通信作者:乔飞,E-mail:229637772@qq.com
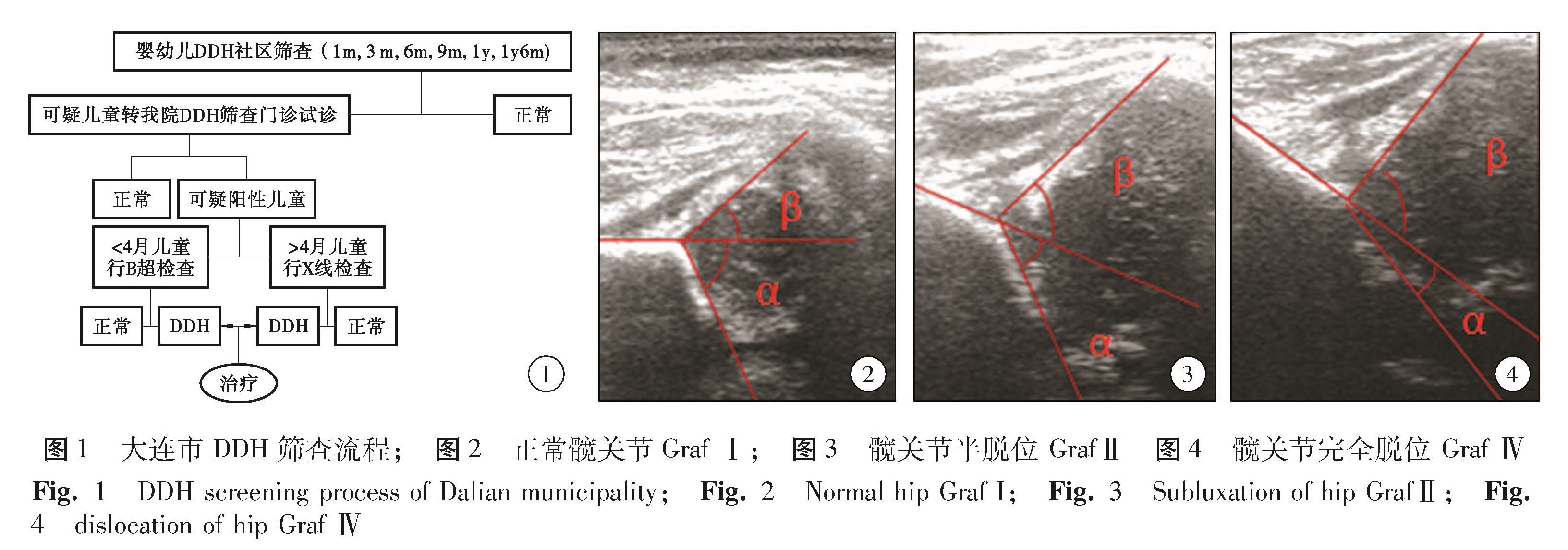
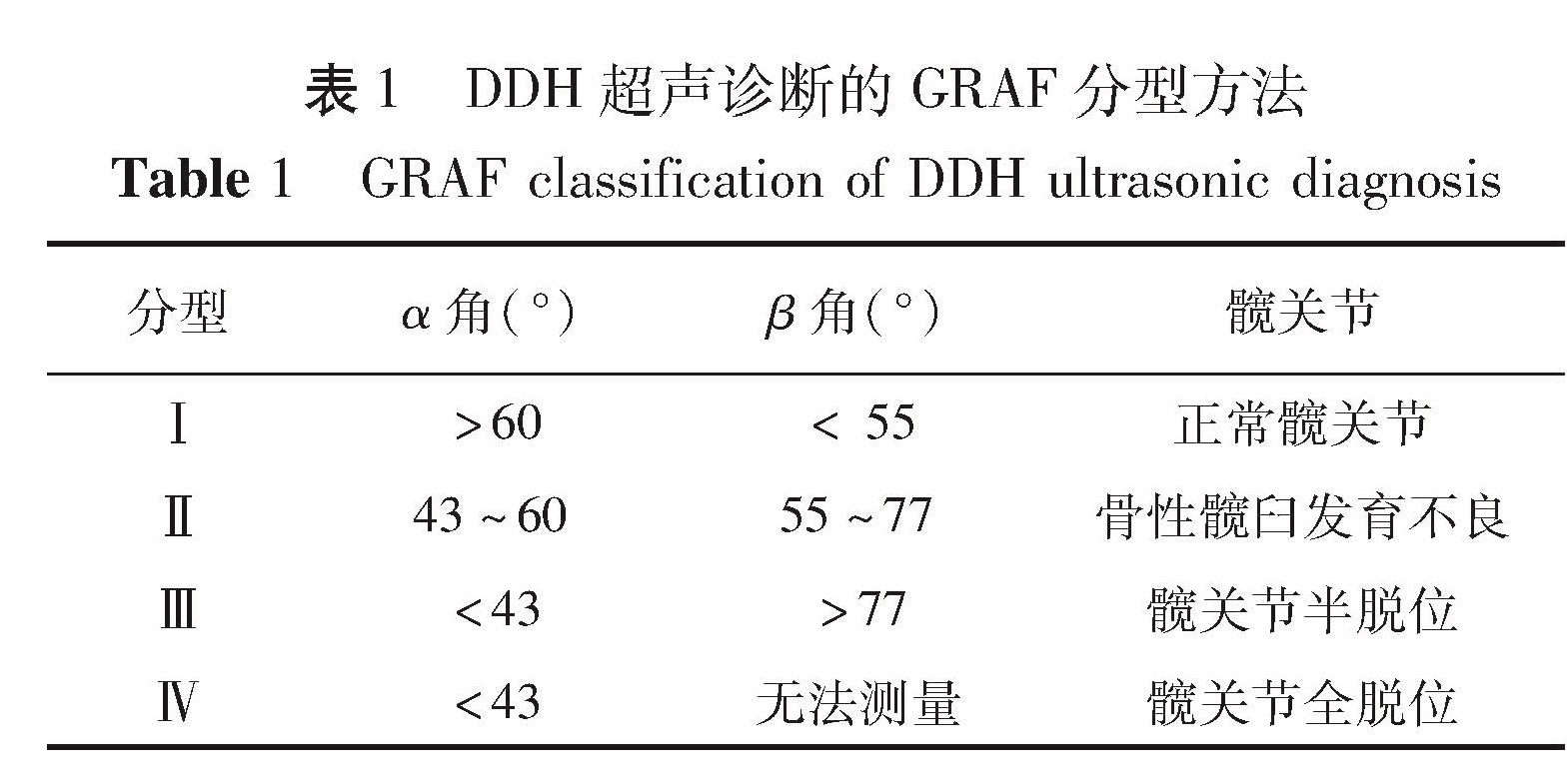
目的 分析大连地区发育性髋关节发育不良(developmental dysplasia of the hip,DDH)的高危因素,探讨符合本地区特点的早期筛查方法和模式。 方法 自2013年1月1日至2014年12月31日由大连市区县妇幼机构和大连市妇女儿童保健中心、大连市儿童医院共计筛查14 736例婴幼儿髋关节发育情况,运用SPSS19.0软件对患者的临床资料进行单因素分析和多因素Logistic回归分析,观察DDH的危险因素。 结果 共计14 736例婴幼儿,可疑患儿472例(32.03‰,472/14736),专科检查后确诊患儿56例(3.80‰,56/14736)(69髋)。男童9例(11髋),女童47例(58髋),男女比1:5.22; 左侧45髋(65.22%),右侧24髋(34.78%),左右侧别比1.87: 1。经过多因素非条件Logistic回归分析,结果显示臀位产、家族史、合并畸形、襁褓捆绑、羊水少、臀纹不对称为DDH发病的危险因素(P<0.05)。 结论 大连市采取对婴幼儿进行初筛-复筛确诊的模式,可以早期发现和确诊DDH,本地区DDH高危因素包括臀位产、家族史、合并畸形、襁褓捆绑、羊水少、臀纹不对称,建议建立完备的筛查体系,推广DDH的早期筛查工作。
Objective To explore the risk factors of developmental dysplasia of the hip(DDH)and validate early screening method in Dalian. Methods From January 1, 2013 to December 31, 2014, a total of 14736 cases from municipal district women & children's organizations, women & children healthcare center and Dalian Children's Hospital were retrospectively analyzed. SPSS19.0 software was used for analyzing their clinical data with single and multivariable Logistic regression. And the risk factors of DDH recorded. Results Among them, there were 472 suspected cases(32.03 ‰, 472/14736). Specialized examinations confirmed 56 cases(3.80 ‰, 56/14736)(69 hips). There were 9 boys(11 hips)and 47 girls(58 hips)with a ratio of boy: girl at 1:5.22. There were 45 left(65.22%)and 24 right(34.78%)hips with a ratio of left: right at 1.87:1. Through unconditioned Logistic regression analysis of multiple factors, breech delivery, family history of DDH, associated malformation, infant bundling, deficient amniotic fluid and asymmetric hip grain were risk factors of disease(P<0.05). Conclusion s The primary-secondary screening diagnosis model helps to diagnose DDH early and identify the risk factors of DDH in Dalian. And a complete system of screening is needed for promoting early screening of DDH.
![表2 确诊DDH患儿流行病学分析的危险因素单因素 χ2检验结果[n,‰]<br/>Table 2 Single factor χ2 test results of risk factors of DDH children](2017年02期/pic23.jpg)