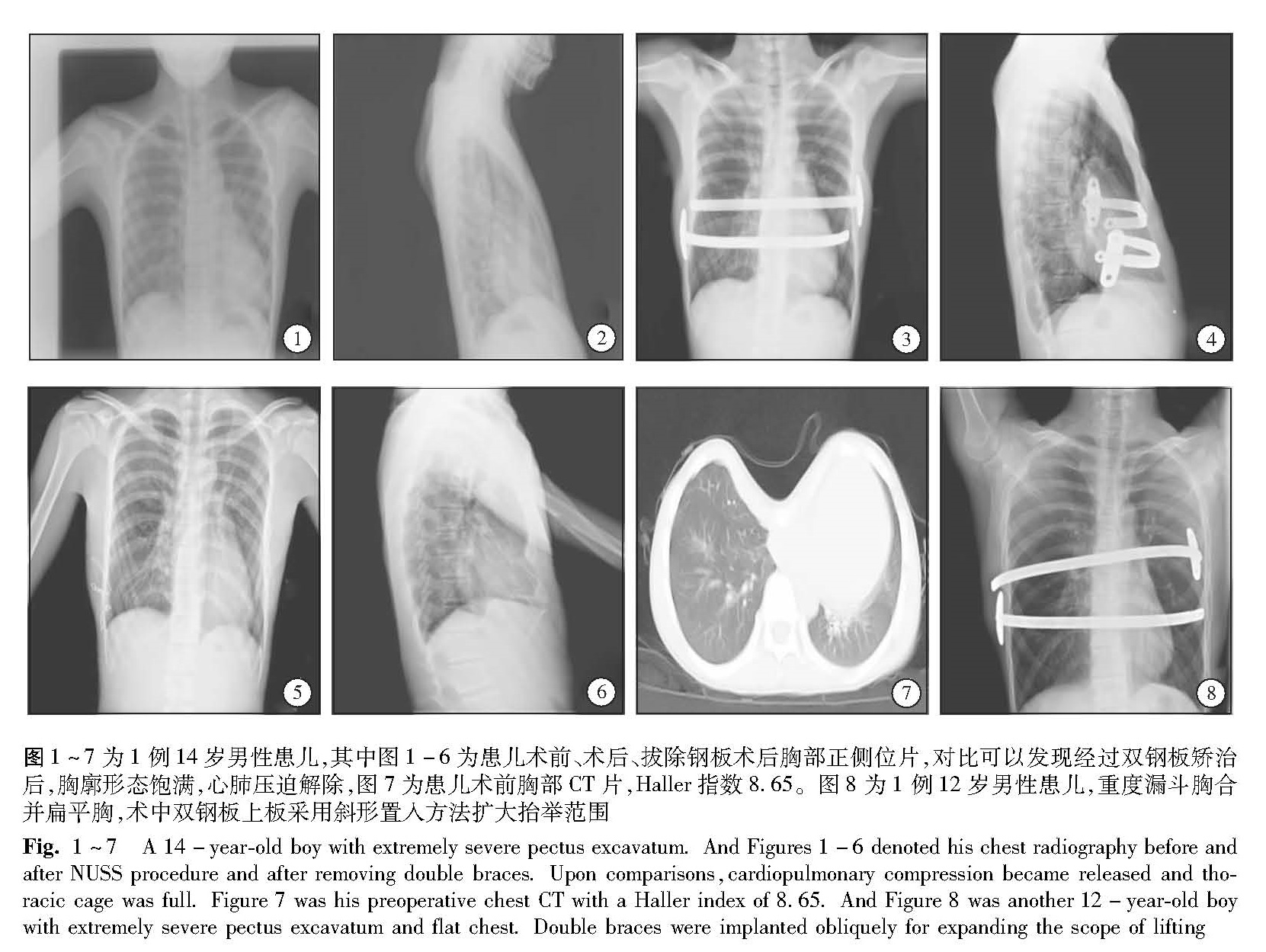
目的 探讨双钢板NUSS手术治大龄重度漏斗胸的可行性及手术技巧。 方法 对22例大龄漏斗胸儿童在胸腔镜辅助下行双钢板Nuss手术,其中男19例,女3例; 年龄10~16岁,平均年龄(12.05±2.04)岁,全组病人按照Haller指数均为极重度漏斗胸,按照个体化矫治的原则,分别选用双钢板矫治漏斗胸,每一个钢板使用一个固定器分置于两侧胸壁,并评价手术的安全性及可行性。 结果 22例均顺利完成手术,手术时间为50~95 min,平均手术时间(65.6±13.5)min; 术中出血10~45 mL。其中11例行剑突下辅助小切口,22例均采用单侧固定翼固定于不同侧胸壁,术后住院时间6~10 d,平均(7.15±1.12)d; 术后3年左右取出钢板,随访3个月至6年,发生少量气胸3例,皮下气肿1例,未发生内固定钢板移位,未见钢板排异反应,未见脊柱侧弯发生,术后无长时间疼痛发生,出院后均未再给予镇痛药物。 结论 对于大龄极重度漏斗胸的患儿,在单钢板矫治难以达到矫治效果时,双钢板矫治是安全有效的,部分极重度漏斗胸配合胸骨下剑突小切口,亦能达到满意矫正效果。
Objective To explore the feasibility of Nuss procedure with double braces for correcting extremely severe pectus excavatum in elder children. Methods A total of 22 elder children,including 19 boys and 3 girls,of extremely severe pectus excavatum were corrected by thoracoscopic Nuss procedure with double braces and used only one support bar for each brace in accordance with the principle of individual treatment. The mean age was(12.05±2.04)(10~16)years. All diagnoses were made according to Haller index. Then the feasibility and safety of Nuss procedure were evaluated. Results All procedures were completed without intraoperative complications. And a small incision under xiphoid was added for 11 patients. The mean operative duration was(65.6±13.5)(50~95)min,intraoperative blood loss 10~35 mL and postoperative hospitalization stay(7.15±1.12)(6~10)days. During a follow-up period of 3~72 months,there was no onset of brace sliding,allergic reaction,secondary scoliosis or persistent pain. There were only minimal pneumothorax(n=3)and subcutaneous emphysema(n=1). Conclusion s Nuss procedure with double braces is both safe and mini-invasive for elder children with extreme severe pectus excavatum.