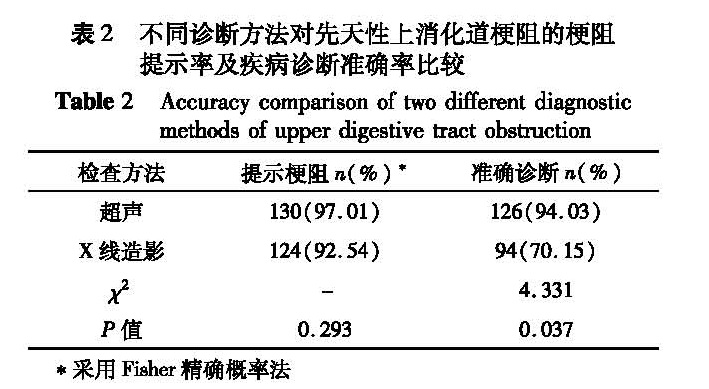
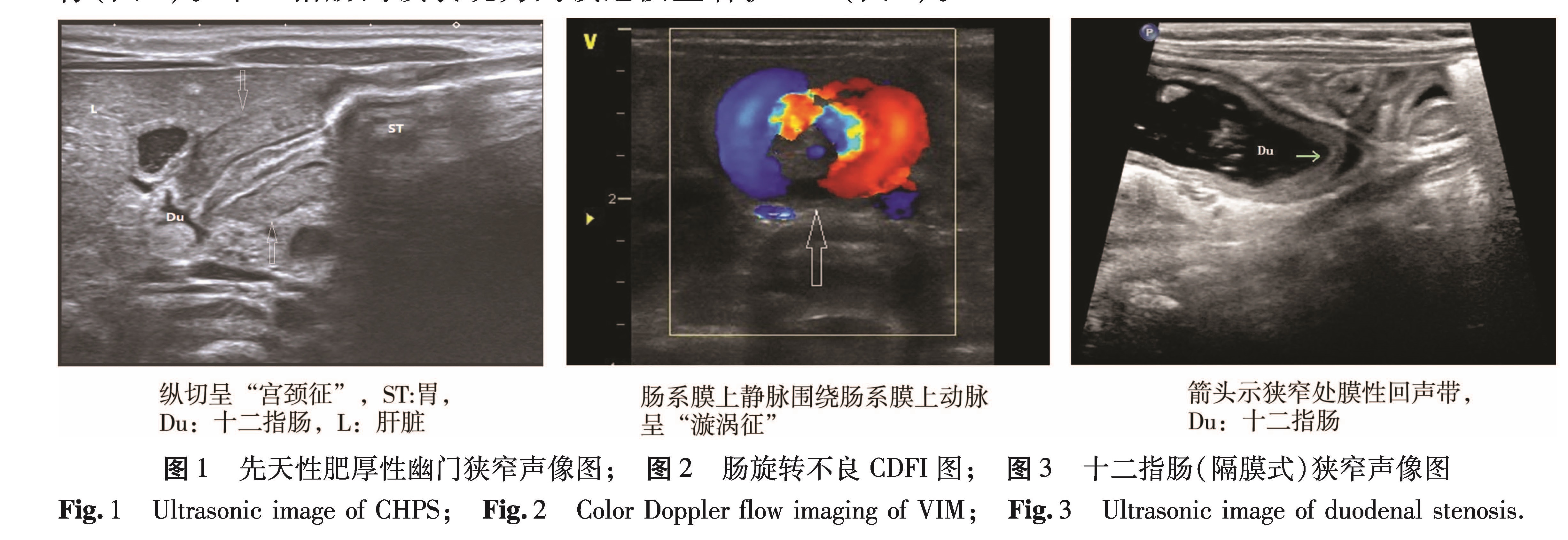
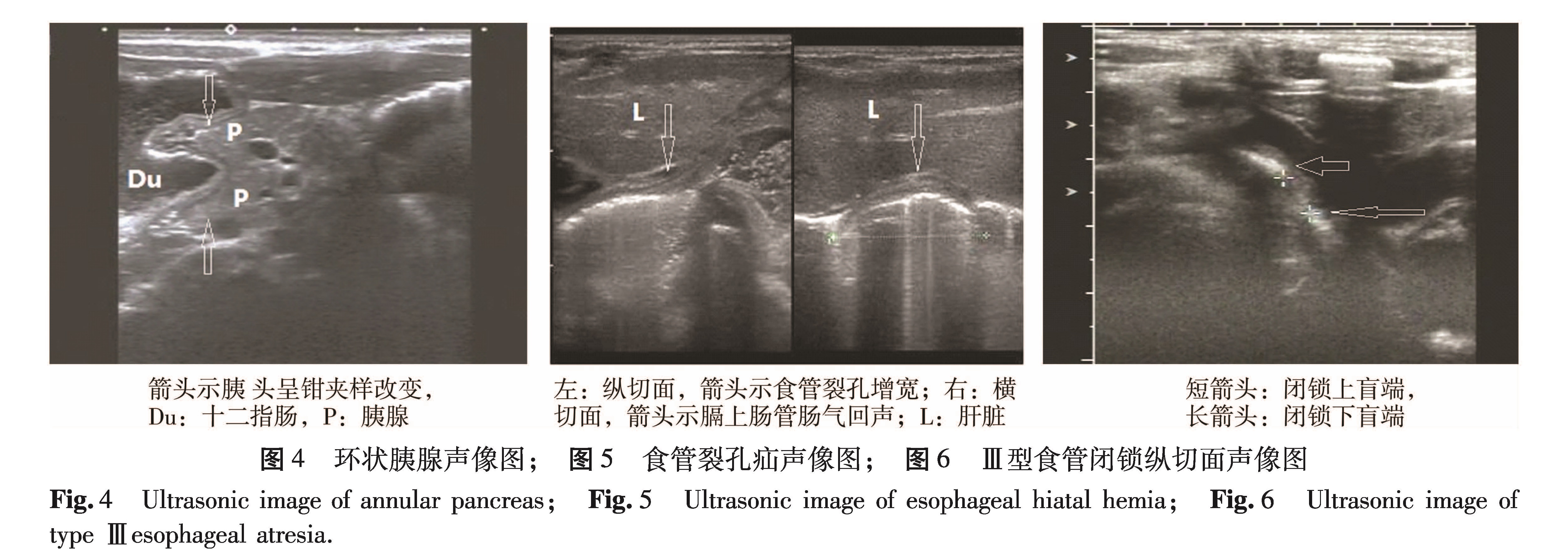
目的 探讨高频超声在新生儿先天性上消化道梗阻中的诊断价值。 方法 本研究在2014年6月至2016年4月收集134例经手术确诊为先天性上消化道梗阻的新生儿,所有患儿均行超声检查和X线消化道造影,比较不同诊断方法对新生儿先天性上消化道梗阻的梗阻提示率及疾病诊断准确率。 结果 134例患儿均得到手术证实,其中肠旋转不良并中肠扭转58例,先天性肥厚性幽门狭窄25例,环状胰腺7例,十二指肠闭锁9例,十二指肠狭窄10例,食道裂孔疝16例,食道闭锁9例。超声梗阻提示率为97.01%,X线上消化道造影梗阻提示率为92.54%,经统计学分析不同诊断方法梗阻提示率不存在差异(P>0.05); 超声疾病诊断准确率为94.03%,上消化道造影疾病诊断准确率为70.15%,差异有统计学意义(x2=4.331,P<0.05)。超声对VIM和CHPS的诊断准确率均高达100%,高于X线上消化道造影。 结论 超声检查在新生儿先天性上消化道梗阻的诊断中具有较高的准确性,对某些疾病的诊断与鉴别诊断优于X线上消化道造影,可作为此类疾病的首选检查方法。
Objective To evaluate the value of high-frequency sonography in diagnosing upper digestive tract obstruction in newborns. Methods A total 134 neonates with suspected upper digestive tract obstruction received the examinations of ultrasonography and upper gastrointestinal radiography. And the diagnostic accuracy of two different methods was compared. Results The causes were intestinal malrotation(n=58), congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis(n=25), annular pancreas(n=7), duodenal atresia(n=9), duodenal stenosis(n=10), esophageal hiatal hemia(n=16)and esophageal atresia(n=9). The diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography and upper gastrointestinal radiography was 97.01% and 92.54% respectively for upper digestive tract obstruction. And the difference was not statistically significant(P>0.05). The total diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound and upper gastrointestinal radiography for congenital disorders was 94.03% and 70.15% respectively. And P<0.05 implied statistically significant difference. Conclusion High-frequency ultrasonography has a higher diagnostic accuracy for congenital upper gastrointestinal obstruction in neonates. And its diagnostic efficiency for some diseases is superior to upper gastrointestinal radiography.
![表1 不同诊断方法对各种疾病的诊断率[n(%)]<br/>Table 1 The diagnostic ratio of different methods in different diseases[n(%)]](2017年05期/pic28.jpg)