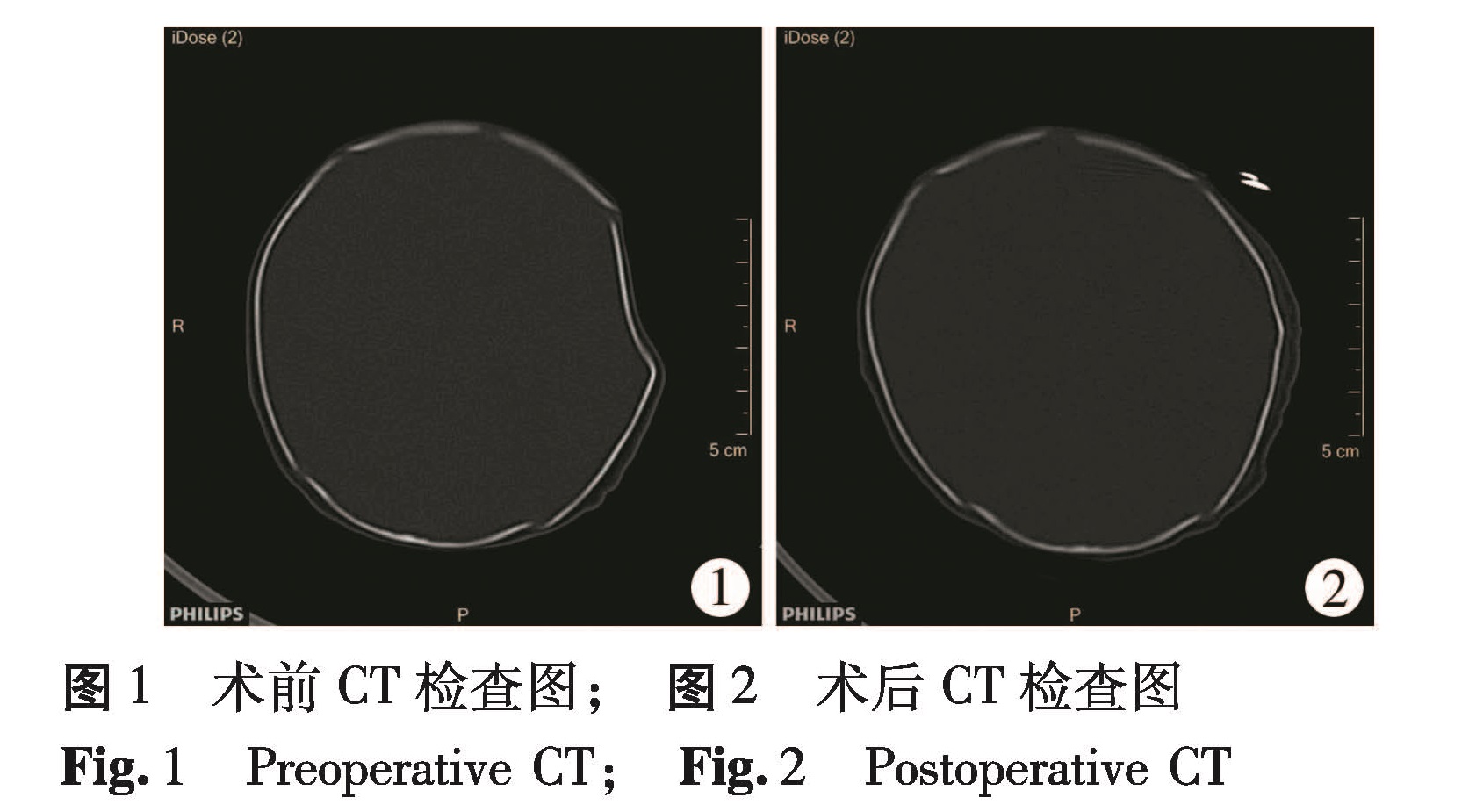
目的 探讨新生儿颅骨凹陷骨折的治疗方法。 方法 回顾性分析本院神经外科自2005年1月至2014年12月收治并确诊的40例新生儿颅骨凹陷骨折患儿的临床资料,分析治疗方式的选择及手术方法,随诊患儿预后。 结果 36例患儿行新生儿颅骨凹陷骨折复位术,术后7 d痊愈出院,随访1~3年,颅骨形态正常,骨质正常,无一例癫痫发生。4例未经手术治疗患儿,颅骨自行复位时间在4~7个月,其中1例在颅骨未复位之前出现癫痫症状。 结论 新生儿凹陷骨折复位术能够达到快速恢复颅骨结构的目的 ,减少颅骨对脑组织的压迫时间,改善患儿预后,比保守治疗更具优势。
Objective To explore the treatment of skull depression in neonates. Methods A total of 40 neonates of skull depression fracture were recruited from January 2005 to December 2014. Their clinical data were collected and analyzed with regards to surgical approaches and outcomes. Results Among them, 36 cases underwent depressed fracture reduction and were discharged at Day 7 post-operation. During a follow-up period of 1-3 years, skull shape and contour were normal and there was no epileptic seizure. Four cases were treated conservatively and skull self-reduction occurred within 4-7 months. One case developed epileptic seizure before skull reduction. Conclusion Surgical reduction of depression fracture may achieve a rapid recovery of skull structure, reduce the time of brain compression and improve the prognosis in neonates.