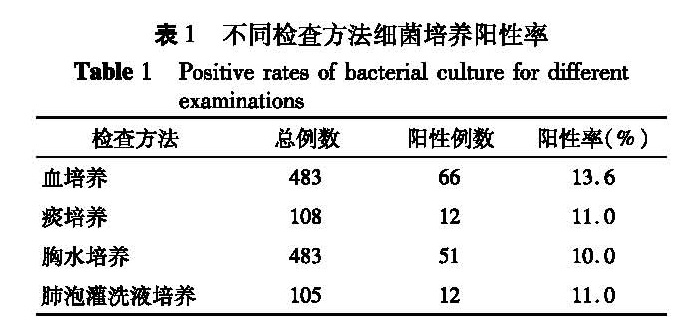
目的 分析小儿脓胸的病原学特征和治疗效果,以提高小儿脓胸的诊治水平。 方法 对本院2006年1月至2015年12月收治的483例小儿脓胸病例进行回顾性分析。 结果 483例脓胸患儿中,来自农村 417 例,城市66 例; 男性 276例,女性 207例,男女比例为1.02:0.76; 每年11月份至次年3月份发病占61%; 1岁以内发病占19.3%,1~3岁发病占33.3%,3~6岁发病占47.4%; 病原学检查为支原体(37.89%)、肺炎链球菌(3.11%)、葡萄球菌(8.70%); 行胸腔闭式引流术治愈144例; 行支气管肺泡灌洗术治愈105例; 胸腔镜下脓液清除及纤维板剥脱术治愈120例; 行开胸纤维板剥脱术治愈106例; 肺叶切除治愈6例; 2例因重度感染多脏器功能衰竭死亡。 结论 小儿脓胸病原学特征以支原体、肺炎链球菌及葡萄球菌为主,早期腔镜治疗效果较好。
Objective To explore the etiological features and therapeutic efficacy of pediatric empyema and improve its overall diagnostic level in children. Methods From January 2006 and December 2015, a total of 483 children with empyema were analyzed retrospectively. Results There were 276 boys and 207 girls. And the origin was rural(n=417)and urban(n=66). Among them, 61% occurred during the period of November to next March. The ages of peak occurrence were 3 to 6 years(19.3% <1 year, 33.3% between 1-3 years and 47.4% between 3-6 years). Mycoplasma(37.89%), Streptococcus pneumoniae(3.11%)and Staphylococcus aureus(8.70%)were the most common etiologies. The interventions included continuous closed thoracic drainage(n=144), bronchoscopic bronchoalveolar lavage(n=105), pus cleaning & pleural fiberboard stripping under thoracoscope(n=120), pleural fiberboard stripping under thoracotomy(n=106)and pulmonary lobectomy(n=6). Two cases died of severe infection and multiple organ failure. Conclusion Mycoplasma, S. pneumoniae and S. aureus are the most common etiologies of pediatric empyema. Pus cleaning and pleural fiberboard stripping under thoracoscope in early stage have excellent outcomes.