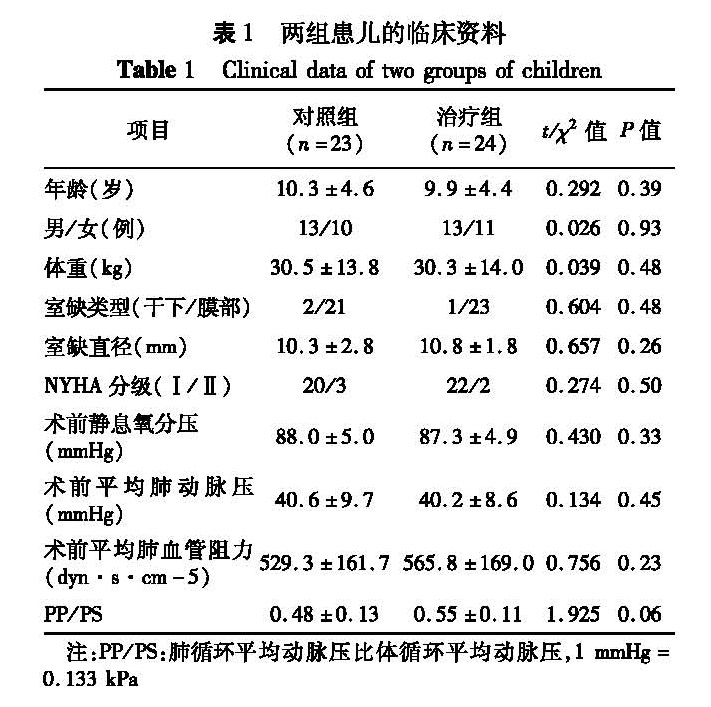
目的 检测东莨菪碱改善先天性室间隔缺损(VSD)合并肺动脉高压(PH)患儿体外循环(CPB)术后氧合指数(OI, PaO2/FiO2)的效果。 方法 将49例VSD合并PH患儿随机分为两组,治疗组26例,均在麻醉前30分钟肌肉注射东莨菪碱(0.01 mg/kg)和术后静脉注射东莨菪碱(初始剂量0.03~0.05 mg·kg-1·h-1); 对照组23例,不用此类药物。两组其它治疗方案均相同。监测和对比两组患儿术后6 h内平均OI、平均气道峰压、机械通气时间,以及拔管后IO,以评价东莨菪碱的疗效。 结果 治疗组术后6 h内平均OI为(268.5±58.0)mmHg,对照组为(233.5±40.8)mmHg,经统计学分析差异有意义(t=2.402,P=0.011); 治疗组平均气道峰压(21.2±2.2 )cmH2O,对照组为(22.0±3.2)cmH2O,经统计学分析差异无意义(t=0.979,P=0.164); 机械通气时间治疗组(13.7±7.9)h,短于对照组的(19.7±13.0)h,经统计学分析差异有意义(t=1.935,P=0.029); 治疗组拔管后氧合指数为(285.0±32.3)mmHg,对照组(243.7±40.1)mmHg,差异有统计学意义(t=3.897,P=0.001)。2例患儿出现用药不良反应(腹胀)。 结论 东莨菪碱的适量应用能明显提高VSD合并PH患儿CPB术后OI,缩短术后机械通气时间。
Objective To detect the improving effect of scopolamine on oxygenation index(OI, PaO2/FiO2)in children with congenital ventricular septal defect(VSD)and pulmonary hypertension(PH)after cardiopulmonary bypass. Methods A total of 49 VSD/PH children were randomly divided into treatment(n=26)and control(n=23)groups. In treatment group, at 30 min before anesthesia, there was an intramuscular injection of scopolamine 0.01 mg·kg-1 and followed by a continuous intravenous infusion of scopolamine at the end of operation(an initial dose 0.03~0.05 mg·kg-1·h-1). In control group, scopolamine was not used. The remaining schedules were the same. The values of average OI within 6h post-operation, average peak airway pressure, mechanical ventilation time(MVT)and OI post-extubation were monitored, compared and used for evaluating the curative effect of scopolamine. Results Two cases were removed out of treatment group. Compared with monitoring values of control group, the average OI of treatment group significantly increased within 6h post-operation(268.5±58.0 vs. 233.5±40.8 mmHg, P<0.05). No significant difference existed in average peak airway pressure(21.2±2.2 vs. 22.0±3.2 cmH2O, P>0.05). MVT(13.7±7.9 vs. 19.7±13.0h,P<0.05)and OI post-extubation(285.0±32.3 vs. 243.7±40.1 mmHg, P<0.05)obviously improved in treatment group. Drug adverse reactions:there were 2 cases of abdominal distension. Conclusion An optimal amount of scopolamine may improve OI and shorten the duration of mechanical ventilation in VSD/PH children after CPB.