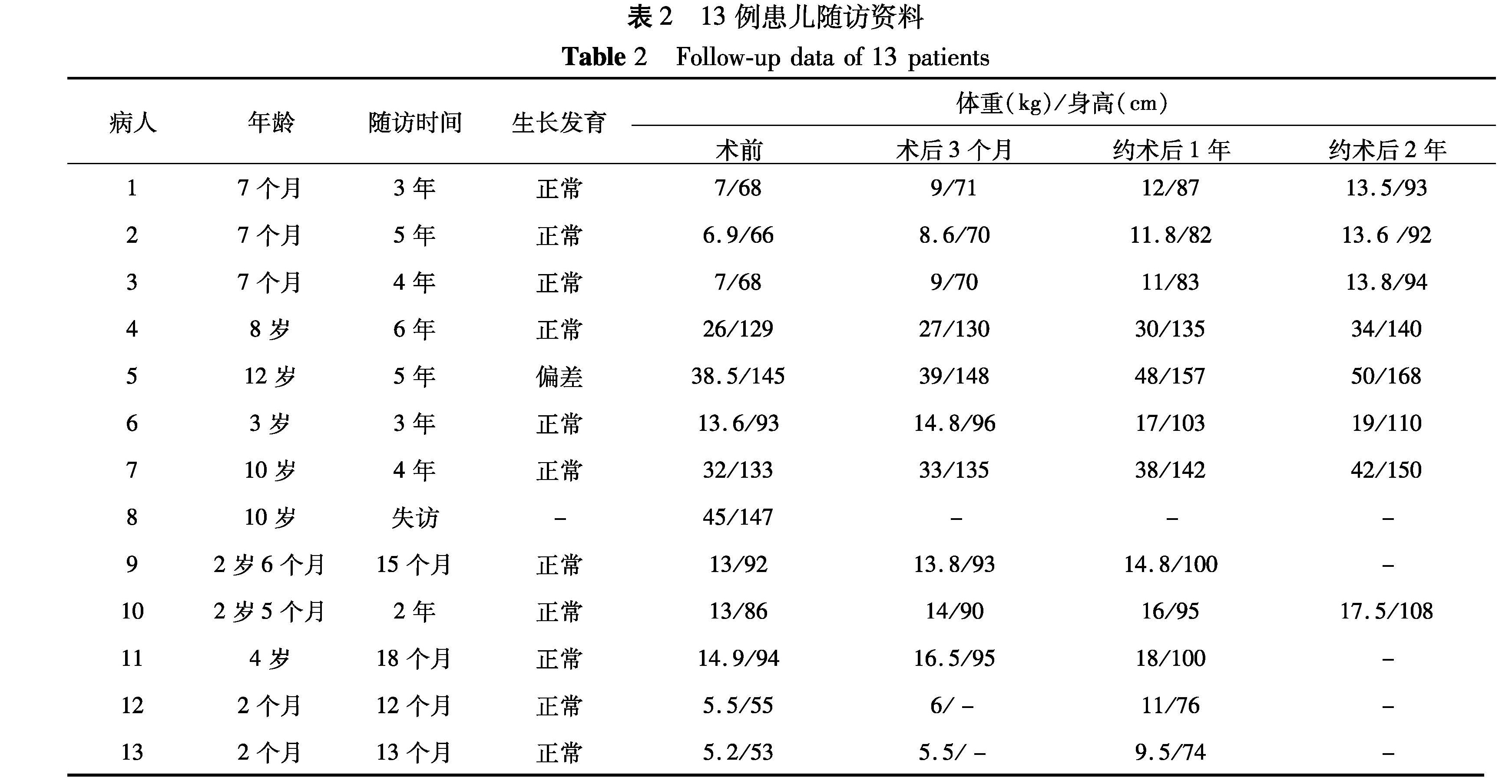
目的 本研究回顾分析本院收治的胃部占位性病变患儿的临床资料,探讨胃占位性病变的诊断和治疗方法。 方法 2000年1月至2015年4月间本院收治胃部占位性病变患儿13例,其中男性9例,女性4例; 中位年龄为2岁6个月。术前所有患儿行超声和CT检查,7例行上消化道造影,6例行胃镜检查。8例直接行开腹手术,4例行腹腔镜探查后转开腹手术,1例腹腔镜探查证实为胃前壁肿物后行腹腔镜下胃壁肿物切除术。除1例患儿放弃治疗以外,其余12例患儿均获得门诊随访,随访时行超声检查,并评估患儿生长发育情况。 结果 术后病理检查证实胃重复畸形5例,胃不成熟畸胎瘤3例,胃炎性纤维母细胞瘤2例,胃脂肪瘤1例,胃间质瘤1例,胃平滑肌肉瘤1例。手术方法:5例行包括肿瘤在内的胃壁部分切除+胃修补术,1例行腹腔镜下胃壁肿瘤剔除术,1例行胃贲门食管下段肿物活检术,1例行腹腔镜探查+毕Ⅰ式胃大部切除手术,胃重复畸形2例行重复胃壁切开+黏膜剥除术,2例行腹腔镜探查+胃壁囊肿切除术,1例行腹腔镜探查+胃壁囊肿切除+胃壁修补术。所有患儿平均随访时间3.8年。毕Ⅰ式胃大部分切除的患儿术后3个月体重减轻,之后生长发育与同龄儿童无异; 其余患儿随访期间生长发育正常,身高、体重与同龄儿童相比无明显差异。 结论 影像学检查对小儿胃占位性病变的术前诊断有重要价值。手术切除是胃占位性病变的主要治疗方式,同时它还可以在影像学诊断不明时起鉴别诊断作用。部分胃壁切除和毕I式手术对患儿远期生长发育无明显影响。
Objective To explore the diagnosis and treatment of stomach mass. Methods From January 2000 to April 2015, 13 patients with stomach mass were reviewed and analyzed. There were 9 boys and 4 girls with a median age of 2.6 years old. All of them received preoperative examinations of ultrasound and computed tomography(CT). Also upper gastrointestinal radiography(n=7)and gastroscopy(n=6)were performed. There were laparotomy(n=8)and laparotomy after exploratory laparoscopy(n=4). One patient with tumor in anterior wall of stomach underwent laparoscopic resection. Except for 1 patient giving up treatment, the remainder were regularly followed up. Results Pathology comfirmed gastric duplication(n=5), immature teratoma(n=3), GISTs(n=1), gastric lipoma(n=1), liomyosarcoma(n=1)and myofibromatosis(n=1). The procedures included partial gastrecomy(n=10), laparoscopic lesion resection(n=1), biopsy alone(n=1)and Billroth I procedure(n=1). All of them had normal long-term heights and weights. There was no developmental difference. Conclusion Preoperative imaging examination is essential for diagnosing stomach mass. Surgical resection is the first choice and it also aids the differential diagnosis. There is no long-term difference of growth and development during follow-ups.