法,具有诊断兼具治疗作用,创伤小,伤口美观,值得推广。
Objective Objective To summarize the experiences of laparoscopic management for pediatric alimentary tract duplication. Methods A retrospective review was conducted for medical records of 24 intestinal duplication patients. The average age was 37 months(5 days to 12 years)and 17 patients were aged under 3 years. Among them, there were gastric duplication(n=1), duodenal duplication(n=1), jejunal duplication(n=3), ileal duplication(n=10)and ileocecal duplication(n=9). Results All of them underwent surgery. Laparoscopy-assisted resection of duplication was performed in 12 children with an average operative duration of(78.3±27.3)min. Laparoscopic resection of duplication was performed in 5 children with an average operative duration of(114.0±13.9)min. Laparoscopic exploration was converted into laparotomy in another 7 cases. The average hospitalization period was(10.5±2.7)days. All patients were cured without complication or relapse during an average follow-up period of(19.2±15.8)months. Conclusion Laparoscopic excision of duplication is mini-invasive and effective. And it is worth wider popularization in clinical practice.
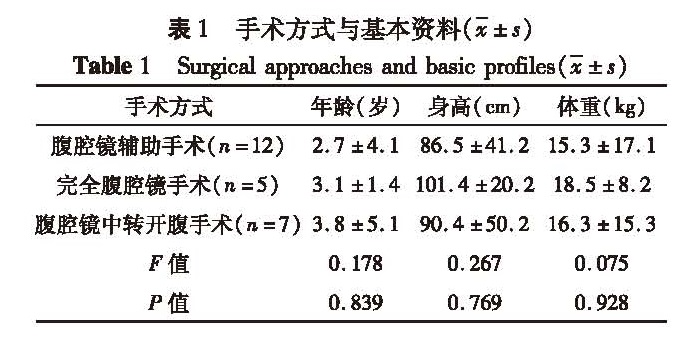
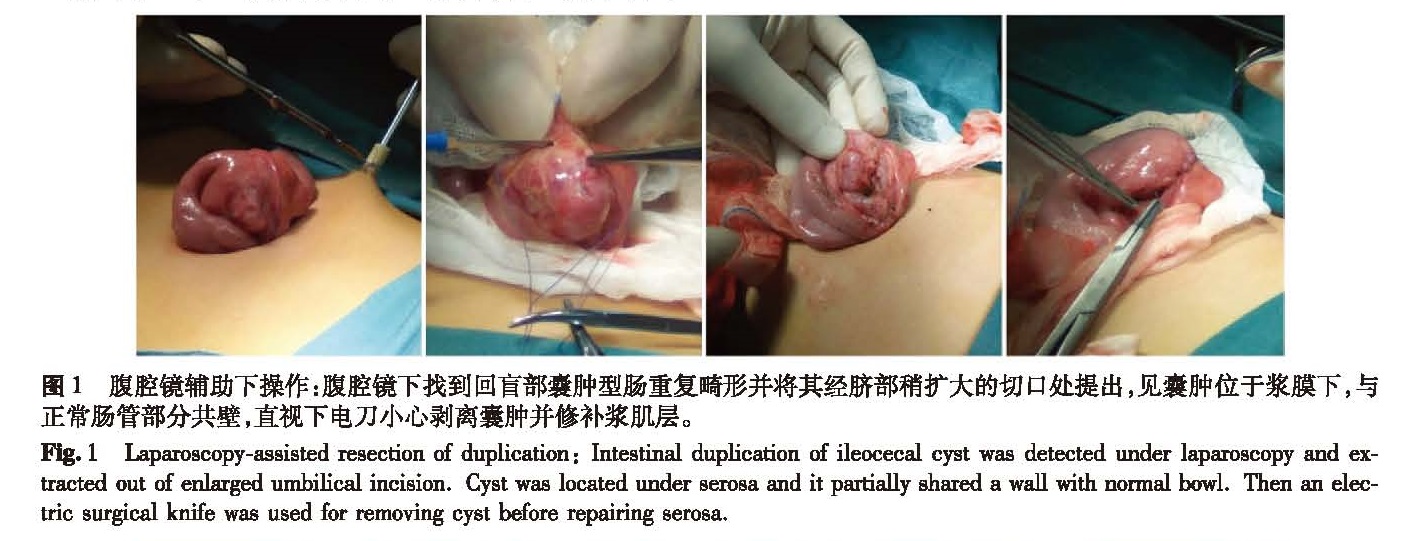
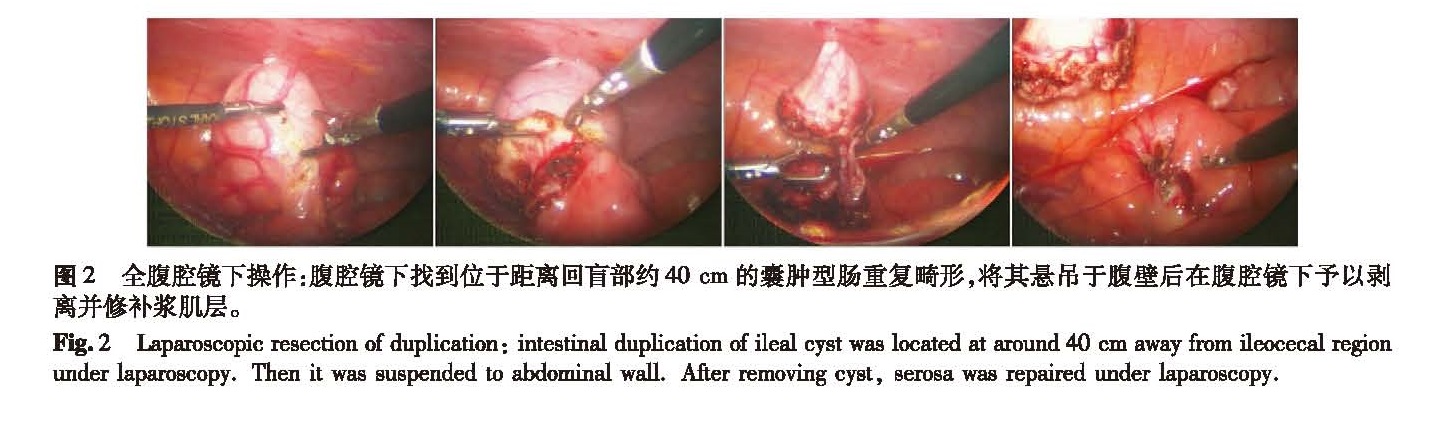
![表2 手术方式与病例数[n(%)]<br/>Table 2 Surgical approaches and case number[n(%)]](2017年06期/pic23.jpg)