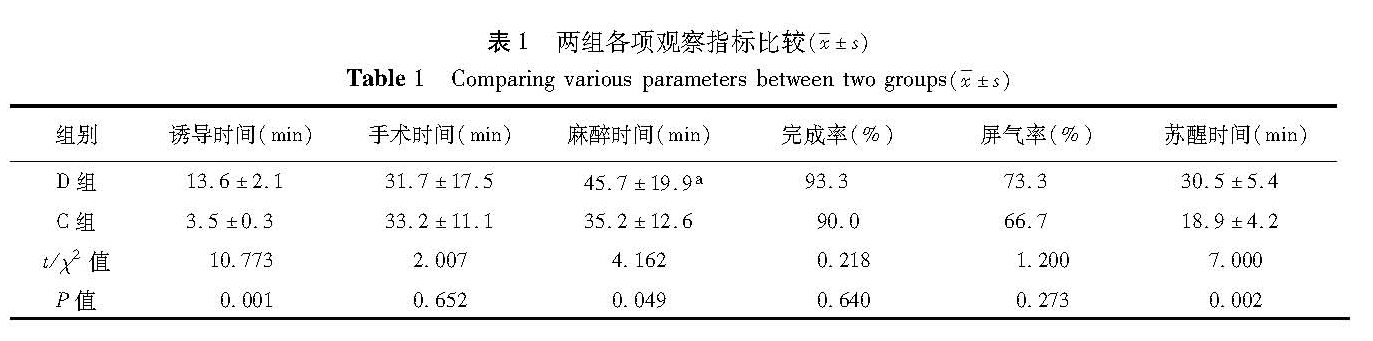
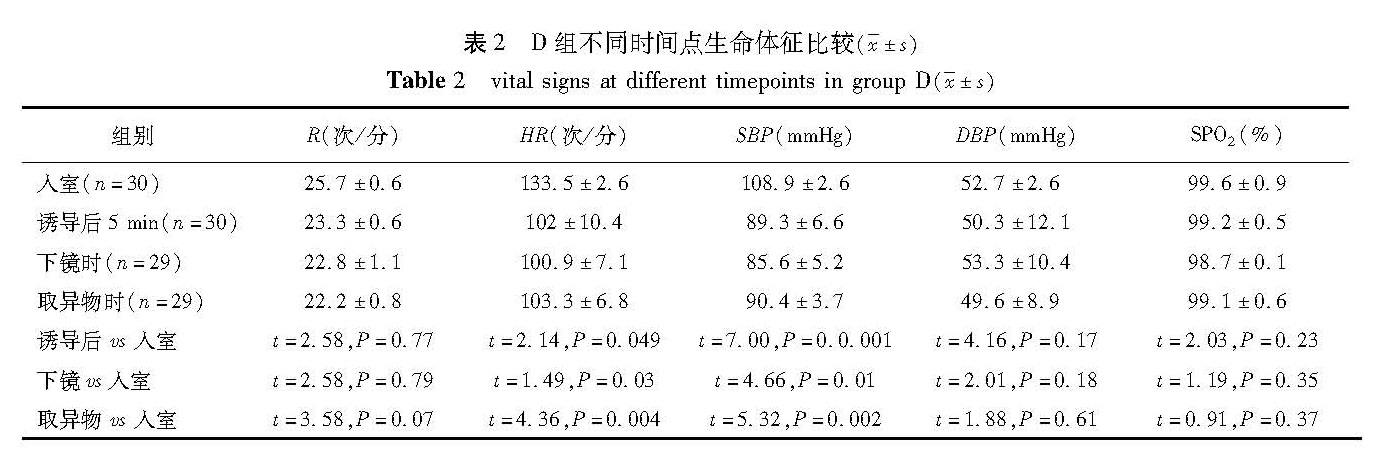
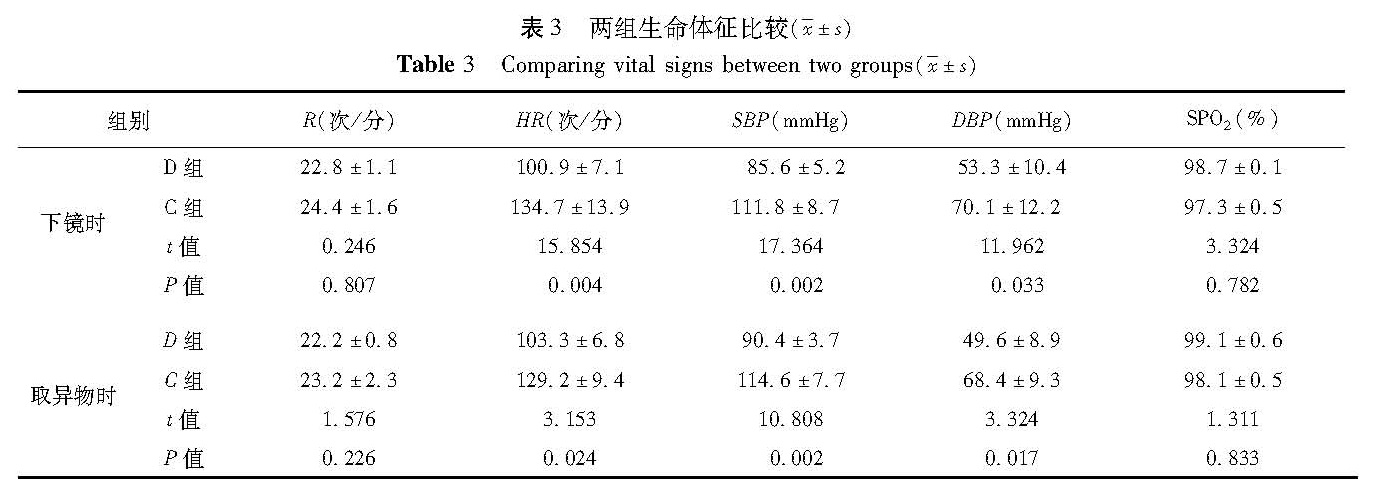
目的 探讨右旋美托咪定在急诊婴幼儿气管异物取出术麻醉中的应用。 方法 选择8个月至3岁拟急诊行左侧或右侧支气管异物取出术的患儿60例,随机分为右美托咪定组(D)及对照组(C),每组30例。麻醉方法: ①诱导: 两组均缓慢静脉注射芬太尼1 μg/kg。 D 组静脉泵入首剂量右旋美托咪定1 μg1/ kg,10 min内输注完成; C 组静脉注射丙泊酚3 mg/kg。面罩吸入8%七氟醚(6 L/min),提下颌患儿无体动后开始手术; ②维持: D组右旋美托咪定改为1 μg-1· kg-1· h-1静脉持续恒速输注,C组七氟醚吸入麻醉; ③术毕: 停用右旋美托咪定或七氟醚,保留自主呼吸送入麻醉恢复室,患儿醉清醒后回病房。记录每例患儿的诱导时间、不同时间点的生命体征情况、术中特殊事件的发生和处理方法以及苏醒时间。 结果 与入室时相比,D组使用右旋美托咪定后5 min心率、血压降低[HR(13 5± 6)次/分 vs(102±10.4)次/min,SBP(10 9± 6)mmHg vs(8 3± 6)mmHg],差异有统计学意义(P<0.05); 呼吸频率、SPO2比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。置入硬支气管镜时、异物取出时,D组生命体征较前无明显变化(P>0.05); 但与 C 组相比心率及血压降低(P<0.05)。 D 组与 C 组患儿支气管痉挛的发生率分别为 7%和10%,差异无统计学意义( χ2=0.220,P>0.05)。两组平均苏醒时间分别为(30.5± 4)min和(1 9± 4)min,差异有统计学意义(t= 000,P<0.05)。 结论 右旋美托咪定能够安全、有效地应用于婴幼儿气管异物取出术麻醉中。
Objective To explore the use of dexmedetomidine in young children undergoing emergent extraction of foreign body by tracheobroncheoscopy. Methods A total of 60 children aged 8 months to 3 years undergoing emergent extraction of foreign body under tracheobroncheoscope were randomly divided into dexmedetomidine(D)and control(C)groups. Anesthetic mode: ① Induction of fentnayl 1 μg/kg iv slowly. Dexmedetomidine 1 μg / kg iv during 10 min in group D and propofol 3 mmg/kg iv in group C and then mask inhalation of 8% sevoflurane 6L/min. Operation began until body was motionless with a pulled jaw; ②Intraoperation: The dose of dexmedetomidine 1 μg/kg/h was adjusted intraoperatively in group D. And continuous inhalation of sevoflurane was offered for group C; ③Operation ending: Dexmedetomidine or sevoflurane was withdrawn and patients were transferred into postanesthesia care unit. If there was crying without stimulation,they returned to the ward. The parameters of induction time,vital signs,events and recovery time were recorded. Results Heart rate( HR)and blood pressure declined after dosing of dexmedetomidine 5 min later(HR13 5± 6 vs 102±0.4,SBP10 9± 6 vs 8 3± 6,P <0.05). Breath frequency and blood oxygen saturation SPO2 showed no change. Vital signs remained stable when rigid bronchoscope was applied for removing foreign body in group D. Meanwhile,HR and BP were higher than those of group C. The percentage of bronchial spasm was 7%(D)versus 10%(C)( χ2 =0.220,P >0.05). And average recoverytime was 30.5± 4 min(D)versus 1 9± 4 min(C)(t= 000,P<0.05). Conclusion Dexmedetomidine is safe and effective for extracting foreign body under rigid bronchoscope in infants.