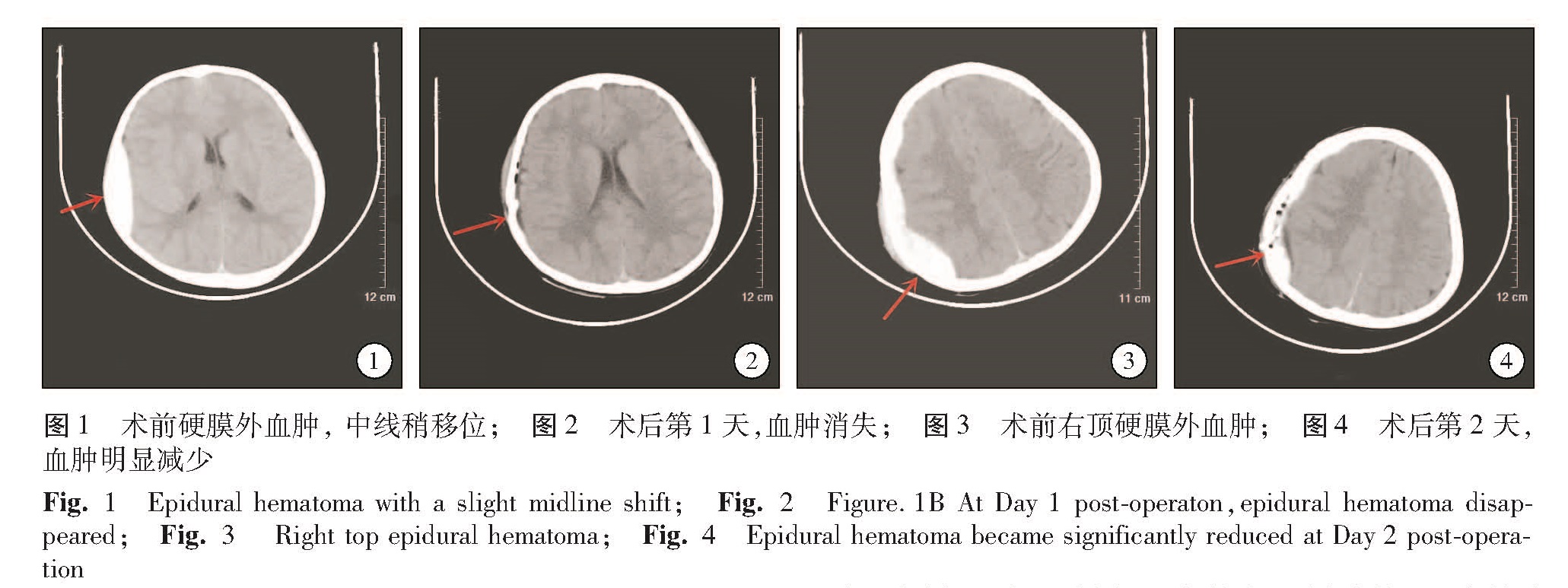
目的 分析微创颅骨钻孔引流治疗小儿急性硬膜外血肿的临床效果。 方法 选取本院25例急性硬膜外血肿儿童患者,颅骨钻孔置管后,应用尿激酶冲洗并引流硬膜外血凝块,总结临床效果。 结果 25例经颅骨钻孔外引流加尿激酶溶解术治疗,住院 6~12 d,平均( 9± 6)d; 引流管留置3~7 d,平均( 4± 1)d; 血肿完全清除17例,绝大部分清除8 例,其中2例术后1 d复查头部CT硬膜外血肿完全消失; 出院时根据格拉斯哥预后评分标准(GOS),均达到恢复良好标准; 术后随访1~3个月,脑组织均膨胀良好,无血肿复发病例。 结论 颅骨钻孔外引流加尿激酶溶解术治疗小儿急性硬膜外血肿创伤小,操作简单,经济有效,可避免开颅手术及输血,手术方法安全,但需掌握手术适应证。
Objective To analyze the clinical effects of mini-invasive surgery of skull drilling and drainage for acute epidural hematoma in children. Methods A total of 25 children of acute epidural hematoma were recruited. After drilling holes and inserting tubes,urokinase was used for washing and draining the clots of epidural hematoma. And the clinical effects were summarized. Results Their average stay was 9± 6(6-12)days drainage tubes were maintained for an average duration of 4± 1(3~7)days. Clearing of hematoma was complete(n =17)and subtotal(n =8). Epidural hematoma of 2 patients disappeared completely on computed tomography(CT)at Day 1 post-operation. At discharge,all patients were good according to the criteria of Glasgow Coma Score(GOS).During a follow-up period of 1-3 months,brain tissues healed well without any relapse. Conclusion Skull drilling,drainage and urokinase dissolution result in minimal traumas. The above procedure is safe,effective and affordable. Furthermore,it may avoid craniotomy and blood transfusion. However,mastering surgical indications is essential.