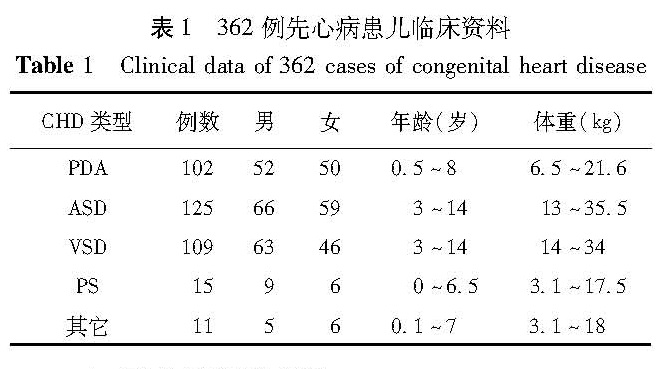
目的 总结分析儿童先天性心脏病介入治疗的效果及并发症。 方法 本研究收集2014年1月至2016年12月在本院治疗的362例先心病患儿为研究对象,针对PDA患儿采用蘑菇伞封堵法、弹簧圈封堵法、国产ADOII封堵法,VSD、ASD患儿采用蘑菇伞封堵法,PS患儿采用肺动脉瓣球囊扩张术单球囊法和双球囊法。 结果 352例患儿成功完成手术,手术成功率为97.24%,术中死亡病例为1例重度PS合并冠状窦间隙开放患儿; 转外科治疗5例,包括术中行心导管检查发现PDA合并主动脉弓离断畸形2例,PDA合并主动脉缩窄1例,ASD合并肺静脉异位引流2例; 中止手术4例,包括术中发现VSD已快愈合而不需手术的3例,VSD术中出现III度房室传导阻滞而中止手术的1例。352例成功完成手术的患儿中7例术后出现并发症,发生率为1.99%,3例残余分流,术后6个月随访时,残余分流均消失; 3例心律失常,术后6个月随访时1例VSD封堵术的患儿仍存在散在室性早搏,其余患儿心电图均恢复正常; 1例股动脉血栓经溶栓治疗痊愈。 结论 儿童先心病介入治疗的成功率高,并发症的发生率较低,但应严格掌握适应证与禁忌症,熟练掌握操作技术,术后需长期随访。
Objective To explore the efficacies and complications of interventional therapy for congenital heart disease(CHD)in children. Methods A total of 362 CHD children treated by interventional therapy at our pediatric cardiovascular center from January 2014 to December 2016 were studied. For patent ductus arteriosus(PDA),mushroom umbrella occlusion,coil occlusion and domestic ADOII occlusion was used. And mushroom umbrella occlusion was utilized for ventricular septal defect(VSD)and atrial septal defect(ASD). For pulmonary stenosis(PS),pulmonary balloon dilation was applied. Results Among them,352 cases were operated smoothly with a success rate of 97.24%. One case of severe PS with concurrent open coronary sinus died intraoperatively. Among 5 cases of surgical transferal,intraoperative cardiac catheterization revealed PDA with aortic coarctation(n=2),PDA with aortic stenosis(n=1)and ASD with ectopic shunting of pulmonary vein(n=2). Surgery was terminated for 4 cases. Intraoperative findings indicated spontaneous healing of VSD without surgery(n=3)and degree III atrioventricular block plus paused operation(n=1). Complications occurred in 7/352(1.99%). During a 6-month follow-up,residual shunting disappeared in 3 cases. Among 3 cases of arrhythmia,discrete early ventricular premature beats persisted in 1 case at 6 months. The remainder had normal electrocardiogram. One case of femoral arterial thrombosis was cured by thrombolysis. Conclusion s Interventional therapy for CHD in children has a high success rate and a low complication rate. However,the indications and contraindications should be strictly grasped. And long-term follow-ups are necessary.